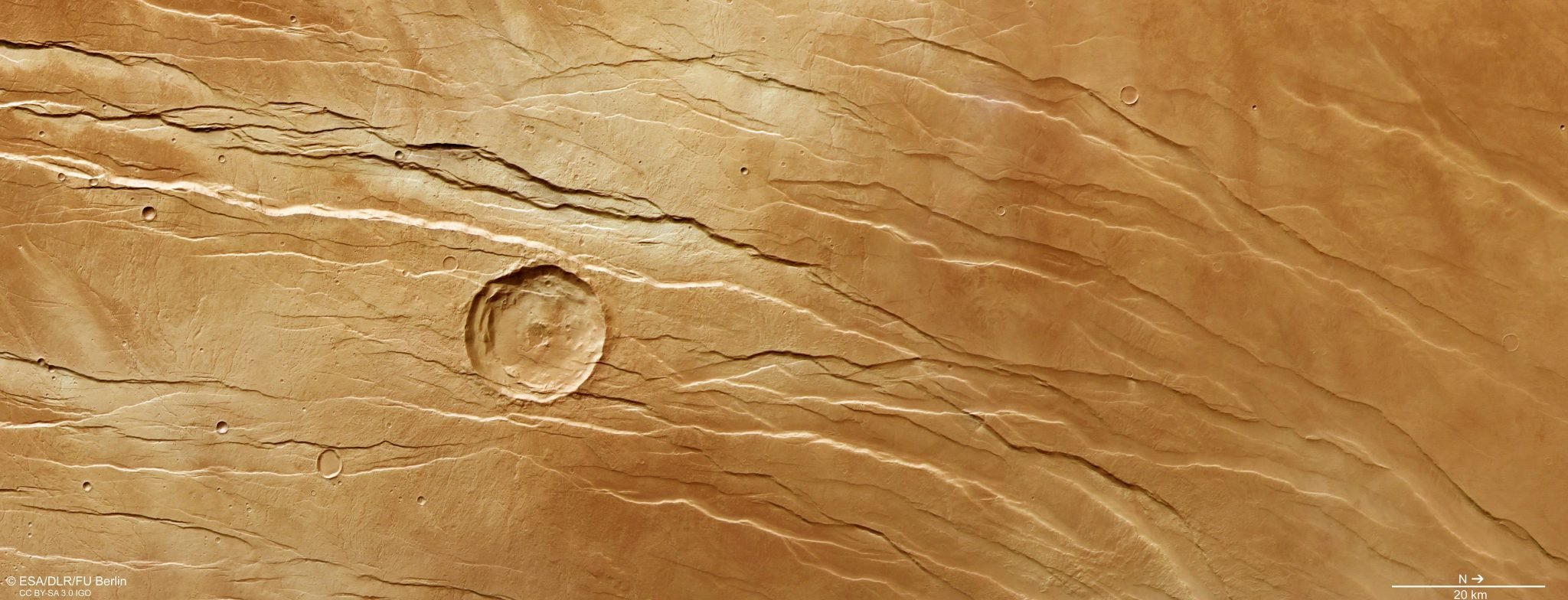
This picture from ESA’s Mars Categorical exhibits half of a big fault system on Mars often known as Tantalus Fossae. This picture contains information gathered by Mars Categorical’ Excessive Decision Stereo Digicam (HRSC) on July 19, 2021. It was created utilizing information from the nadir channel, the sphere of view aligned perpendicular to the floor of Mars, and the colour channels of the HRSC. It's a ‘true colour’ picture, reflecting what could be seen by the human eye if taking a look at this area of Mars. The bottom decision is roughly 18 m/pixel and the photographs are centered at about 43°N/257°E. North is to the appropriate. Credit score: ESA/DLR/FU Berlin, CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO
This community of lengthy grooves and scratches kinds a part of an enormous fault system on Mars often known as Tantalus Fossae, and is proven right here as seen by the European House Company’s Mars Categorical.
At first look, these options seem like the results of somebody raking their fingernails, or claws, throughout the floor of the Crimson Planet, gouging out lengthy trenches within the course of.
Whereas not fairly so dramatic in its formation, Tantalus Fossae (‘fossae’ that means a hole or melancholy) is a noticeable characteristic on Mars. This technique of troughs flanks a sprawling, low-relief martian volcano named Alba Mons, operating alongside the volcano’s jap facet.
