
A dusty lunar panorama, as envisioned by NASA’s Superior Ideas Laboratory. Credit score: NASA
On a chilly winter day, the heat of the solar is welcome. But as humanity emits increasingly greenhouse gases, the Earth’satmosphere traps increasingly of the solar’s vitality and steadily will increase the Earth’s temperature. One technique for reversing this development is to intercept a fraction of daylight earlier than it reaches our planet. For many years, scientists have thought-about utilizing screens, objects, or mud particles to dam simply sufficient of the solar’s radiation—between 1 or 2%—to mitigate the results of worldwide warming.
A College of Utah-led examine explored the potential of utilizing mud to protect daylight. They analyzed totally different properties of mud particles, portions of mud, and the orbits that will be greatest fitted to shading Earth. The authors discovered that launching mud from Earth to a manner station on the “Lagrange Level” between Earth and the solar (L1) could be only however would require astronomical price and energy. An alternate is to make use of moondust. The authors argue that launching lunar mud from the moon as an alternative may very well be an affordable and efficient technique to shade the Earth.
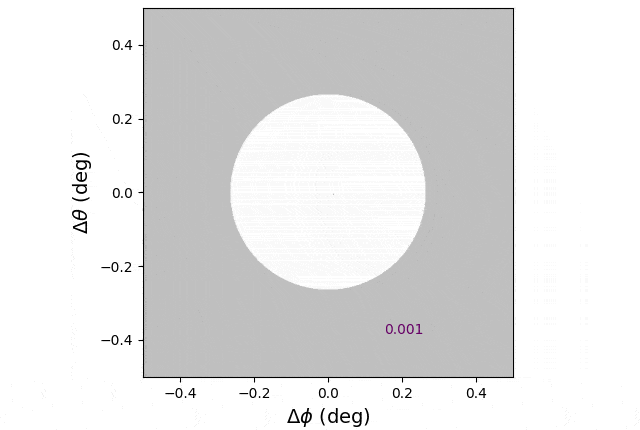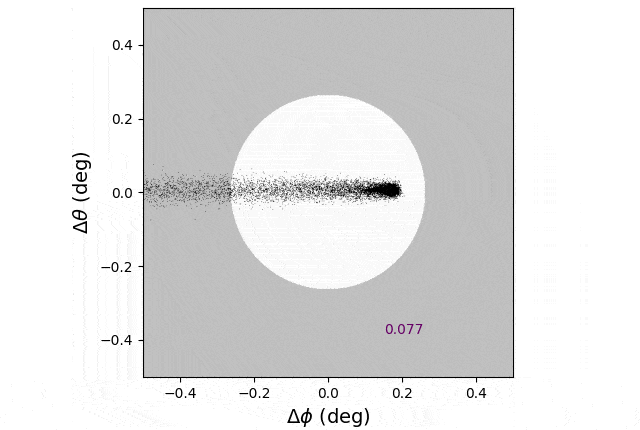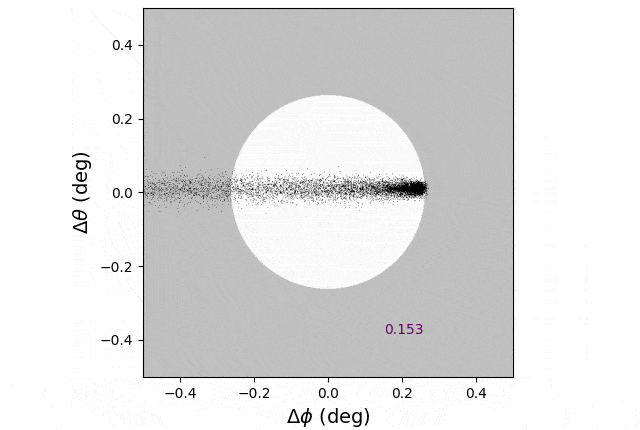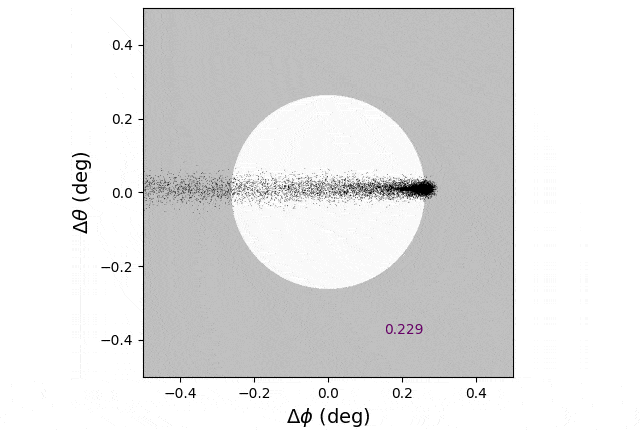
Simulated stream of mud launched between Earth and the solar. This mud cloud is proven because it crosses the disk of the solar, considered from Earth. Streams like this one, together with these launched from the moon’s floor, can act as a brief sunshade. Credit score: Ben Bromley/College of Utah
The staff of astronomers utilized a method used to check planet formation round distant stars, their common analysis focus. Planet formation is a messy course of that kicks up a number of astronomical mud that may kind rings across the host star. These rings intercept gentle from the central star and re-radiate it in a manner that we are able to detect it on Earth. One technique to uncover stars which can be forming new planets is to search for these dusty rings.
