Think about a gaseous exoplanet 5 occasions the dimensions of Jupiter however a lot nearer to its star as Mercury is to our Solar. This planet orbits its star in simply a few days and at all times exhibits the identical face in the direction of it. Now, think about a tiny rocky planet, solely a 3rd of the dimensions of Earth orbiting its star in solely 4.5 hours. These sorts of worlds actually exist. Exoplanets fluctuate in dimension, orbit, composition, and extra. However how can we all know all these features?
Totally different characterization strategies have been developed and adopted by the European House Company’s (ESA) exoplanet missions. On this endeavor, 1000's of exoplanets can be topic to a examine of mass, dimension, density, composition, and age. Under you will discover explanations of the varied characterization strategies.
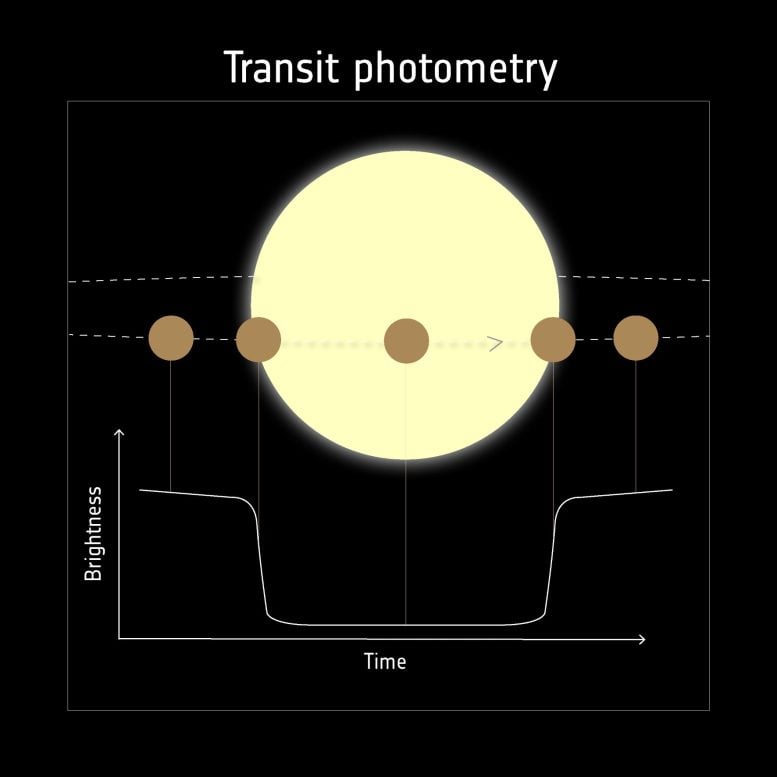
Transiting exoplanets are detected as they go in entrance of – transit – their host star, inflicting a dip within the starlight as seen from the observer’s viewpoint. The transit repeats, with the time interval relying on the time it takes the exoplanet to orbit its star. For instance, an observer of our personal Photo voltaic System must wait a yr to see a repeat of Earth transiting the Solar. Credit score: ESA
Measurement – transit methodology
The transit methodology supplies a approach to study exoplanets. When a planet passes in entrance of their star (from the viewpoint of the observer), it causes a few of the starlight to be blocked. The observer quickly receives much less mild from the star. ESA’s mission Cheops will take a look at planets recognized to transit and decipher their dimension. Plato will search for new, unknown exoplanets utilizing the transit methodology. The larger the planet, the deeper the dip in star brightness it causes. Cheops focuses on planets with sizes between that of Earth and Neptune and shorter orbital intervals (<50 days). The orbital interval is the time it takes for a planet to finish one orbit round their host star. For transiting exoplanets, this orbital interval is straightforward to find out as it's simply the time between two consecutive dips in mild. Plato will be capable to observe Earth-sized planets with longer orbital intervals (>90 days).
