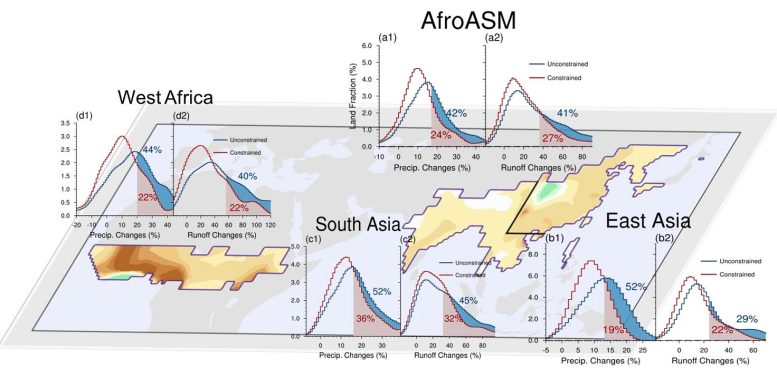
The shadings and percentages within the subplots are the fractions of land space that may expertise a major improve in rainfall (left) and runoff (proper) within the unconstrained (blue) and constrained (purple) projections. Credit score: IAP
Local weather projections are important for adaptation and mitigation planning. The output of the most recent spherical of the Coupled Mannequin Intercomparison Venture, section 6 (CMIP6) has been broadly utilized in local weather projections.
Nonetheless, a subset of CMIP6 fashions is “too scorching” and the projected warming because of greenhouse gases is extreme. It was beforehand unclear methods to tackle the “scorching mannequin” downside on the regional scale.
The newest CMIP6 local weather fashions are inclined to overestimate future Afro-Asian summer time monsoon (AfroASM) rainfall and runoff resulting from present-day biases in warming patterns, in accordance with a analysis group from the Chinese language Academy of Sciences’ Institute of Atmospheric Physics (IAP). By constraining biases, nonetheless, the rainfall improve is 70% of the uncooked projection.
The examine shall be revealed right this moment (Could 10, 2022) within the journal Nature Communications.
The AfroASM consists of the West African monsoon, South Asian monsoon, and East Asian monsoon.
The analysis group recognized the main mode of variability amongst CMIP6 fashions in projecting future modifications in AfroASM rainfall. They discovered that projection uncertainty was associated to the bias in present-day interhemispheric thermal distinction (ITC). Since large-scale monsoon circulation is pushed by ITC resulting from moist static power gradients, fashions with a bigger ITC development over the previous thirty years are inclined to undertaking extra precipitation will increase.
Since most CMIP6 fashions are inclined to overestimate present-day ITC developments, the group corrected the uncooked projection by designing an emergent constraint approach. The rise in precipitation within the constrained projection is ~70% of the ensemble imply of the CMIP6 fashions. The realm of land with a major improve in precipitation is ~57% of the uncooked projection.
The analysis group additional prolonged its evaluation to runoff, which is a mirror of potential water availability. Within the constrained projection, ~27% of land space within the AfroASM area will witness a major improve in potential water availability, which is ~66% of the uncooked projection. Regionally, the impression of the observational constraint is most pronounced within the West African monsoon area the place the fraction of land space with elevated water availability is ~55% of the uncooked projection.
This examine offers an answer for tackling the “scorching mannequin” downside at regional scales. The emergent constraint approach reported within the examine relies on the bodily hyperlink between a modeled however observable variable within the current day and a projected variable sooner or later local weather system.
“This method is helpful for correcting the bias of CMIP6 fashions and at last improve the reliability of rainfall projection within the Afro-Asian summer time monsoon area. The underlying bodily mechanism is the impression of equilibrium local weather sensitivity on the interhemispheric thermal distinction in each the historic and future durations,” mentioned Dr. ZHOU Tianjun from IAP, corresponding creator of the examine.
“Smaller will increase in precipitation and runoff will possible cut back flooding danger, whereas additionally posing a problem to future water useful resource administration,” mentioned CHEN Ziming, a Ph.D. pupil on the College of the Chinese language Academy of Sciences, first creator of the examine.
Reference: “Observationally constrained projection of Afro-Asian monsoon precipitation” by Ziming Chen, Tianjun Zhou, Xiaolong Chen, Wenxia Zhang, Lixia Zhang, Mingna Wu and Liwei Zou, 10 Could 2022, Nature Communications.
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-30106-z
The examine was supported by the Nationwide Key Analysis and Growth Program of China and the Nationwide Pure Science Basis of China.
Post a Comment