“That was the seed of the thought; if we took a small quantity of fabric and put it on a particular orbit between the Earth and the solar and broke it up, we may block out a number of daylight with somewhat quantity of mass,” mentioned Ben Bromley, professor of physics and astronomy and lead writer of the examine.
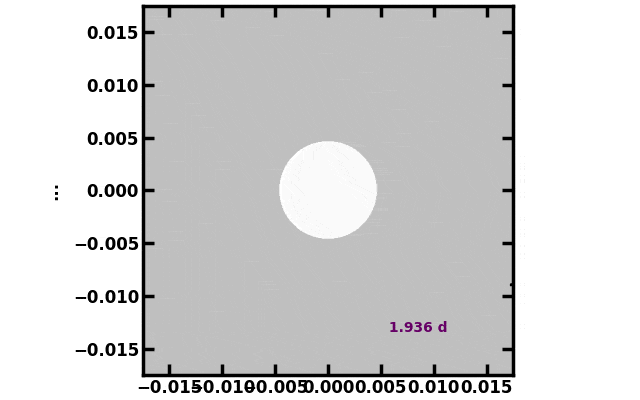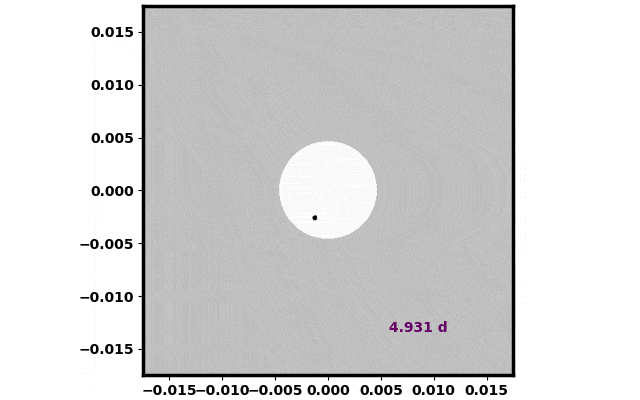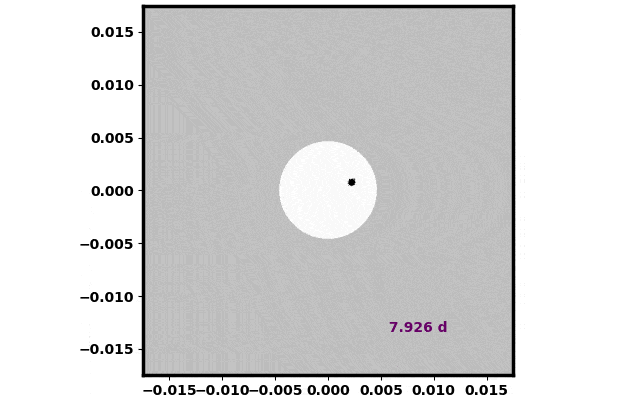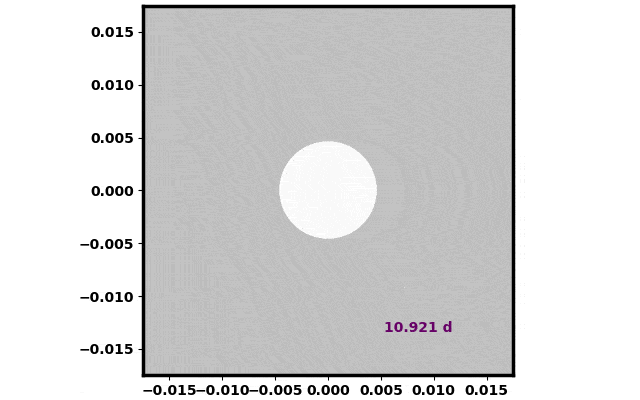
A simulation from mud launched from the best way station at Lagrange level 1. The shadow solid on Earth is exaggerated for readability. Credit score: Ben Bromley
“It's superb to ponder how moon mud—which took over 4 billion years to generate—would possibly assist sluggish the rise in Earth’s temperature, an issue that took us lower than 300 years to provide,” mentioned Scott Kenyon, co-author of the examine from the Heart for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian.
