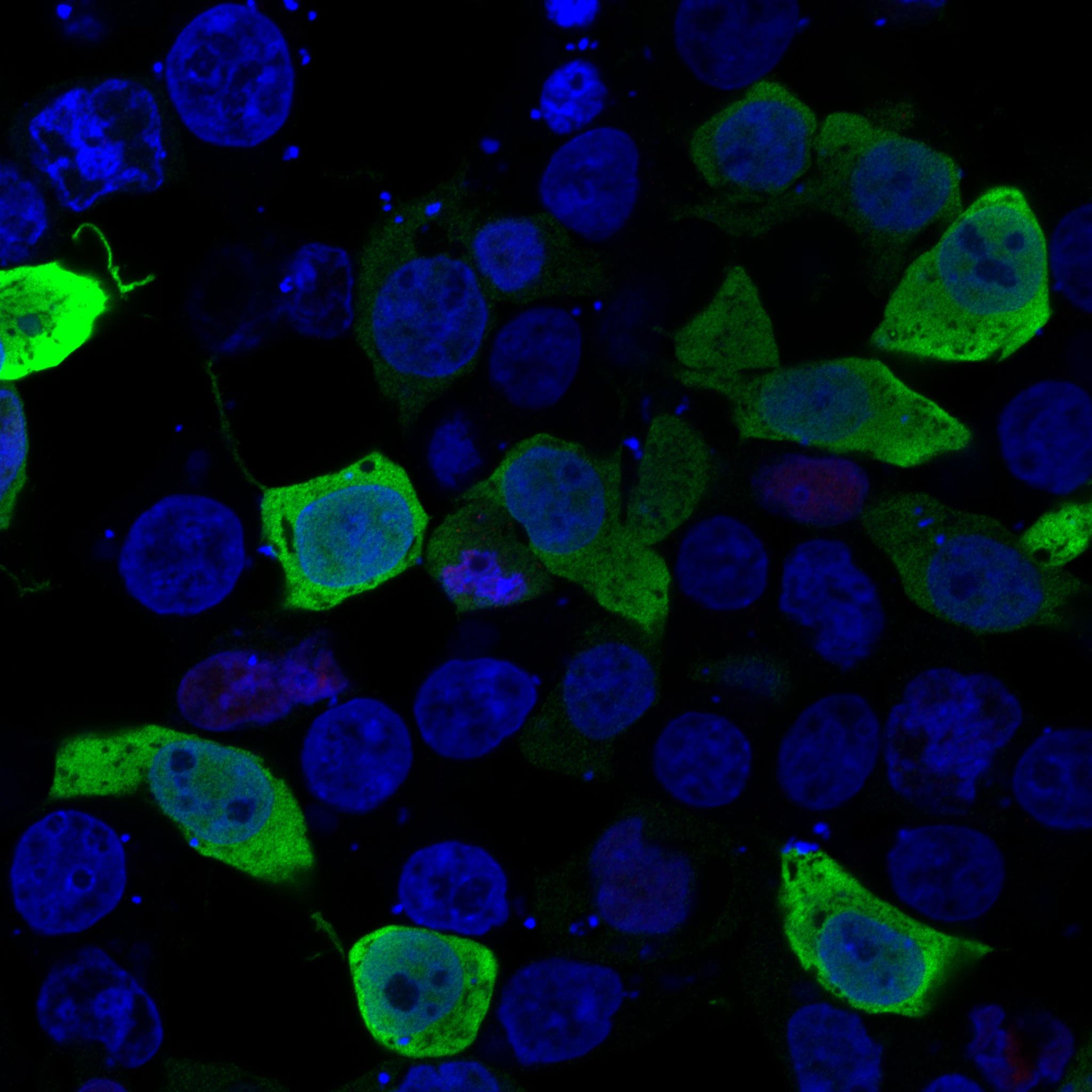
Daniel Greene, Ph.D., and colleagues used a computational strategy to determine beforehand unknown genetic causes of three uncommon illnesses: major lymphedema, thoracic aortic aneurysm illness, and congenital deafness. On this microscopy picture of cells, a mutated type of a protein known as ERG, which is current in some lymphedema sufferers, is proven in inexperienced, whereas cell nuclei are proven in blue. Usually, the ERG protein exists solely contained in the nuclei of cells. Nonetheless, the mutant kind noticed in sufferers is distributed outdoors of the nucleus, within the cytoplasm of cells. Credit score: Daniela Pirri, Ph.D., and Graeme Birdsey, Ph.D., of the Nationwide Coronary heart and Lung Institute, Imperial Faculty London, who're each co-authors of the Nature Medication paper.
