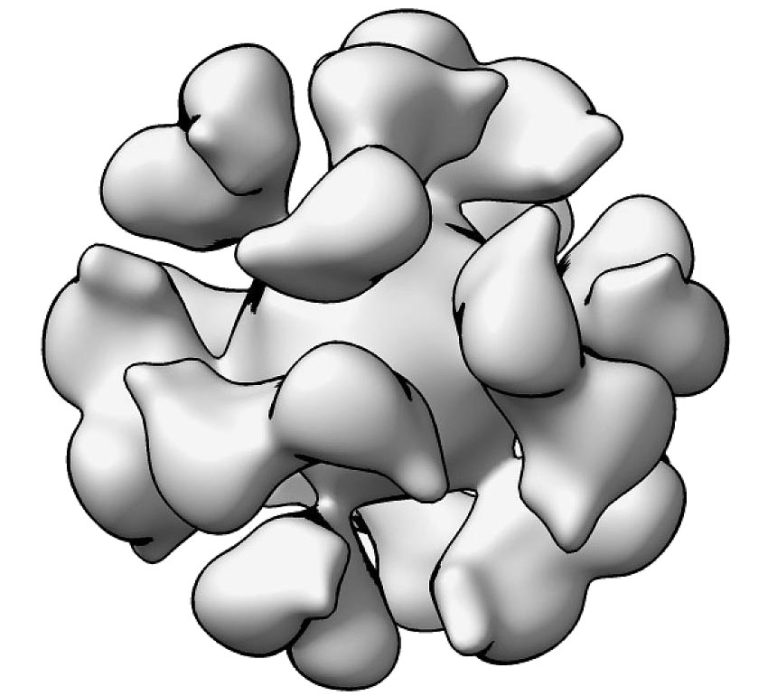
A cryoelectron microscopic reconstruction mannequin of the Epstein-Barr virus gp350-ferritin nanoparticle. Credit score: Geng Meng, Purdue College
The Nationwide Institute of Allergy and Infectious Illnesses (NIAID), a part of the Nationwide Institutes of Well being (NIH), has launched an early-stage medical trial to judge an investigational preventative vaccine for Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). EBV is the first explanation for infectious mononucleosis (“mono”) and is related to sure cancers and autoimmune ailments. The Part 1 examine is considered one of solely two research to check an investigational EBV vaccine in additional than a decade. Will probably be carried out on the NIH Scientific Heart in Bethesda, Maryland.
EBV is a member of the herpes virus household and one of the vital widespread human viruses. It spreads by means of bodily fluids, most notably saliva. In the USA, an estimated 125,000 circumstances of infectious mononucleosis happen every year; roughly 10% of these individuals develop fatigue lasting six months or longer. Roughly 1% of all EBV-infected people develop severe issues, together with hepatitis, neurologic issues, or extreme blood abnormalities. EBV is also related to a number of malignancies, together with abdomen and nasopharyngeal cancers and Hodgkin and Burkitt lymphomas, in addition to autoimmune ailments, corresponding to systemic lupus erythematosus and a number of sclerosis.
“A vaccine that would stop or scale back the severity of an infection with the Epstein-Barr virus might scale back the incidence of infectious mononucleosis and may additionally scale back the incidence of EBV-associated malignancies and autoimmune ailments,” stated NIAID Director Anthony S. Fauci, M.D.
Led by principal investigator Jessica Durkee-Shock, M.D., of NIAID’s Laboratory of Infectious Illnesses, the examine will consider the security and immune response of an investigational EBV gp350-Ferritin nanoparticle vaccine with a saponin-based Matrix-M adjuvant. The experimental vaccine was developed by the Laboratory of Infectious Illnesses in collaboration with NIAID’s Vaccine Analysis Heart. The Matrix-M adjuvant was developed by the biotechnology firm Novavax, based mostly in Gaithersburg, Maryland.
The vaccine works by focusing on EBV glycoprotein gp350, which is discovered on the floor of the virus and virus-infected cells. EBV gp350 can also be the first goal for neutralizing antibodies discovered within the blood of individuals naturally contaminated with EBV. Ferritin, a pure iron storage protein present in cells of all dwelling species, is taken into account a promising vaccine platform as a result of it could actually show proteins from the focused virus in a dense array on its floor. The adjuvant is meant to reinforce the immune response induced by the investigational vaccine.
The examine will enroll 40 wholesome volunteer adults ages 18 to 29 years, half of whom have proof of prior EBV an infection and half of whom do not need proof of prior EBV an infection. Contributors might be given a sequence of three 50-microgram injections of the experimental vaccine within the higher arm muscle, adopted by 30 to 60 minutes of remark after every dose. The second and third doses might be administered 30 days and 180 days after the preliminary dose, with follow-up visits between every vaccination and cellphone calls between visits. Participation is anticipated to be required for 18 to 30 months, and the trial is anticipated to final 4 years. Extra details about this examine is on the market utilizing the identifier NCT04645147 on ClinicalTrials.gov.
Post a Comment