If left untreated, continual wounds reminiscent of diabetic pores and skin ulcers can turn out to be contaminated, finally resulting in amputations and even loss of life. An experimental new "good" bandage is designed to assist hold that from occurring, by each watching and treating such accidents.
Taking the type of an digital skin-adhered patch, the dressing is being developed on the California Institute of Know-how by a group led by Asst. Prof. Wei Gao.
It incorporates a versatile, stretchable, biocompatible polymer substrate, on the underside of which is an array of sensory electrodes, a pair of voltage-modulated electrodes, and a layer of drug-loaded hydrogel. Mounted on high of that substrate is a small, versatile printed circuit board which accommodates electronics reminiscent of a battery, Bluetooth chip, and temperature sensor.
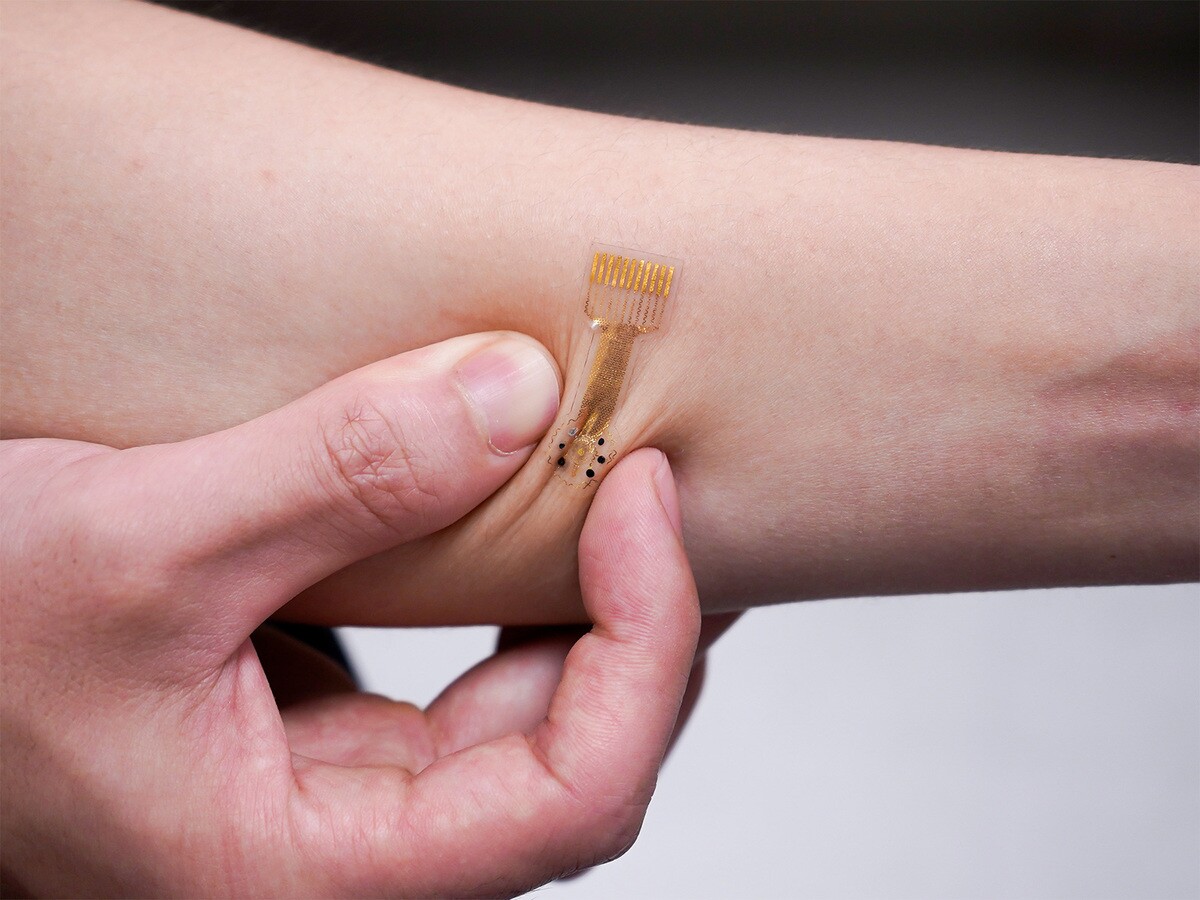
As soon as utilized on to a wound web site, the bandage repeatedly makes use of its sensors to verify the focus of chemical compounds like uric acid, ammonium, glucose and lactate – plus it checks for adjustments within the wound's pH and temperature – all of that are indicators of an infection or irritation.
