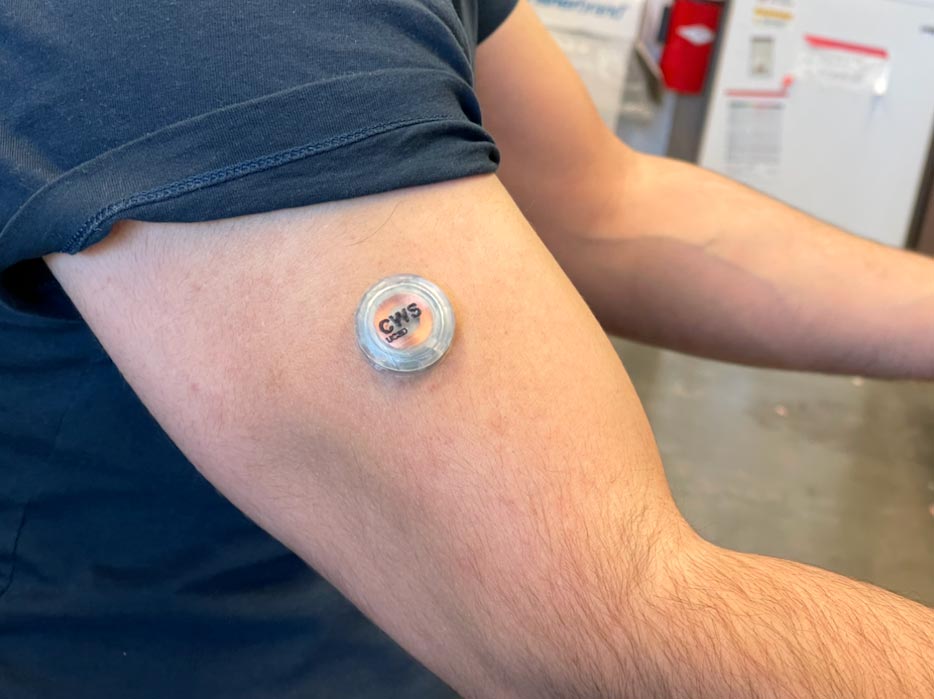
The gadget could be worn on the higher arm whereas the wearer goes about their day. Credit score: Laboratory for Nanobioelectronics / UC San Diego
Think about with the ability to measure your blood sugar ranges, know when you’ve had an excessive amount of alcohol to drink, and observe your muscle fatigue throughout a exercise, multi function small gadget worn in your pores and skin. Engineers on the College of California San Diego (UCSD) have developed a prototype of such a wearable that may constantly monitor a number of well being stats—glucose, alcohol, and lactate ranges—concurrently in real-time.
“This is sort of a full lab on the pores and skin.” — Joseph Wang
The multi-tasking gadget is just in regards to the measurement of a stack of six quarters. It's utilized to the pores and skin via a Velcro-like patch of microscopic needles, or microneedles, which are every about one-fifth the width of a human hair. Sporting the gadget just isn't painful—the microneedles barely penetrate the floor of the pores and skin to sense biomolecules in interstitial fluid, which is the fluid surrounding the cells beneath the pores and skin. The gadget could be worn on the higher arm and sends information wirelessly to a customized smartphone app.
Researchers on the UC San Diego Heart for Wearable Sensors describe their gadget in a paper printed right now (Could 9, 2022) within the journal Nature Biomedical Engineering.
The gadget could be worn on the higher arm and sends information wirelessly to a customized smartphone app. Credit score: Laboratory for Nanobioelectronics / UC San Diego
“This is sort of a full lab on the pores and skin,” stated heart director Joseph Wang, a professor of nanoengineering at UC San Diego and co-corresponding creator of the paper. “It's able to constantly measuring a number of biomarkers on the identical time, permitting customers to watch their well being and wellness as they carry out their day by day actions.”
Most industrial well being screens, similar to steady glucose screens for sufferers with diabetes, solely measure one sign. The issue with that, the researchers stated, is that it leaves out info that would assist individuals with diabetes, for instance, handle their illness extra successfully. Monitoring alcohol ranges is beneficial as a result of consuming alcohol can decrease glucose ranges. Realizing each ranges may also help individuals with diabetes forestall their blood sugar from dropping too low after having a drink. Combining details about lactate, which could be monitored throughout train as a biomarker for muscle fatigue, can also be helpful as a result of bodily exercise influences the physique’s means to manage glucose.
“With our wearable, individuals can see the interaction between their glucose spikes or dips with their eating regimen, train, and consuming of alcoholic drinks. That would add to their high quality of life as nicely,” stated Farshad Tehrani, a nanoengineering Ph.D. scholar in Wang’s lab and one of many co-first authors of the examine.
Microneedles merged with electronics
The wearable consists of a microneedle patch related to a case of electronics. Totally different enzymes on the information of the microneedles react with glucose, alcohol and lactate in interstitial fluid. These reactions generate small electrical currents, that are analyzed by digital sensors and communicated wirelessly to an app that the researchers developed. The outcomes are displayed in actual time on a smartphone.
