
This picture from ESA’s Mars Categorical exhibits Nectaris Fossae and Protva Valles, advanced geological options discovered on Mars. Spherical affect craters are scattered throughout the body, and a band of fractured grooves, resembling scratches and scars carved into the rock, stretches from the highest left to backside proper.
This picture contains knowledge gathered by Mars Categorical’ Excessive Decision Stereo Digital camera (HRSC) on Might 23, 2022. It was created utilizing knowledge from the nadir channel, the sector of view aligned perpendicular to the floor of Mars, and the color channels of the HRSC. It's a ‘true colour’ picture, reflecting what can be seen by the human eye if taking a look at this area of Mars.
Credit score: ESA/DLR/FU Berlin, CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO
Mars shows fascinating geology all over the place you look – and nowhere is that this extra true than within the fractured, wrinkled floor seen on this picture from the European Area Company’s (ESA) Mars Categorical.
The scene, captured by the Excessive Decision Stereo Digital camera (HRSC) on the Mars Categorical orbiter, options the flanks of an enormous volcanic plateau named Thaumasia Planum. The very best options seen listed below are a whopping 4500 m taller than the bottom, as seen most clearly within the related topographical map. Many thought to have modified little or no since they shaped almost 4 billion years in the past, giving an thrilling glimpse into Mars’ earliest days.

This color-coded topographic picture exhibits Nectaris Fossae and Protva Valles on Mars. It was created from knowledge collected by ESA’s Mars Categorical on 23 Might 2022. It's primarily based on a digital terrain mannequin of the area, from which the topography of the panorama could be derived. Decrease elements of the floor are proven in blues and purples, whereas increased altitude areas present up in whites and reds, as indicated on the dimensions to the highest proper. Credit score: ESA/DLR/FU Berlin, CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO
Shifting plates
This advanced area seems to have been formed by each tectonics (deformation of the planetary crust) and by previous working water.
Whereas Mars now not shows indicators of lively tectonics, this has not at all times been the case.
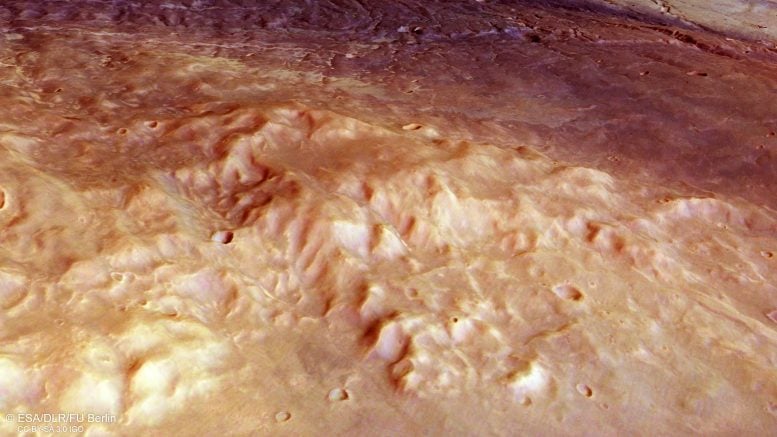
This indirect perspective view of Nectaris Fossae and Protva Valles on Mars was generated from the digital terrain mannequin and the nadir and colour channels of the Excessive Decision Stereo Digital camera on ESA’s Mars Categorical. Bumpy textured mounds and grooves could be seen within the foreground, whereas a deeper fissure working roughly parallel to the highest of the body could be seen within the distance. Credit score: ESA/DLR/FU Berlin, CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO
Mars’ crust as soon as skilled important stresses on this area, creating the deep floor fractures at present generally known as Nectaris Fossae. These are seen as near-vertical scars on the middle of this picture and have since been crammed by light-colored mud. They're thought to have shaped in relation to the colossal Valles Marineris canyon system, the most important such system not solely on Mars however within the Photo voltaic System. Valles Marineris lies simply to the north (proper) of this area.
Flowing water
After tectonism reworked this patch of Mars, water flowed throughout the floor, reducing into the rock and carving out deep valleys because it did so (options named Protva Valles – the plural ‘Valles’ referring to a number of channels). These channels could be seen unfold throughout these photos; some are broad and superficial and a few far deeper. The dense patch of water-carved valleys to the underside proper of the picture is extremely eroded.