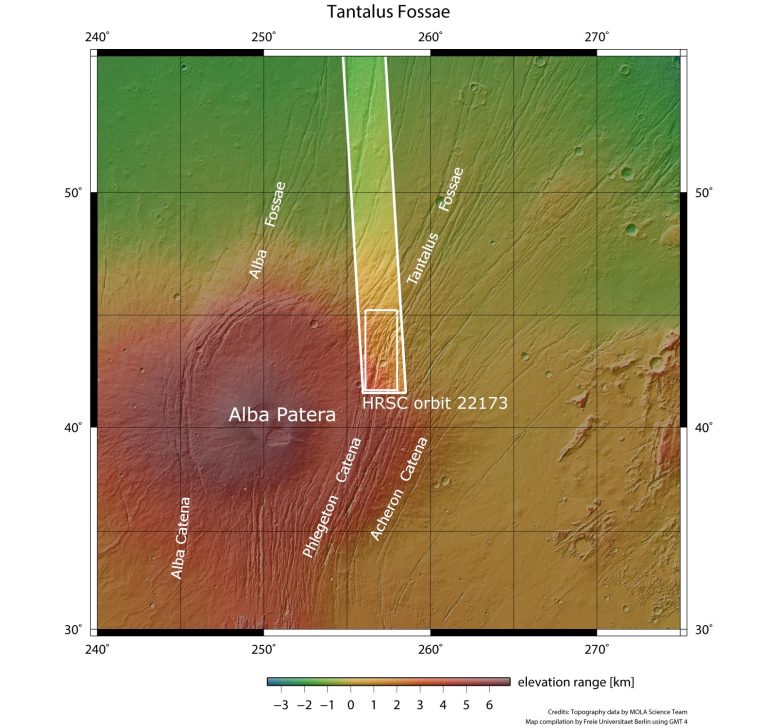
This picture from ESA’s Mars Categorical exhibits a part of Tantalus Fossae, a big system of faults discovered on Mars, in wider context.
The world outlined by the daring white field signifies the realm imaged by the Mars Categorical Excessive Decision Stereo Digicam on July 19, 2021, throughout orbit 22173. Credit score: NASA/MGS/MOLA Science Workforce
The fossae had been created because the summit of Alba Mons rose in elevation, inflicting the encompassing floor to turn out to be warped, prolonged, and damaged. The Tantalus Fossae faults are a terrific instance of a floor characteristic often known as grabens; every trench shaped as two parallel faults opened up, inflicting the rock between to drop down into the ensuing void.

This indirect perspective view of Tantalus Fossae on Mars was generated from the digital terrain mannequin and the nadir and colour channels of the Excessive Decision Stereo Digicam on ESA’s Mars Categorical. Credit score: ESA/DLR/FU Berlin, CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO
The identical options may be discovered on the western facet of Alba Mons, forming an incomplete ring across the volcano. Total, this volcano’s related grabens stretch out for as much as 1000 km (620 miles) in size, as much as 10 km (6.2 miles) in width, and are as much as 350 m (1,150 toes) deep.
A fancy historical past
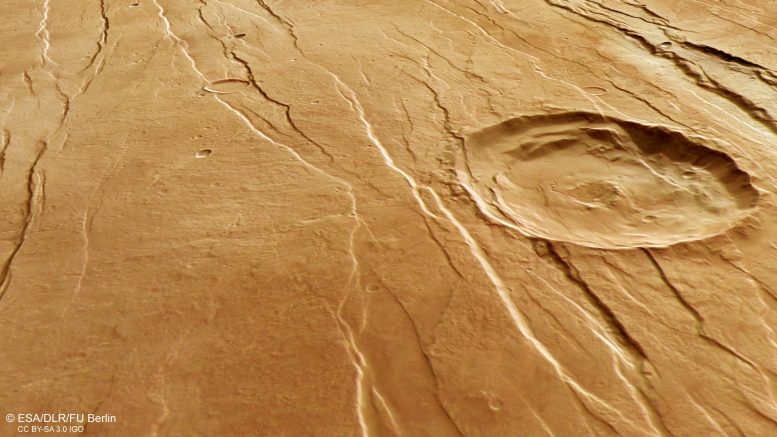
All through this Mars Categorical picture, quite a few grabens may be seen operating roughly northeast (bottom-right) to southwest (top-left).
These buildings are thought to have shaped not on the similar time however one after the opposite, offering scientists the chance to reconstruct a previous timeline and film of what created this dramatic panorama.
The big influence crater on the middle of the picture, for instance, is crosscut by grabens, indicating that it was already current earlier than the volcano was uplifted to create the Tantalus Fossae faults. The second-largest influence crater (far smaller and to the bottom-left of the central crater) seems to superpose the faults, and is subsequently prone to be youthful.
