Russian scientists have synthesized a brand new ultra-hard materials containing scandium and carbon. It consists of polymerized fullerene molecules with scandium and carbon atoms inside. The work paves the way in which for future research of fullerene-based ultra-hard supplies, making them a possible candidate to be used in photovoltaic and optical gadgets, parts of nanoelectronics and optoelectronics, biomedical engineering as high-performance distinction brokers, and many others. The analysis examine was revealed within the journal Carbon.
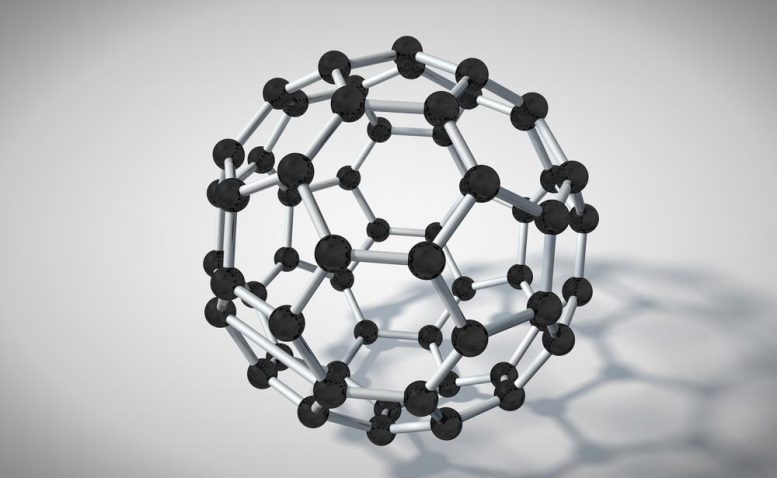
The invention of latest, all-carbon molecules generally known as fullerenes nearly forty years in the past was a revolutionary breakthrough that paved the way in which for fullerene nanotechnology. Fullerenes have a spherical form fabricated from pentagons and hexagons that resembles a soccer ball, and a cavity throughout the carbon body of fullerene molecules can accommodate a wide range of atoms.
The introduction of metallic atoms into carbon cages results in the formation of endohedral metallofullerenes (EMF) that are technologically and scientifically essential owing to their distinctive buildings and optoelectronic properties.
A workforce of researchers from the Nationwide College of Science and Expertise (NUST) MISIS, Technological Institute for Superhard and Novel Carbon Supplies, and Kirensky Institute of Physics FRC KSC SB RAS have obtained, for the primary time, scandium containing EMFs and studied the method of their polymerization. Polymerization is the method by which unbound molecules hyperlink collectively to type a chemically bonded polymerized materials. Most polymerization reactions proceed at a quicker fee below excessive stress.
After the scandium containing fullerenes had been obtained from carbon condensate utilizing a high-frequency arc discharge plasma, they had been positioned in a diamond anvil cell, essentially the most versatile and in style system used to create very excessive pressures.
“We've discovered that visitor atoms facilitate the polymerization course of. Scandium atoms change the fullerene bonding course of fully by the polarization of the carbon bonds, which ends up in a rise of their chemical exercise. The fabric obtained was much less inflexible than pristine polymerized fullerenes, it was simpler to acquire,” stated Pavel Sorokin, senior researcher on the NUST MISIS Laboratory of Inorganic Nanomaterials.
The examine will pave the way in which for research of fullerite endohedral complexes as a macroscopic materials and make it attainable to think about EMF not solely as a nanostructure of elementary curiosity but in addition as a promising materials that could be in demand in numerous fields of science and expertise sooner or later, the researchers consider.
Reference: “Insights into fullerene polymerization below the excessive stress: The position of endohedral Sc dimer” by S. V. Erohin, V. D. Churkin, N. G. Vnukov, M. A. Visotin, E. A. Kovalev, V. V. Zhukov, L. Yu. Antipina, Ye. V. Tomashevich, Yu. L. Mikhlin, M. Yu. Popov, G. N. Churilov, P. B. Sorokin and A. S. Fedorov, 8 December 2021, Carbon.
DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon.2021.12.040


Post a Comment