Senescent cells, or “zombie cells,” are distinctive in that they finally stop multiplying however don't die off as anticipated.
Researchers have discovered a brand new pathway for the buildup of “zombie cells,” which promote getting old.
Senescent cells, or cells which have misplaced their capability to divide, enhance with age and are main contributors to age-related diseases resembling most cancers, dementia, and heart problems. In a brand new examine, a crew led by the College of Pittsburgh and UPMC Hillman Most cancers Heart researchers found a technique by means of which senescent, or “zombie,” cells develop.

Patricia Opresko, Ph.D., professor of environmental and occupational well being and of pharmacology and chemical biology on the College of Pittsburgh and co-leader of the Genome Stability Program at UPMC Hillman Most cancers Heart. Credit score: Patricia Opresko
The examine, which was lately revealed within the journal Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, demonstrates for the primary time that oxidative injury to telomeres — the protective ideas of chromosomes that behave like plastic caps on the finish of a shoelace — could cause mobile senescence. These discoveries may finally lead to new therapies that promote wholesome getting old or combat most cancers.
“Zombie cells are nonetheless alive, however they will’t divide, in order that they don’t assist replenish tissues,” mentioned senior writer Patricia Opresko, Ph.D., professor of environmental and occupational well being and of pharmacology and chemical biology at Pitt. “Though zombie cells don’t operate correctly, they’re not sofa potatoes — they actively secrete chemical compounds that promote irritation and injury neighboring cells. Our examine helps reply two large questions: How do senescent cells accumulate with age, and the way do telomeres contribute to that?”
When a wholesome human cell divides to create two similar cells, somewhat little bit of DNA is shaved off the tip of every chromosome, inflicting telomeres to get shorter with every division. Nonetheless, it's unknown if a cell could divide so usually in an individual’s lifetime that its telomeres totally degrade, leading to a zombie-like situation. For many years, scientists have recognized that telomere shortening causes senescence in lab-grown cells, however they might solely assume that DNA injury at telomeres may convert cells into zombies.
This speculation couldn't beforehand be examined because the methods used to wreck DNA have been non-specific, creating lesions throughout the complete chromosome.
“Our new device is sort of a molecular sniper,” defined first writer Ryan Barnes, Ph.D., a postdoctoral fellow in Opresko’s lab. “It creates oxidative injury solely on the telomeres.”
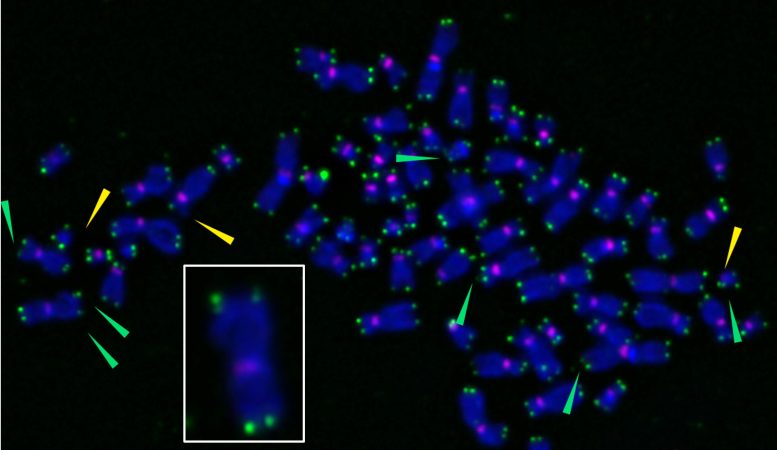
X-shaped chromosomes are stained purple, and telomeres seem as inexperienced spots at chromosome ideas. When researchers used a novel device to induce oxidative injury particularly at telomeres, they will change into fragile (inexperienced arrows), sending cells into senescence. The inset reveals an enlarged chromosome with fragile telomeres, indicated by a number of inexperienced spots at chromosome ideas. Credit score: Barnes et al., Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, (2022)
To develop such marksman-like precision, the crew used a particular protein that binds solely to telomeres. This protein acts like a catcher’s mitt, grabbing maintain of light-sensitive dye “baseballs” that the researchers tossed into the cell. When activated with mild, the dye produces DNA-damaging reactive oxygen molecules. As a result of the dye-catching protein binds solely to telomeres, the device creates DNA lesions particularly at chromosome ideas.
Utilizing human cells grown in a dish, the researchers discovered that injury at telomeres despatched the cells right into a zombie state after simply 4 days — a lot sooner than the weeks or months of repeated cell divisions that it takes to induce senescence by telomere shortening within the lab.
“We discovered a brand new mechanism for inducing senescent cells that's utterly depending on telomeres,” defined Opresko, who additionally co-leads the Genome Stability Program at UPMC Hillman. “These findings additionally remedy the puzzle of why dysfunctional telomeres will not be all the time shorter than purposeful ones.”
Daylight, alcohol, smoking, poor weight-reduction plan, and different elements generate reactive oxygen molecules that injury DNA. Cells have restore pathways to patch up DNA lesions, however, in line with Opresko, telomeres are “exquisitely delicate” to oxidative injury. The researchers discovered that injury at telomeres disrupted DNA replication and induced stress signaling pathways that led to senescence.
“Now that we perceive this mechanism, we are able to begin to take a look at interventions to forestall senescence,” mentioned Barnes. “For instance, possibly there are methods to focus on antioxidants to the telomeres to guard them from oxidative injury.”
The findings may additionally inform the event of latest medication referred to as senolytics that residence in on zombie cells and kill them.
“By decreasing the buildup of zombie cells, which contribute to degenerative ailments, we'd be capable to promote ‘healthspan’ — the size of time that an individual is wholesome,” he added.
Reference: “Telomeric 8-oxo-guanine drives fast untimely senescence within the absence of telomere shortening” by Ryan P. Barnes, Mariarosaria de Rosa, Sanjana A. Thosar, Ariana C. Detwiler, Vera Roginskaya, Bennett Van Houten, Marcel P. Bruchez, Jacob Stewart-Ornstein, and Patricia L. Opresko, 30 June 2022, Nature Structural & Molecular Biology.
DOI: 10.1038/s41594-022-00790-y

Post a Comment