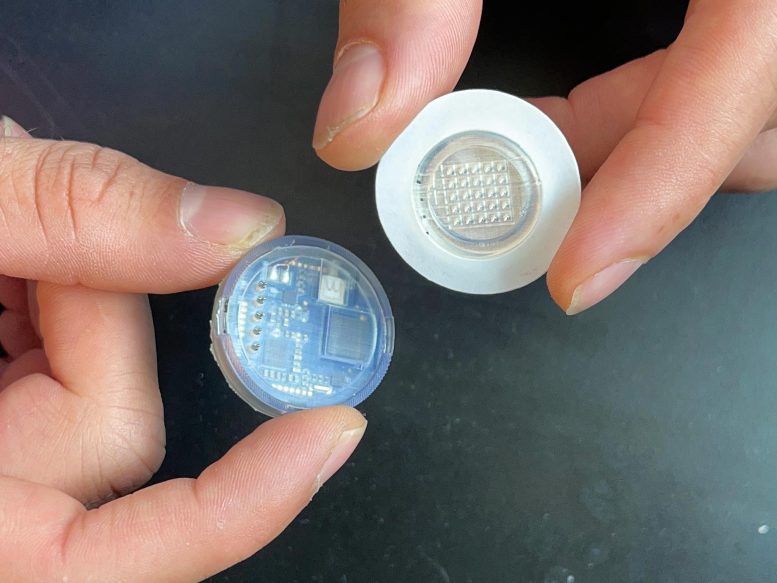
The disposable microneedle patch detaches from the reusable digital case. Credit score: Laboratory for Nanobioelectronics / UC San Diego
A bonus of utilizing microneedles is that they immediately pattern the interstitial fluid, and analysis has proven that biochemical ranges measured in that fluid correlate nicely with ranges in blood.
“We’re beginning at a extremely good place with this know-how when it comes to scientific validity and relevance,” stated Patrick Mercier, a professor of electrical and pc engineering at UC San Diego and co-corresponding creator of the paper. “That lowers the obstacles to scientific translation.”
The microneedle patch, which is disposable, could be indifferent from the digital case for straightforward alternative. The digital case, which is reusable, homes the battery, digital sensors, wi-fi transmitter, and different digital elements. The gadget could be recharged on any wi-fi charging pad used for telephones and smartwatches.
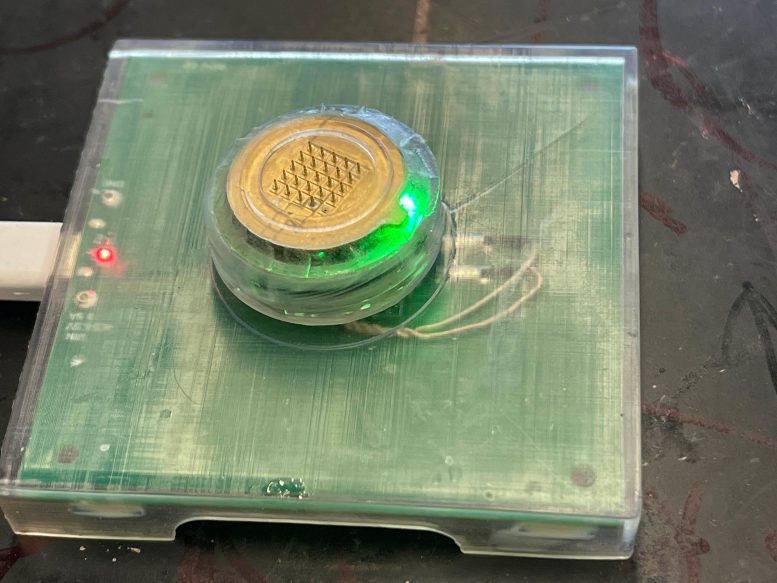

The gadget could be recharged on an off-the-shelf wi-fi charging pad. Credit score: Laboratory for Nanobioelectronics / UC San Diego
Integrating all these elements collectively into one small, wi-fi wearable was one of many crew’s greatest challenges. It additionally required some intelligent design and engineering to mix the reusable electronics, which should keep dry, with the microneedle patch, which will get uncovered to organic fluid.
“The great thing about that is that it's a totally built-in system that somebody can put on with out being tethered to benchtop gear,” stated Mercier, who can also be the co-director of the UC San Diego Heart for Wearable Sensors.
Testing
The wearable was examined on 5 volunteers, who wore the gadget on their higher arm, whereas exercising, consuming a meal, and consuming a glass of wine. The gadget was used to constantly monitor the volunteers’ glucose ranges concurrently with both their alcohol or lactate ranges. The glucose, alcohol and lactate measurements taken by the gadget carefully matched the measurements taken respectively by a industrial blood glucose monitor, Breathalyzer, and blood lactate measurements carried out within the lab.
Subsequent steps
Farshad Tehrani and fellow co-first creator Hazhir Teymourian, who's a former postdoctoral researcher in Wang’s lab, co-founded a startup firm known as AquilX to additional develop the know-how for commercialization. Subsequent steps embrace testing and bettering upon how lengthy the microneedle patch can final earlier than being changed. The corporate can also be enthusiastic about the potential of including extra sensors to the gadget to watch treatment ranges in sufferers and different well being indicators.
Reference: “An built-in wearable microneedle array for the continual monitoring of a number of biomarkers in interstitial fluid” 9 Could 2022, Nature Biomedical Engineering.
DOI: 10.1038/s41551-022-00887-1
Funding: NIH/Nationwide Institute of Neurological Issues and Stroke
Post a Comment