NIH discovery sheds mild on tissue focused by age-related macular degeneration and different ailments
Researchers have recognized distinct variations among the many cells comprising a tissue within the retina that's very important to human visible notion. The scientists from the Nationwide Eye Institute (NEI) found 5 subpopulations of retinal pigment epithelium (RPE)—a layer of tissue that nourishes and helps the retina’s light-sensing photoreceptors. Utilizing synthetic intelligence, the researchers analyzed pictures of RPE at single-cell decision to create a reference map that locates every subpopulation throughout the eye. A report on the analysis was revealed on Could 6, 2022, in Proceedings of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences.
“These outcomes present a first-of-its-kind framework for understanding totally different RPE cell subpopulations and their vulnerability to retinal ailments, and for creating focused therapies to deal with them,” mentioned Michael F. Chiang, M.D., director of the NEI, a part of the Nationwide Institutes of Well being.
“The findings will assist us develop extra exact cell and gene therapies for particular degenerative eye ailments,” mentioned the research’s lead investigator, Kapil Bharti, Ph.D., who directs the NEI Ocular and Stem Cell Translational Analysis Part.
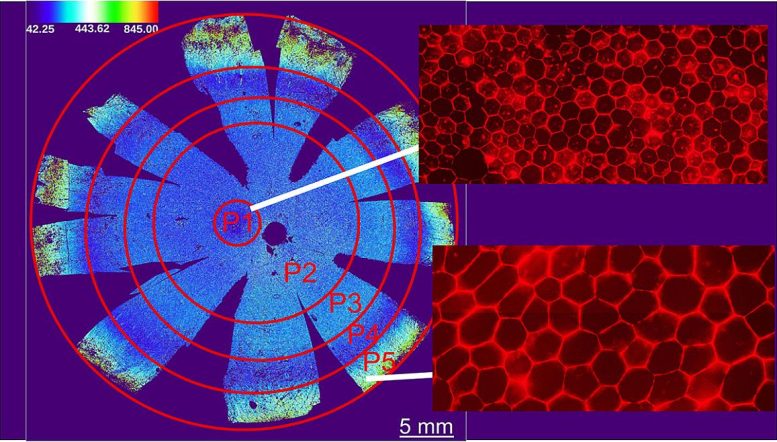
Utilizing synthetic intelligence, the researchers analyzed RPE from 9 donor and recognized 5 subpopulations of RPE. These populations are alongside a spectrum by way of cell space, side ratio, hexagonality and variety of neighbors. Foveal RPE (P1) required for central imaginative and prescient are usually excellent hexagons and are tightly packed collectively. Peripheral RPE (P5) are much less excellent hexagons and are extra unfold out. Credit score: Davide Ortolan, Ph.D.
When mild hits the rod and cone photoreceptors that line the retina behind the attention, imaginative and prescient begins. As soon as triggered, photoreceptors transmit alerts through an advanced community of different retinal neurons that converge on the optic nerve earlier than continuing to different mind areas. The RPE is a monolayer that resides one cell deep beneath the photoreceptors.
Age and sickness could set off metabolic alterations in RPE cells, which might contribute to photoreceptor degradation. The impact of those RPE adjustments on imaginative and prescient varies enormously relying on the severity and placement of the RPE cells throughout the retina. Late-onset retinal degeneration (L-ORD), for instance, principally impacts the peripheral retina and therefore peripheral imaginative and prescient. Age-related macular degeneration (AMD), a number one explanation for visible loss, predominantly damages RPE cells within the macula, that are important for central imaginative and prescient.
Bharti and colleagues sought to find out if there are totally different RPE subpopulations which may clarify the vast spectrum of retinal illness phenotypes.
Scientists clarify extra about RPE and what the single-cell decision map reveals. Credit score: Nationwide Eye Institute
The workforce used synthetic intelligence (AI) to investigate RPE cell morphometry, the exterior form and dimensions of every cell. They educated a pc utilizing fluorescently labelled pictures of RPE to investigate all the human RPE monolayer from 9 cadaver donors with no historical past of great eye illness.
Morphometry options have been calculated for every RPE cell – on common, about 2.8 million cells per donor; 47.6 million cells have been analyzed in whole. The algorithm assessed every cell’s space, side ratio (width to peak), hexagonality, and variety of neighbors. Earlier research had instructed that RPE perform is tied to the tightness of mobile junctions; the extra crowded, the higher for indicating mobile well being.
They recognized 5 distinctive RPE cell subpopulations, labeled as P1-P5, based mostly on morphometry and grouped them in concentric rings across the fovea, which is the middle of the macula and essentially the most light-sensitive space of the retina. When in comparison with peripheral RPE, foveal RPE is completely hexagonal and extra compactly located, with a larger variety of neighboring cells.
Unexpectedly, they found that the peripheral retina comprises a hoop of RPE cells (P4) with a cell space similar to RPE in and across the macula.
“The presence of the P4 subpopulation highlights the variety inside retinal periphery, suggesting that there may very well be useful variations amongst RPE that we're at present unaware of,” mentioned the research’s first writer, Davide Ortolan, Ph.D. a analysis fellow within the NEI Ocular and Stem Cell Translational Analysis Part. “Future research are wanted to assist us perceive the function of this subpopulation.”
Subsequent, they analyzed RPE from cadavers with AMD. Foveal (P1) RPE tended to be absent attributable to illness injury, and the variations amongst cells within the P2-P5 subpopulations weren't statistically important. Total, the AMD RPE subpopulations tended to be elongated relative to RPE cells not affected by AMD.
To additional check the speculation that totally different retinal degenerations have an effect on particular RPE subpopulations, they analyzed ultrawide-field fundus autofluorescence pictures from sufferers affected by choroideremia, L-ORD, or a retinal degeneration with no recognized molecular trigger. Whereas these research have been performed at a single cut-off date, they nonetheless demonstrated that totally different RPE subpopulations are susceptible to various kinds of retinal degenerative ailments.
“Total, the outcomes counsel that AI can detect adjustments of RPE cell morphometry previous to the event of visibly obvious degeneration,” mentioned Ortolan.
Age-related morphometric adjustments additionally could seem in some RPE subpopulations earlier than they’re detectable in others. These discovering will assist inform future research utilizing noninvasive imaging applied sciences, reminiscent of adaptive optics, which resolve retinal cells in unprecedented element and will doubtlessly be used to foretell adjustments in RPE well being in dwelling sufferers.
Reference: “Single-cell–decision map of human retinal pigment epithelium helps uncover subpopulations with differential illness sensitivity” by Ortolan D, Sharma R, Volkov A, Maminishkis A, Hotaling NA, Huryn LA, Cukras C, Di Marco S, Bisti S and Bharti Ok, 6 Could 2022, Proceedings of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences.
DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2117553119
The research was funded by the NEI Intramural Analysis Program.
Post a Comment