This picture from ESA’s Mars Categorical exhibits Nectaris Fossae and Protva Valles, advanced geological options discovered on Mars. Key options are labeled throughout the body: the broad, deep incised, and intensely eroded valleys of Protva Valles; three distinguished wrinkle ridges; and the dust-filled fractures of Nectaris Fossae. Credit score: ESA/DLR/FU Berlin, CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO
Protva Valles shaped when water was way more plentiful throughout the floor of Mars, some 3.8 billion years in the past, and has remained largely unchanged since.
Constructed on lava
The underlying terrain right here – Thaumasia Planum – shaped within the very earliest days of Mars and is basically made up of immense lava flows a number of kilometers thick.
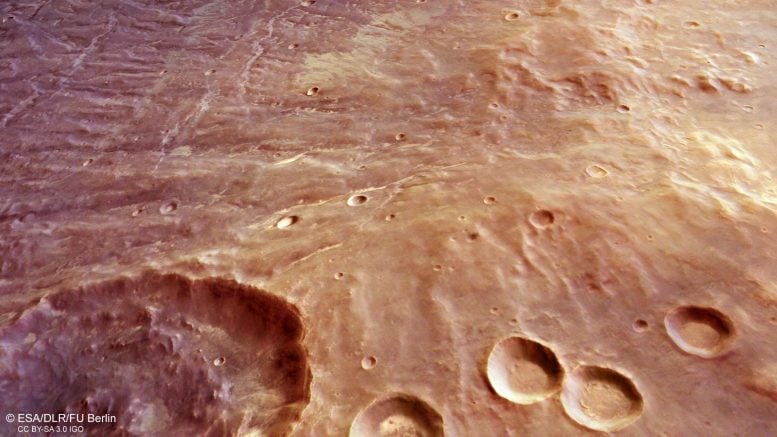
This indirect perspective view of Nectaris Fossae and Protva Valles on Mars was generated from the digital terrain mannequin and the nadir and colour channels of the Excessive Decision Stereo Digital camera on ESA’s Mars Categorical. A big affect crater options within the backside left, stretching partially out of body, with 4 smaller craters dotted throughout to its proper. Some textures and grooves could be seen within the extra distant floor. Credit score: ESA/DLR/FU Berlin, CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO
This time was a turbulent one, with lots of Mars’ standout options simply starting to kind. The Tharsis volcanoes, among the largest within the Photo voltaic System, are positioned close to to Thaumasia Planum; the load and stress of those volcanoes forming could have prompted this area to start fracturing, earlier than these volcanoes then flooded the world with lava.
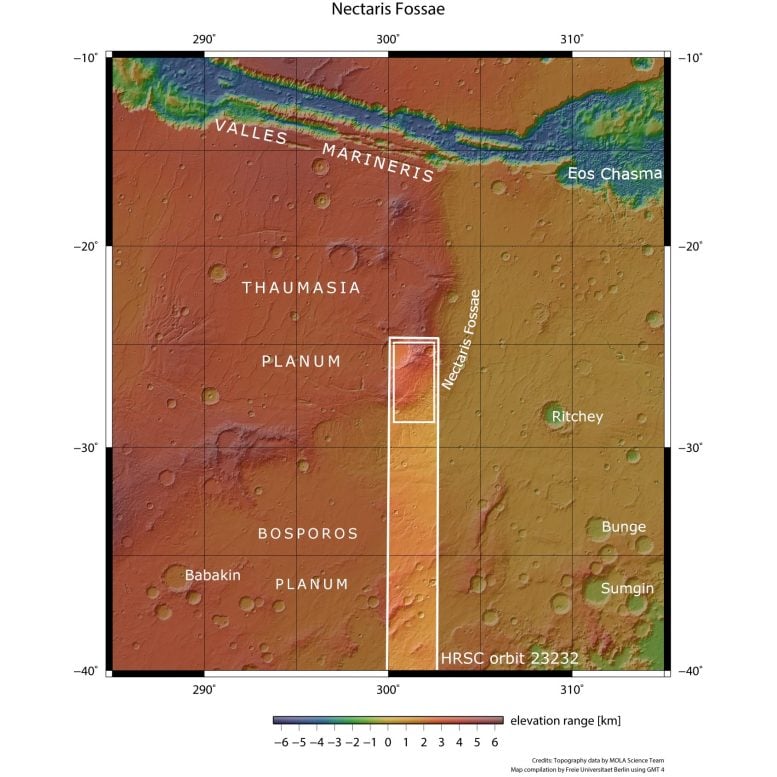
This picture from ESA’s Mars Categorical exhibits Nectaris Fossae and Protva Valles on Mars. The world outlined by the daring white field signifies the world imaged by the Mars Categorical Excessive Decision Stereo Digital camera on Might 23, 2022, throughout orbit 23232. Credit score: NASA/MGS/MOLA Science Group
As these lava flows cooled and solidified on unstable, shifting floor, they turned compressed, leading to ‘wrinkle ridges’. One of the crucial substantial ridges is seen to the bottom-right of middle as an unsteady diagonal line scored into the floor.
Following this intensive resurfacing by lava, Thaumasia Planum was coated in volcanic ash and mud, earlier than the water flows reduce by way of the lava to kind the Protva Valles. The origin of those water flows stays unclear; they seem to emerge at completely different heights, implying that water could have seeped by way of subsurface layers of Mars.

This stereoscopic picture exhibits Nectaris Fossae and Protva Valles on Mars. It was generated from knowledge captured by the Excessive Decision Stereo Digital camera (HRSC) on ESA’s Mars Categorical orbiter on Might 23, 2022, throughout orbit 23232. The anaglyph, derived from knowledge acquired by the nadir channel and one stereo channel of the HRSC, presents a three-dimensional view when considered utilizing red-green or red-blue glasses. Credit score: ESA/DLR/FU Berlin, CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO
Exploring Mars
Mars Categorical has been orbiting the Pink Planet since 2003, imaging the floor of Mars, mapping its minerals, figuring out the composition and circulation of its tenuous environment, probing beneath its crust, and exploring how varied phenomena work together within the martian atmosphere.
Mars Categorical is a robotic area probe developed by the European Area Company (ESA) that was launched in 2003 to review the planet Mars. It's the first planetary mission undertaken by the ESA and is presently nonetheless in operation.
The Excessive Decision Stereo Digital camera (HRSC) is among the main devices onboard Mars Categorical. It's a high-resolution digicam able to producing 3D photos of the Martian floor. The HRSC has been used to create detailed maps of Mars, together with topographic maps and colour photos of geological options corresponding to canyons, valleys, and affect craters. The information collected by the HRSC has contributed considerably to our understanding of the geological and morphological traits of Mars. HRSC was developed and is operated by the German Aerospace Heart (Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt; DLR).
Post a Comment