
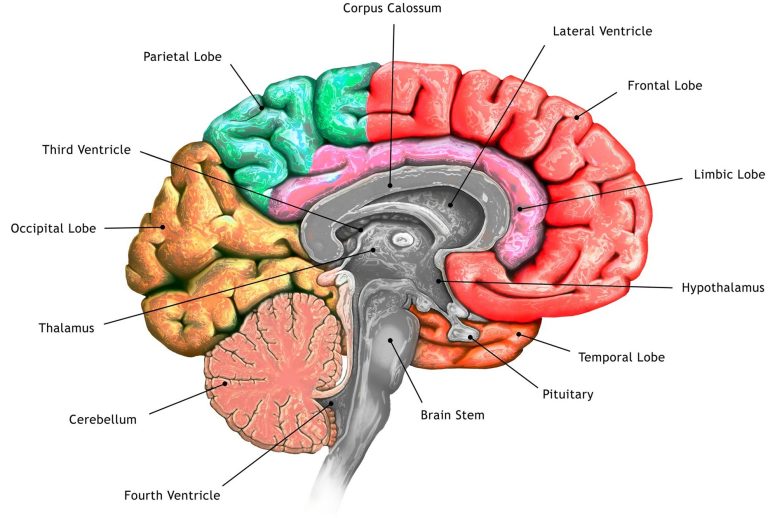
On this picture of the parafascicular (PF) thalamus, the blue cells take part in reward processing/melancholy, the purple cells are crucial for motor studying, and the inexperienced cells are essential for normal locomotion. The ‘fr’ stands for a fiber bundle. Credit score: Ying Zhang and Dheeraj Roy
Focusing on these mind circuits may provide a brand new approach to reverse motor dysfunction and melancholy in Parkinson’s sufferers.
Parkinson’s illness is primarily acknowledged as a dysfunction of motion. Sufferers often expertise tremors, lack of steadiness, and issue initiating motion. The illness additionally has lesser-known signs, together with melancholy, which are nonmotor.
In a examine of a small area of the thalamus, MIT neuroscientists have now recognized three distinct circuits that affect the event of each motor and nonmotor signs of Parkinson’s Illness. Moreover, the researchers found that by manipulating these circuits, they may reverse Parkinson’s signs in mice.
In response to the researchers, the brand new findings counsel that these circuits could possibly be good targets for brand new medicine that might assist fight most of the signs of Parkinson’s illness.
“We all know that the thalamus is essential in Parkinson’s illness, however a key query is how will you put collectively a circuit that that may clarify many alternative issues occurring in Parkinson’s illness. Understanding totally different signs at a circuit stage might help information us within the improvement of higher therapeutics,” says Guoping Feng, the James W. and Patricia T. Poitras Professor in Mind and Cognitive Sciences at MIT, a member of the Broad Institute of Harvard and MIT, and the affiliate director of the McGovern Institute for Mind Analysis at MIT.
Feng is the senior writer of the examine, which was revealed on June 8, 2022, in Nature. Ying Zhang, a J. Douglas Tan Postdoctoral Fellow on the McGovern Institute, and Dheeraj Roy, a NIH K99 Awardee and a McGovern Fellow on the Broad Institute, are the lead authors of the paper.
Tracing circuits
The thalamus consists of a number of totally different areas that carry out quite a lot of features. Many of those, together with the parafascicular (PF) thalamus, assist to manage motion. Degeneration of those buildings is usually seen in sufferers with Parkinson’s illness, which is believed to contribute to their motor signs.
On this examine, the MIT group got down to attempt to hint how the PF thalamus is related to different mind areas, in hopes of studying extra about its features. They discovered that neurons of the PF thalamus undertaking to a few totally different elements of the basal ganglia, a cluster of buildings concerned in motor management and different features: the caudate putamen (CPu), the subthalamic nucleus (STN), and the nucleus accumbens (NAc).
“We began with exhibiting these totally different circuits, and we demonstrated that they’re largely nonoverlapping, which strongly means that they've distinct features,” Roy says.