If any such indicators are detected, the bandage responds by sending an alert to a close-by smartphone or different system. It additionally makes use of its voltage-modulated electrodes to set off the discharge of medicine from the hydrogel, and to ship a low-voltage electrical present to the wound mattress, stimulating the regrowth of latest tissue.
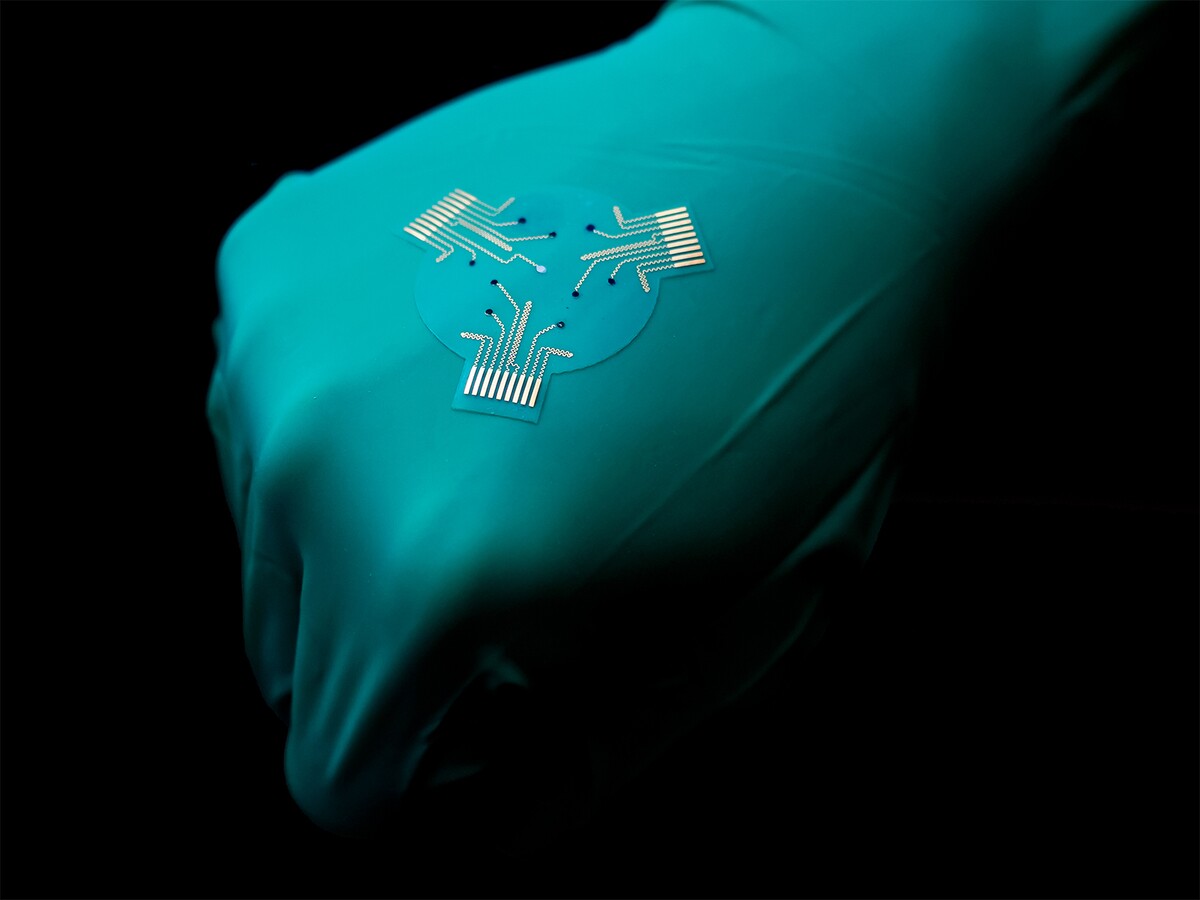
In lab assessments carried out on rats, the know-how proved to achieve success at precisely relaying wound-status information, killing dangerous micro organism reminiscent of E. coli, and at rushing the therapeutic of continual wounds much like diabetic pores and skin ulcers. Plans now name for human trials to be carried out.
"Now we have confirmed this proof of idea in small animal fashions, however down the street, we want to improve the soundness of the system but in addition to check it on bigger continual wounds as a result of the wound parameters and microenvironment could range from web site to web site," stated Gao.
A paper on the analysis was not too long ago printed within the journal Science Advances.
Supply: Caltech
Post a Comment