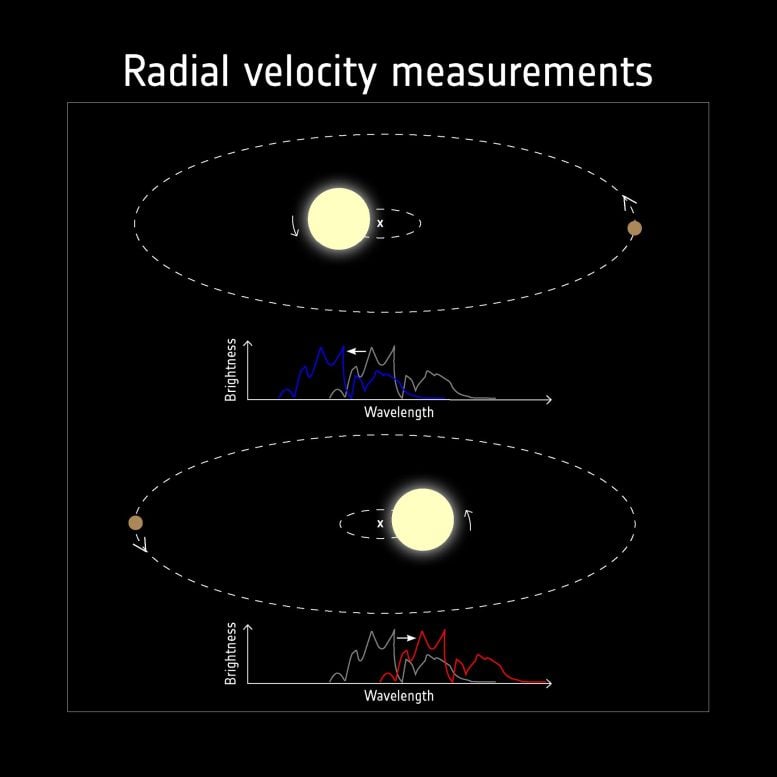
Exoplanets might be detected by measuring the ‘wobble’ in its star’s movement brought on by the gravitational pull of a planet because the planet and star orbit round a standard centre of mass. When considered from afar, the star seems to maneuver in the direction of and away from the observer. This movement makes the sunshine from the star seem barely bluer when it's shifting in the direction of the observer, and barely redder when shifting away. This shift in frequency is named the Doppler impact, the identical impact because the change in pitch of an ambulance siren because it rushes previous you. Most early exoplanet discoveries had been made utilizing this so-called radial velocity methodology.
Credit score: ESA
Mass – radial velocity and transit time variations
The mass is a basic attribute of an exoplanet. Scientists can be taught so much about how planets kind round their stars by evaluating how huge completely different exoplanets are. Two strategies can present us with data on the mass of exoplanets. One is the radial velocity methodology, utilized by a number of ground-based observatories. When a star has a planet, the system strikes round a standard level, referred to as the mass heart. Throughout this orbit, the celebs’ mild seems bluer when it strikes in the direction of the observer and redder when it strikes away. This shift in frequency is named the Doppler impact, the identical impact because the change in pitch of an ambulance siren because it rushes previous you. By measuring the shift in mild coming from the star, it's potential to find out the rate – the velocity and route – by which the star strikes across the heart of mass. The rate is straight correlated with the mass of the planet.