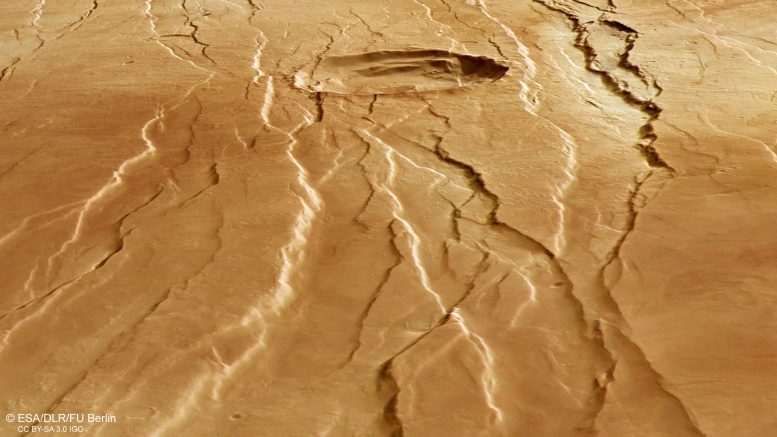

This indirect perspective view of Tantalus Fossae on Mars was generated from the digital terrain mannequin and the nadir and colour channels of the Excessive Decision Stereo Digicam on ESA’s Mars Categorical. Credit score: ESA/DLR/FU Berlin, CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO
Upon nearer look, many small, branching valleys may be seen throughout this area. These valleys seem to chop immediately by the grabens, and so are assumed to be older.
As proven most clearly within the related topographic view, the northern (proper) half incorporates far decrease terrain than the southern (left) half – in locations, as a lot as three kilometers decrease in altitude. We might anticipate any small, branching valleys to run alongside the slopes of Alba Mons and merge the place the bottom is lowest, however this isn't seen right here, implying that the valleys should originate from extra historic instances – earlier than Alba Mons rose to sculpt this terrain into what we see at this time.
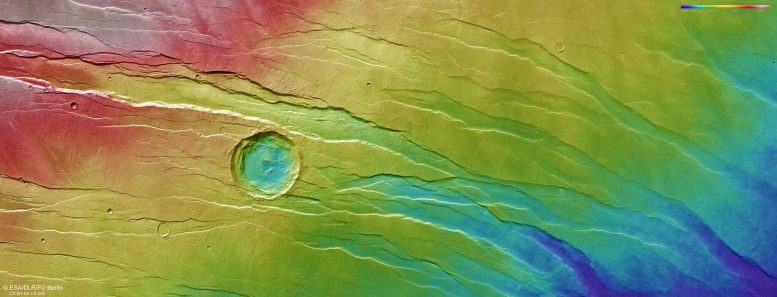
This color-coded topographic picture of Tantalus Fossae was created from information collected by ESA’s Mars Categorical on July 19, 2021, throughout orbit 22173. It's based mostly on a digital terrain mannequin of the area, from which the topography of the panorama may be derived. Decrease elements of the floor are proven in blues and purples, whereas greater altitude areas present up in whites and reds, as indicated on the dimensions to the highest proper. North is to the appropriate. The bottom decision is roughly 18 m/pixel and the photographs are centered at about 43°N/257°E. Credit score: ESA/DLR/FU Berlin, CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO
This space is known as after Tantalus, a son of Zeus and Plouto (Pluto) who, based on Greek legend, betrayed the gods and was compelled by Hades to face in water beneath a fruit tree. When he tried to drink the water retreated, and when he tried to eat the branches moved past his attain – a punishment often known as the torments of Tantalus.
Exploring Mars
Mars Categorical has been orbiting the Crimson Planet since 2003, imaging Mars’ floor, mapping its minerals, figuring out the composition and circulation of its tenuous ambiance, probing beneath its crust, and exploring how numerous phenomena work together within the martian setting.

This stereoscopic picture exhibits Tantalus Fossae on Mars, and was generated from information captured by the Excessive Decision Stereo Digicam (HRSC) on ESA’s Mars Categorical orbiter on July 19, 2021, throughout orbit 22173. The anaglyph, derived from information acquired by the nadir channel and one stereo channel of the HRSC, presents a three-dimensional view when considered utilizing red-green or red-blue glasses. Credit score: ESA/DLR/FU Berlin, CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO
The mission’s Excessive Decision Stereo Digicam (HRSC), chargeable for these new photos, has revealed a lot about Mars’ numerous floor options, with current photos exhibiting every thing from mind terrain and wind-sculpted ridges and grooves to volcanoes, influence craters, tectonic faults, river channels, and historic lava swimming pools.
Post a Comment