
Artist’s illustration of China’s Chang’e 5 lander on the Moon. Researchers have found that influence glass beads in Chang’e-5 lunar soils comprise water. These glass beads are thought to signify a brand new water reservoir on the Moon, capturing the dynamic alternate of water derived from photo voltaic wind. This discovering means that these beads play a job within the lunar floor water cycle as a buffer. Credit score: CNSA/NASA
On account of its potential for in-situ useful resource utilization by future lunar exploration missions and different house missions, lunar floor water has attracted vital consideration.
Now, a analysis group led by Prof. Sen Hu from the Institute of Geology and Geophysics (IGG) of the Chinese language Academy of Sciences (CAS) has discovered that influence glass beads in Chang’e-5 (CE5) lunar soils comprise some water.
Detailed research present that these glass beads are probably a brand new water reservoir on the Moon, recording the dynamic ingress and egress of photo voltaic wind-derived water and performing as a buffer for the lunar floor water cycle.
This work shall be revealed right this moment (March 27) within the journal </span></div>' data-gt-translate-attributes='["attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"]'>Nature Geoscience.
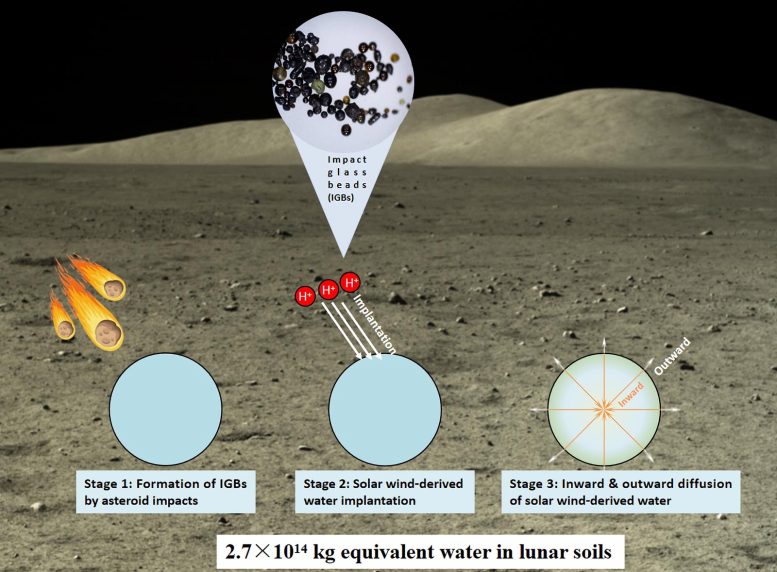
A schematic diagram of the lunar floor water cycle related to influence glass beads Credit score: Prof. Sen Hu’s group
Many lunar missions have confirmed the presence of structural water or water ice on the Moon. There may be little doubt that many of the Moon’s floor harbors water, although the quantity is far lower than on Earth.
Floor water on the Moon shows diurnal cycles and loss to house, indicating that there needs to be a hydrated layer or reservoir at depth in lunar soils to maintain the retention, launch, and replenishment of water on the floor of the Moon. Nonetheless, earlier research of water stock of effective mineral grains in lunar soils, impact-produced agglutinates, volcanic rocks, and pyroclastic glass beads have been unable to clarify the retention, launch, and replenishment of water on the floor of the Moon (i.e., the lunar floor water cycle). Subsequently, there should be a yet-unidentified water reservoir in lunar soils that has the capability to buffer the lunar floor water cycle.
Doctoral scholar Huicun He, underneath the steerage of Prof. Sen Hu, proposed that influence glass beads, a ubiquitous part in lunar soils with an amorphous nature, have been a possible candidate for investigation of the unidentified hydrated layer or reservoir in lunar soils.
She systematically characterised the petrography, main component composition, water abundance, and hydrogen isotope composition of the influence glass beads returned by the CE5 mission, aiming to establish and characterize the lacking water reservoir on the Moon’s floor.
The CE5 influence glass beads have homogeneous chemical compositions and clean uncovered surfaces. They're characterised by water abundance as much as about 2,000 μg.g-1, with excessive deuterium-depleted traits. The adverse correlation between water abundance and hydrogen isotope composition displays the truth that water within the CE5 influence glass beads comes from photo voltaic winds.
The researchers additionally analyzed water abundance alongside six transects in 5 glass beads, which confirmed the hydration profiles of photo voltaic wind-derived water. Some glass beads have been overlapped by a later degassing occasion. The influence glass beads acted as a sponge for buffering the lunar floor water cycle. The researchers estimate that the quantity of water contributed by influence glass beads to lunar soils varies from 3.0 × 1011 kg to 2.7 × 1014 kg.
“These findings point out that the influence glasses on the floor of the Moon and different airless our bodies within the photo voltaic system are able to storing photo voltaic wind-derived water and releasing it into house,” stated Prof Hu.
Reference: “A photo voltaic wind-derived water reservoir on the Moon hosted by influence glass beads” 27 March 2023, Nature Geoscience.
DOI: 10.1038/s41561-023-01159-6
The research was a collaboration with Nanjing College, The Open College, The Pure Historical past Museum, The College of Manchester, and the College of Science and Know-how of China.
Post a Comment