The paper was revealed lately within the journal PLOS Local weather.
Casting a shadow
A protect’s total effectiveness depends upon its skill to maintain an orbit that casts a shadow on Earth. Sameer Khan, undergraduate scholar and the examine’s co-author, led the preliminary exploration into which orbits may maintain mud in place lengthy sufficient to supply sufficient shading. Khan’s work demonstrated the issue of conserving mud the place you want it to be.
“As a result of we all know the positions and much of the key celestial our bodies in our photo voltaic system, we are able to merely use the legal guidelines of gravity to trace the place of a simulated sunshield over time for a number of totally different orbits,” mentioned Khan.
Two eventualities have been promising. Within the first state of affairs, the authors positioned an area platform on the L1 Lagrange level, the closest level between Earth and the solar the place the gravitational forces are balanced. Objects at Lagrange factors have a tendency to remain alongside a path between the 2 celestial our bodies, which is why the James Webb House Telescope (JWST) is situated at L2, a Lagrange level on the alternative aspect of the Earth.
A simulation of mud launched from the moon’s floor as seen from Earth. Credit score: Ben Bromley
In pc simulations, the researchers shot take a look at particles alongside the L1 orbit, together with the place of Earth, the solar, the moon, and different photo voltaic system planets, and tracked the place the particles scattered. The authors discovered that when launched exactly, the mud would comply with a path between Earth and the solar, successfully creating shade, at the least for some time. In contrast to the 13,000-pound JWST, the mud was simply blown off beam by the photo voltaic winds, radiation, and gravity inside the photo voltaic system. Any L1 platform would wish to create an limitless provide of recent mud batches to blast into orbit each few days after the preliminary spray dissipates.
“It was reasonably troublesome to get the protect to remain at L1 lengthy sufficient to solid a significant shadow. This shouldn’t come as a shock, although, since L1 is an unstable equilibrium level. Even the slightest deviation within the sunshield’s orbit could cause it to quickly drift misplaced, so our simulations needed to be extraordinarily exact,” Khan mentioned.
Within the second state of affairs, the authors shot lunar mud from the floor of the moon in the direction of the solar. They discovered that the inherent properties of lunar mud have been excellent to successfully work as a solar protect. The simulations examined how lunar mud scattered alongside varied programs till they discovered glorious trajectories aimed towards L1 that served as an efficient solar protect. These outcomes are welcome information, as a result of a lot much less vitality is required to launch mud from the moon than from Earth. That is essential as a result of the quantity of mud in a photo voltaic protect is massive, similar to the output of an enormous mining operation right here on Earth. Moreover, the invention of the brand new sun-shielding trajectories means delivering the lunar mud to a separate platform at L1 will not be needed.
Only a moonshot?
The authors stress that this examine solely explores the potential influence of this technique, reasonably than consider whether or not these eventualities are logistically possible.
“We aren’t consultants in local weather change, or the rocket science wanted to maneuver mass from one place to the opposite. We’re simply exploring totally different sorts of mud on a wide range of orbits to see how efficient this method could be. We don't wish to miss a recreation changer for such a important downside,” mentioned Bromley.
One of many greatest logistical challenges—replenishing mud streams each few days—additionally has a bonus. Ultimately, the solar’s radiation disperses the mud particles all through the photo voltaic system; the solar protect is momentary and protect particles don't fall onto Earth. The authors guarantee that their method wouldn't create a completely chilly, uninhabitable planet, as within the science fiction story, “Snowpiercer.”
“Our technique may very well be an possibility in addressing local weather change,” mentioned Bromley, “if what we'd like is extra time.”
Reference: “Mud as a photo voltaic protect” by Benjamin C. Bromley, Sameer H. Khan and Scott J. Kenyon, 8 February 2023, PLOS Local weather.
DOI: 10.1371/journal.pclm.0000133
Post a Comment