
An artist’s impression of what a lunar base may appear to be. Scientists exploring whether or not lunar sources can be utilized to facilitate human exploration on the moon or past have reported that lunar soil comprises lively compounds that may convert carbon dioxide into oxygen and fuels. Credit score: ESA – P. Carril
Soil on the moon comprises lively compounds that may convert carbon dioxide into oxygen and fuels, based on a brand new research by scientists in China that was printed on Could 5, 2022, within the journal Joule. They're presently investigating whether or not lunar sources can be utilized to facilitate human exploration on the moon or past.
Nanjing College materials scientists Yingfang Yao and Zhigang Zou hope to design a system that takes benefit of lunar soil and photo voltaic radiation, the 2 most considerable sources on the moon. After analyzing the lunar soil introduced again by China’s Chang’e 5 spacecraft, their analysis workforce discovered the pattern comprises compounds—together with iron-rich and titanium-rich substances—that would work as a catalyst to make desired merchandise reminiscent of oxygen utilizing daylight and carbon dioxide.
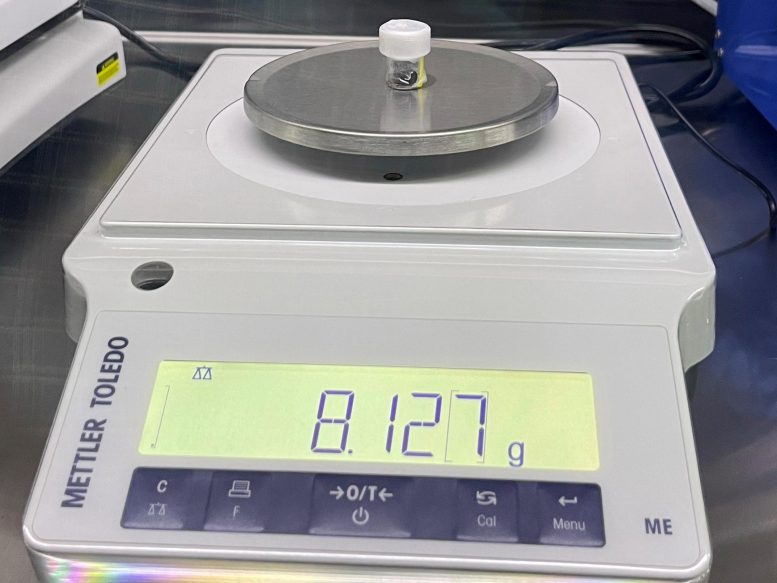

This photograph reveals a lunar soil pattern returned by China’s Chang’e 5 spacecraft. Credit score: Yingfang Yao
Based mostly on the remark, the workforce proposed an “extraterrestrial photosynthesis” technique. Primarily, the system makes use of lunar soil to electrolyze water extracted from the moon and in astronauts’ respiratory exhaust into oxygen and hydrogen powered by daylight. The carbon dioxide exhaled by moon inhabitants can be collected and mixed with hydrogen from water electrolysis throughout a hydrogenation course of catalyzed by lunar soil.
The method yields hydrocarbons reminiscent of methane, which may very well be used as gasoline. The technique makes use of no exterior vitality however daylight to supply a wide range of fascinating merchandise reminiscent of water, oxygen, and gasoline that would assist life on a moonbase, the researchers say. The workforce is searching for a chance to check the system in house, possible with China’s future crewed lunar missions.
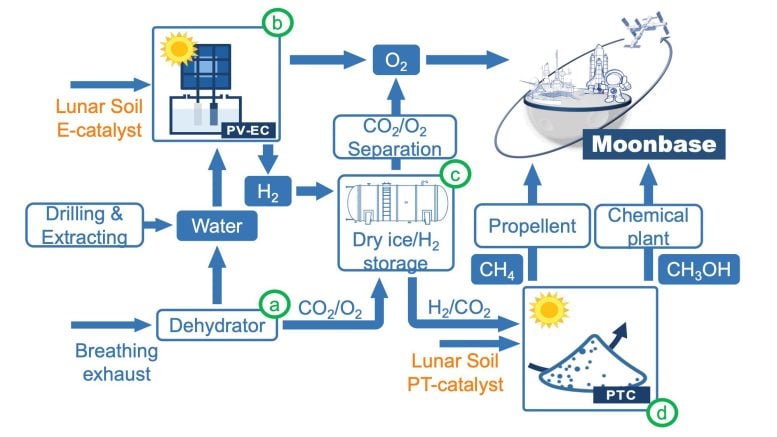
This schematic reveals how lunar soil can work as a catalyst for extraterrestrial photosynthesis to make oxygen and fuels wanted for long-term survival on the moon. Credit score: Yingfang Yao
“We use in-situ environmental sources to reduce rocket payload, and our technique gives a state of affairs for a sustainable and inexpensive extraterrestrial dwelling atmosphere,” Yao says.
Whereas the catalytic effectivity of lunar soil is lower than catalysts out there on Earth, Yao says the workforce is testing totally different approaches to enhance the design, reminiscent of melting the lunar soil right into a nanostructured high-entropy materials, which is a greater catalyst.
This video reveals photovoltaic-driven water electrolysis catalyzed by lunar soil. Credit score: Yingfang Yao
Beforehand, scientists have proposed many methods for extraterrestrial survival. However most designs require vitality sources from Earth. For instance, NASA’s Perseverance Mars rover introduced an instrument that may use carbon dioxide within the planet’s environment to make oxygen, but it surely’s powered by a nuclear battery onboard.

This photograph reveals the analysis workforce at Nanjing College holding the lunar soil pattern. Credit score: Yingfang Yao
“Within the close to future, we'll see the crewed spaceflight business growing quickly,” says Yao. “Similar to the ‘Age of Sail’ within the 1600s when tons of of ships head to the ocean, we'll enter an ‘Age of Area.’ But when we wish to perform large-scale exploration of the extraterrestrial world, we might want to consider methods to scale back payload, that means counting on as little provides from Earth as attainable and utilizing extraterrestrial sources as an alternative.”
Reference: “Extraterrestrial photosynthesis by Chang’E-5 lunar soil” by Yingfang Yao, Lu Wang, Xi Zhu, Wenguang Tu, Yong Zhou, Rulin Liu, Junchuan Solar, Bo Tao, Cheng Wang, Xiwen Yu, Linfeng Gao, Yuan Cao, Bing Wang, Zhaosheng Li, Wei Yao, Yujie Xiong, Mengfei Yang, Weihua Wang and Zhigang Zou, 5 Could 2022, Joule.
DOI: 10.1016/j.joule.2022.04.011
This work was supported by the Nationwide Key Analysis and Improvement Program of China, the Main Analysis Plan of the Nationwide Pure Science Basis of China, the Nationwide Pure Science Basis of China, the Basic Analysis Funds for the Central Universities, the Program for Guangdong Introducing Revolutionary and Entrepreneurial Groups, the Pure Science Basis of Jiangsu Province. the open fund of Wuhan Nationwide Laboratory for Optoelectronics, the Hefei Nationwide Laboratory for Bodily Sciences on the Microscale, the Civil Aerospace Expertise Analysis Venture: Extraterrestrial In-situ water Extraction and Photochemical Synthesis of Hydrogen and Oxygen, and Foshan Xianhu Laboratory of the Superior Power Science and Expertise Guangdong Laboratory.
Post a Comment