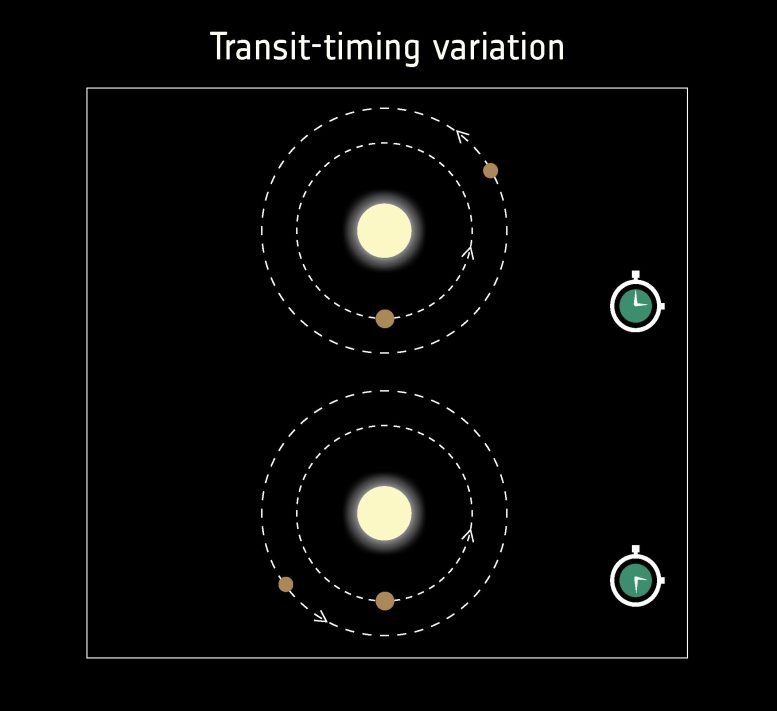
A variation on the transit method to detect exoplanets – referred to as transit timing variation (TTV) – can be used to seek out extra planets in a system. By measuring tiny variations within the timing of the transit of a recognized planet, astronomers can reveal the presence of potential different planets orbiting the identical dad or mum star. Credit score: ESA, CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO
One other methodology that gives us with data on the mass of exoplanets is that of Transit Time Variations or TTV for brief. This methodology works just like the transit methodology for a planetary system with a number of planets. Usually the time between transits of the identical planet is just not anticipated to fluctuate. When a planet is seen crossing the face of its star earlier or later than anticipated, the system possible has one other planet gravitationally tugging or pushing on its neighbor. This methodology has already led to the invention of greater than 40 exoplanets. What's fascinating, is that the time distinction between the transits additionally reveals data on the plenty of the planets. This system is utilized by ESA’s missions Cheops and Plato.
Density – mix two strategies
As soon as each the mass and dimension are recognized, the density of the exoplanet might be decided. That is important data as it will probably reveal its nature: is the exoplanet rocky like Earth and Mars or of a gaseous nature corresponding to Saturn and Jupiter? Learning the range in exoplanets can shine a lightweight on the formation of planetary methods.
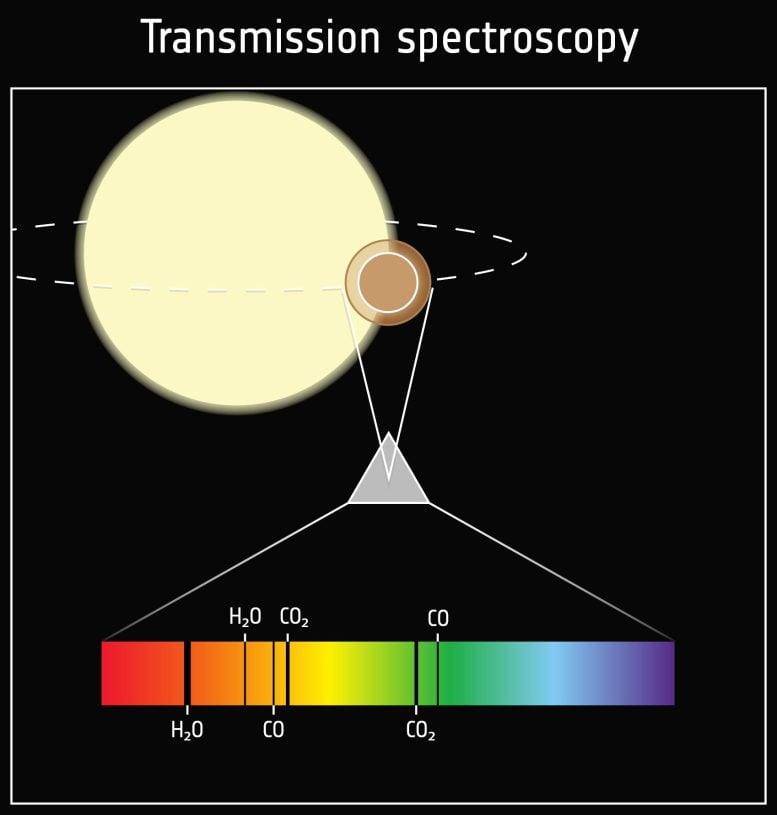
Spectroscopy is the strategy of splitting acquired starlight into its completely different colours utilizing a prism. Exoplanets orbit their stars, once they transit – go by from our viewpoint – a few of the starlight passes via the planet’s ambiance. Particles within the ambiance like water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane and others take up a few of that mild. This absorption occurs at particular wavelengths of sunshine. By finding out at which wavelengths the starlight is absorbed, we