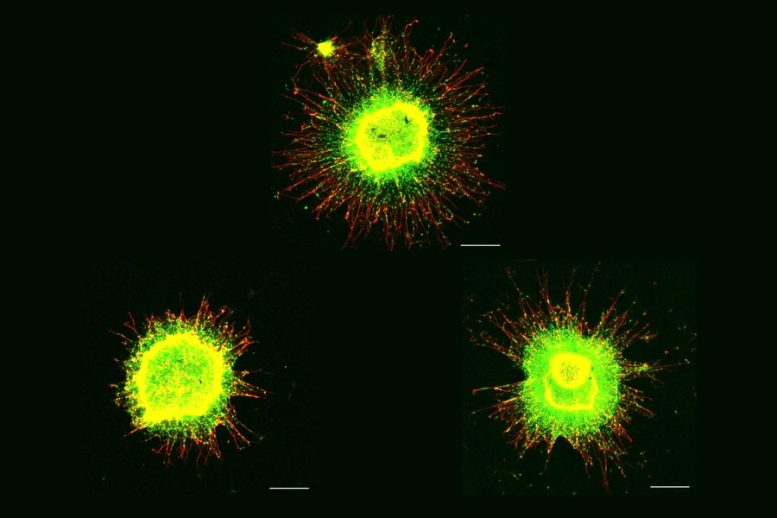
Neural progenitor cells with the everyday variety of chromosomes present important outward migration in tradition (prime). The cells within the backside left are untreated trisomy 21 cells. On the underside proper are cells handled with anti-senecence medication, which restored migration. Credit score: Picture courtesy of the Alana Down Syndrome Heart/Tsai lab
Additional chromosome alters chromosomal conformation and DNA accessibility in neural progenitor cells; examine establishes senescence as a probably targetable mechanism for future therapy.
In Down syndrome, the third copy of chromosome 21 causes a reorganization of the 3D configuration of your entire genome in a key cell kind of the growing mind, a brand new examine reveals. The ensuing disruption of gene transcription and cell operate are so just like these seen in mobile ageing, or senescence, that the scientists main the examine discovered they may use anti-senescence medication to right them in cell cultures.
The examine printed in Cell Stem Cell due to this fact establishes senescence as a probably targetable mechanism for future therapy of Down syndrome, says Hiruy Meharena, who led the work as a Senior Alana Fellow within the Alana Down Syndrome Heart at MIT and is now an assistant professor on the College of California at San Diego.
“There's a cell-type-specific genome-wide disruption that's impartial of the gene dosage response,” Meharena says. “It’s a really related phenomenon to what’s noticed in senescence. This means that extreme senescence within the growing mind induced by the third copy of chromosome 21 might be a key purpose for the neurodevelopmental abnormalities seen in Down syndrome.”
Li-Huei Tsai and Hiruy Meharena seek the advice of about photos produced in the course of the analysis on this 2019 picture. Credit score: David Orenstein/The Picower Institute
The examine’s discovering that neural progenitor cells (NPCs), which grow to be main cells within the mind together with neurons, have a senescent character is outstanding and novel, says senior writer Li-Huei Tsai, however it's substantiated by the workforce’s in depth work to elucidate the underlying mechanism of the consequences of irregular chromosome quantity, or aneupoloidy, inside the nucleus of the cells.
“This examine illustrates the significance of asking elementary questions in regards to the underlying mechanisms of neurological problems,” says Tsai, Picower Professor of Neuroscience, director of the Alana Heart, and of the Picower Institute for Studying and Reminiscence at MIT. “We didn’t start this work anticipating to see senescence as a translationally related characteristic of Down syndrome, however the information emerged from asking how the presence of an additional chromosome impacts the structure of all of a cell’s chromosomes throughout improvement.”
Genome-wide adjustments
Meharena and co-authors spent years measuring distinctions between human cell cultures that differed solely by whether or not they had a 3rd copy of chromosome 21. Stem cells derived from volunteers had been cultured to show into NPCs. In each the stem cells and the NPCs, the workforce examined 3D chromosome structure, a number of metrics of DNA construction and interplay, gene accessibility and transcription, and gene expression. Additionally they appeared on the penalties of the gene expression variations on vital features of those developmental cells, reminiscent of how effectively they proliferated and migrated in 3D mind tissue cultures. Stem cells weren't notably completely different, however NPCs had been considerably affected by the third copy of chromosome 21.
General, the image that emerged in NPCs was that the presence of a 3rd copy causes all the opposite chromosomes to squish inward, not in contrast to when folks in a crowded elevator should slim their stance when yet one more individual squeezes in. The primary results of this “chromosomal introversion,” meticulously quantified within the examine, are extra genetic interactions inside every chromosome and fewer interactions amongst them. These adjustments and variations in DNA conformation inside the cell nucleus result in adjustments in how genes are transcribed and due to this fact expressed, inflicting vital variations in cell operate that have an effect on mind improvement.
Handled as senescence
For the primary couple of years as these information emerged, Meharena says, the total significance of the genomic adjustments weren't obvious, however then he learn a paper exhibiting very related genomic rearrangement and transcriptional alterations in senescent cells.
After validating that the Down syndrome cells certainly bore such an identical signature of transcriptional variations, the workforce determined to check whether or not anti-senecence medication may undo the consequences. They examined a mix of two: dasatinib and quercetin. The medicines improved not solely gene accessibility and transcription, but in addition the migration and proliferation of cells.
That stated, the medication have very important unintended effects — dasatinib is just given to most cancers sufferers when different remedies haven't performed sufficient — so they aren't applicable for making an attempt to intervene in mind improvement amid Down syndrome, Meharena says. As a substitute, an end result of the examine might be to encourage a seek for medicines that might have anti-senolytic results with a safer profile.
Senescence is a stress response of cells. On the identical time, years of analysis by the late MIT professor of biology Angelika Amon, who co-directed the Alana Heart with Tsai, has proven that aneuploidy is a supply of appreciable stress for cells. A query raised by the brand new findings, due to this fact, is whether or not the senescence-like character of Down syndrome NPCs is certainly the results of an aneuploidy-induced stress and, if that's the case, precisely what that stress is.
One other implication of the findings is how extreme senescence amongst mind cells would possibly have an effect on folks with Down syndrome later in life. The danger of Alzheimer’s illness is way increased at a considerably earlier age within the Down syndrome inhabitants than amongst folks basically. Largely that is believed to be as a result of a key Alzheimer’s danger gene, APP, is on chromosome 21, however the newly recognized inclination for senescence may additionally speed up Alzheimer’s improvement.
Reference: “Down-syndrome-induced senescence disrupts the nuclear structure of neural progenitors” by Hiruy S. Meharena, Asaf Marco, Vishnu Dileep, Elana R. Lockshin, Grace Y. Akatsu, James Mullahoo, L. Ashley Watson, Tak Ko, Lindsey N. Guerin, Fatema Abdurrob, Shruthi Rengarajan, Malvina Papanastasiou, Jacob D. Jaffe and Li-Huei Tsai, 6 January 2022, Cell Stem Cell.
DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2021.12.002
Along with Meharena and Tsai, the paper’s different authors are Asaf Marco, Vishnu Dileep, Elana Lockshin, Grace Akatsu, James Mullahoo, Ashley Watson, Tak Ko, Lindsey Guerin, Fatema Abdurrob, Shruti Rengarajan, Malvina Papanastasiou and Jacob Jaffe.
The Alana Basis, the LuMind Basis, Burroughs Wellcome Fund, UNCF-Merck, and the Nationwide Institutes of Well being funded the analysis.
Post a Comment