Researchers uncover important modifications within the thermal properties of vitality storage units throughout operation, paving the best way in the direction of higher thermal administration.
Trendy vitality storage units, comparable to supercapacitors and batteries, have extremely temperature-dependent efficiency. If a tool will get too scorching, it turns into prone to ‘thermal runaway.’ Thermal runaway—or uncontrolled overheating—can in the end lead to harmful explosions or fires. Adopting a well-informed thermal administration technique is required for the secure and secure operation of units. To do that, it's needed to know how sure thermal properties, like warmth capability (Cp), dynamically change throughout charging and discharging.
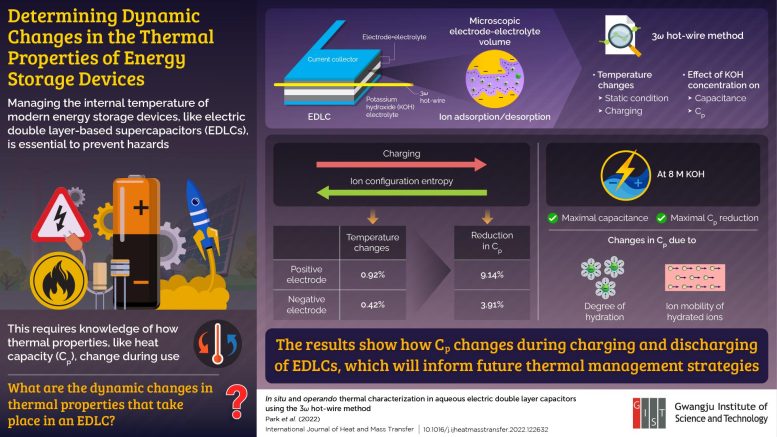
Not too long ago, researchers from the Gwangju Institute of Science and Expertise (GIST) investigated the thermal properties of electrical double-layer capacitors (EDLCs)—a sort of supercapacitor having excessive energy and lengthy life—for a technical basis in thermal measurement and revealed vital info. “Utilizing the threeω hot-wire technique, we had been capable of measure the change in warmth capability of EDLCs in real-time in a microscopic electrode-electrolyte quantity, which is an energetic website for the adsorption and desorption of ions,” explains Prof. Jae Hun Seol, who led the examine.
The examine was made accessible on-line on February 5, 2022, and will likely be printed in Quantity 188, Challenge 122632 of Worldwide Journal of Warmth and Mass Switch on June 1, 2022.
Successfully managing the thermal properties of vitality storage units is the important thing to avoiding thermal runaway and making certain security. Not too long ago, scientists from the Gwangju Institute of Science and Expertise uncovered key modifications to the thermal properties of electrical double-layer capacitors throughout charging and discharging, which can assist inform future thermal administration methods. Credit score: Gwangju Institute of Science and Expertise (GIST)
The analysis staff carried out experiments each in situ (beneath static circumstances) and operando (throughout charging). They discovered that the temperatures of the constructive and damaging electrodes modified by 0.92% and 0.42% throughout charging, which corresponded to 9.14% and three.91% reductions of their respective Cp. “In keeping with thermodynamic concept, the ionic configuration entropy (a measure of randomness) of a system decreases throughout adsorption, i.e., charging. This additionally impacts the free vitality of the system. Collectively, this results in a lower in Cp,” explains Prof. Seol.
The staff additionally diverse the focus of the electrolyte, potassium hydroxide, to see the way it affected EDLC efficiency. They discovered that the EDLC displayed most capacitance and Cp discount when the electrolyte focus was 8 M. They attributed this to variations within the diploma of hydration of ions and their ionic mobility.
“An vital facet of this examine is that charging and discharging additionally alters Cp of EDLCs,” says Prof. Seol. “These findings will lengthen our understanding of the underlying thermal physics of EDLCs.”
Certainly, these outcomes might be thought-about a significant step in the direction of future efficient thermal administration methods, which can create safer and extra dependable vitality storage units.
Reference: “In situ and operando thermal characterization in aqueous electrical double layer capacitors utilizing the threeω hot-wire technique” by Yeongcheol Park, Jaehoon Kim, Changho Kim, Seung-Mo Lee, Chul Kang and Jae Hun Seol, 5 February 2022, Worldwide Journal of Warmth and Mass Switch.
DOI: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2022.122632

Post a Comment