are able to decide what sort of particles are current within the ambiance. The NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb House Telescope makes use of this system to characterize exoplanets and ESA’s Ariel mission will examine the atmospheres of as many as 1000 exoplanets this fashion. Each missions concentrate on infrared mild as a result of the signatures of molecules are very distinguished in these colours. Credit score: ESA, CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO
Composition of ambiance – transmission spectroscopy
With spectroscopy we are able to examine what the atmospheres of exoplanets are product of. Spectroscopy is the strategy of splitting acquired starlight into its completely different colours utilizing a prism. Throughout a transit of a planet a few of the starlight passes via the planet’s ambiance. Particles within the ambiance like water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, and others take up a few of that mild. This absorption occurs at particular wavelengths of sunshine. By finding out at which wavelengths the starlight is absorbed, we are able to decide what sort of particles are current within the ambiance. Monitoring modifications within the ambiance over time offers perception in processes occurring on the floor of those exoplanets. The NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb House Telescope makes use of this system to characterize exoplanets and ESA’s Ariel mission will examine the atmospheres of as many as 1000 exoplanets this fashion.
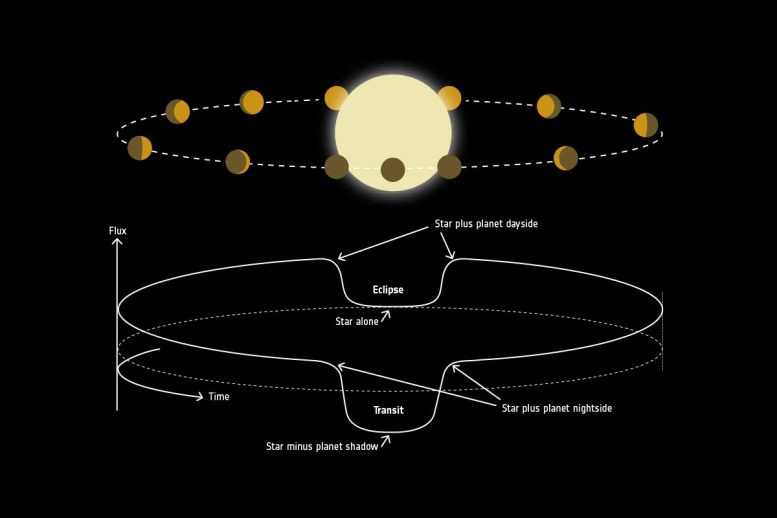
The part curve methodology to review extrasolar planets, or exoplanets. Relying on a planet’s place with respect to its host star, the overall mild collected by a telescope will embrace a various fraction of sunshine mirrored off the planet, in the same method to how we expertise the phases of the Moon.
The planet displays no mild throughout a part referred to as secondary eclipse, when it's hidden from view, whereas it displays some mild shortly earlier than and after this part. Along with that, the planet blocks a fraction of the sunshine because it transits in entrance of the star.