Additional research revealed these features. The circuit that initiatives to the CPu seems to be concerned on the whole locomotion, and features to dampen motion. When the researchers inhibited this circuit, mice spent extra time transferring across the cage they have been in.
The circuit that extends into the STN, alternatively, is essential for motor studying — the flexibility to be taught a brand new motor talent by means of apply. The researchers discovered that this circuit is critical for a activity by which the mice be taught to steadiness on a rod that spins with rising velocity.
Lastly, the researchers discovered that, in contrast to the others, the circuit that connects the PF thalamus to the NAc isn't concerned in motor exercise. As an alternative, it seems to be linked to motivation. Inhibiting this circuit generates depression-like behaviors in wholesome mice, and they'll now not search a reward resembling sugar water.
Druggable targets
As soon as the researchers established the features of those three circuits, they determined to discover how they is likely to be affected in Parkinson’s illness. To try this, they used a mouse mannequin of Parkinson’s, by which dopamine-producing neurons within the midbrain are misplaced.
They discovered that on this Parkinson’s mannequin, the connection between the PF thalamus and the CPu was enhanced, and that this led to a lower in total motion. Moreover, the connections from the PF thalamus to the STN have been weakened, which made it tougher for the mice to be taught the accelerating rod activity.
Lastly, the researchers confirmed that within the Parkinson’s mannequin, connections from the PF thalamus to the NAc have been additionally interrupted, and that this led to depression-like signs within the mice, together with lack of motivation.
Utilizing chemogenetics or optogenetics, which permits them to manage neuronal exercise with a drug or gentle, the researchers discovered that they may manipulate every of those three circuits and in doing so, reverse every set of Parkinson’s signs. Then, they determined to search for molecular targets that is likely to be “druggable,” and located that every of the three PF thalamus areas have cells that categorical several types of cholinergic receptors, that are activated by the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. By blocking or activating these receptors, relying on the circuit, they have been additionally in a position to reverse the Parkinson’s signs.
“We discovered three distinct cholinergic receptors that may be expressed in these three totally different PF circuits, and if we use antagonists or agonists to modulate these three totally different PF populations, we will rescue motion, motor studying, and likewise depression-like habits in PD mice,” Zhang says.
Parkinson’s sufferers are often handled with L-dopa, a precursor of dopamine. Whereas this drug helps sufferers regain motor management, it doesn’t assist with motor studying or any nonmotor signs, and over time, sufferers develop into immune to it.
The researchers hope that the circuits they characterised on this examine could possibly be targets for brand new Parkinson’s therapies. The kinds of neurons that they recognized within the circuits of the mouse mind are additionally discovered within the nonhuman primate mind, and the researchers are actually utilizing RNA sequencing to seek out genes which are expressed particularly in these cells.
“RNA-sequencing expertise will permit us to do a way more detailed molecular evaluation in a cell-type particular method,” Feng says. “There could also be higher druggable targets in these cells, and as soon as you realize the particular cell varieties you need to modulate, you possibly can establish all types of potential targets in them.”
Reference: “Focusing on thalamic circuits rescues motor and temper deficits in PD mice” by Ying Zhang, Dheeraj S. Roy, Yi Zhu, Yefei Chen, Tomomi Aida, Yuanyuan Hou, Chenjie Shen, Nicholas E. Lea, Margaret E. Schroeder, Keith M. Skaggs, Heather A. Sullivan, Kyle B. Fischer, Edward M. Callaway, Ian R. Wickersham, Ji Dai, Xiao-Ming Li, Zhonghua Lu and Guoping Feng, 8 June 2022, Nature.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-04806-x
The analysis was funded, partially, by the Ok. Lisa Yang and Hock E. Tan Heart for Molecular Therapeutics in Neuroscience at MIT, the Stanley Heart for Psychiatric Analysis on the Broad Institute, the James and Patricia Poitras Heart for Psychiatric Problems Analysis at MIT, the Nationwide Institutes of Well being BRAIN Initiative, and the Nationwide Institute of Psychological Well being.
Post a Comment