Researchers at Mount Sinai have created a computational technique that allows the identification of beforehand unknown genetic causes for major lymphedema, thoracic aortic aneurysm illness, and congenital deafness.
Researchers from the Icahn College of Medication at Mount Sinai, together with their colleagues, have found new genetic causes for 3 uncommon situations – major lymphedema, thoracic aortic aneurysm illness, and congenital deafness – utilizing a novel computational strategy they developed to investigate in depth genetic datasets from uncommon illness cohorts.
The undertaking was a collaborative effort that concerned researchers from numerous elements of the world, together with the College of Bristol within the UK, KU Leuven in Belgium, the College of Tokyo, the College of Maryland, Imperial Faculty London, and others.
The newly acquired information in regards to the roles performed by genes related to these and different issues could present a basis for growing potential therapies. The outcomes have been revealed within the journal Nature Medication.
Uncommon illnesses have an effect on roughly 1 in 20 folks, however solely a minority of sufferers obtain a genetic prognosis. Fewer than half of the ten,000 recorded uncommon illnesses have a identified genetic trigger. Genome sequencing of huge cohorts of uncommon illness sufferers gives a route towards discovering the genetic causes that stay unknown. Nonetheless, giant genetic datasets are difficult to work with, slowing down analysis considerably, say the investigators.
“Whereas uncommon illnesses are individually uncommon, collectively they're fairly widespread. It will be important for our understanding of human biology and for the event of diagnostics and therapeutics that the remaining causes are discovered,” stated senior research writer Ernest Turro, Ph.D., Affiliate Professor of Genetics and Genomics Sciences at Icahn Mount Sinai. “Many individuals with a uncommon illness battle for a few years to acquire a genetic prognosis. By growing and making use of statistical strategies and computational approaches to seek out new causes of uncommon illnesses, we hope to broaden information of the underlying causes of those illnesses, hasten the time to prognosis for sufferers, and pave the way in which for the event of therapies.”
The investigators studied a group of 269 uncommon illness lessons utilizing information from 77,539 contributors within the 100,000 Genomes Undertaking, one of many largest datasets of phenotyped and whole-genome-sequenced uncommon illness sufferers. The researchers recognized 260 associations between genes and uncommon illness lessons, together with 19 associations beforehand absent from the literature. By way of a global tutorial collaboration, the authors validated the three most believable novel associations by figuring out further instances in different international locations and thru experimental and bioinformatic approaches.
“We hope that our computational framework will assist speed up the invention of the remaining unknown etiologies of uncommon illnesses throughout the board. For now, we anticipate that a genetic prognosis will likely be attainable for sure households with beforehand unexplained major lymphedema, thoracic aortic aneurysm illness, and deafness,” stated Daniel Greene, Ph.D., a postdoctoral fellow at Icahn Mount Sinai and lead writer of the research. “We additionally plan to use our strategies in novel methods and in different datasets, with the purpose of continuous to unravel the genetic causes of uncommon illnesses.”
Reference: “Genetic affiliation evaluation of 77,539 genomes reveals uncommon illness etiologies” by Daniel Greene, Genomics England Analysis Consortium, Daniela Pirri, Karen Frudd, Ege Sackey, Mohammed Al-Owain, Arnaud P. J. Giese, Khushnooda Ramzan, Sehar Riaz, Itaru Yamanaka, Nele Boeckx, Chantal Thys, Bruce D. Gelb, Paul Brennan, Verity Hartill, Julie Harvengt, Tomoki Kosho, Sahar Mansour, Mitsuo Masuno, Takako Ohata, Helen Stewart, Khalid Taibah, Claire L. S. Turner, Faiqa Imtiaz, Saima Riazuddin, Takayuki Morisaki, Pia Ostergaard, Bart L. Loeys, Hiroko Morisaki, Zubair M. Ahmed, Graeme M. Birdsey, Kathleen Freson, Andrew Mumford and Ernest Turro, 16 March 2023, Nature Medication.
DOI: 10.1038/s41591-023-02211-z
Post a Comment