The modifications in starlight mirrored by the planet because it orbits its star present perception into the bodily processes that drive the transport of warmth from the new day aspect to the cooler evening aspect. Evaluation of the part curves additionally reveals particulars of the planet’s ambiance, together with the presence of clouds, and presumably even hints of the cloud composition.
Credit score: ESA, CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO
Clouds and floor – part curve
When a planet orbits its star, it displays starlight similar to our Moon does with daylight. In the identical manner, exoplanets have completely different ‘phases’ the place completely different fractions of their floor replicate mild. By finding out the small variations in acquired daylight through the planet’s orbit, it's potential to find out how reflective the planet’s floor is. Apparently, additionally the presence of clouds within the exoplanets’ ambiance might be revealed this fashion. The missions Cheops and Plato, and likewise Ariel (in parallel to their transit spectroscopy, see above) will use this system to disclose the floor colours of exoplanets.
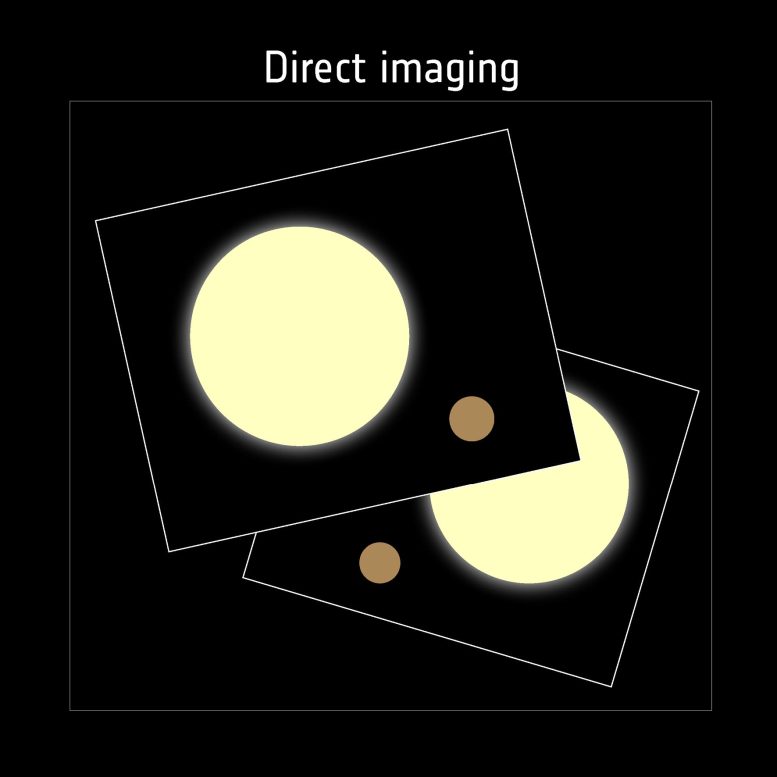
Direct imaging depends on measuring mild from the exoplanet itself. That is significantly difficult at optical wavelengths, as a result of the comparatively dim planet might be misplaced within the glare of the a lot brighter host star.
Credit score: ESA
Construction of exoplanetary methods – direct imaging
The above strategies gave numerous traits of particular person exoplanets. If we wish to be taught extra about exoplanetary methods as a complete, we are able to make a direct picture of the system. Taking an image of planets is tough as a result of the sunshine of stars outshines that of their planets. You want a really high-resolution digital camera or a approach to block out the intense starlight and never all area missions are geared up for the duty. The Hubble and James Webb area telescopes have the wanted decision and have been capable of make photographs of planets round stars apart from our Solar. With this system, we are able to additionally be taught concerning the planets’ orbital intervals and the distances to their stars. The brand new area telescope Roman will be capable to picture Jupiter-sized planets on orbits much like Jupiter across the Solar. The telescope will do that by blocking the sunshine of the star and picture the fainter mild of the planets round it.

Post a Comment