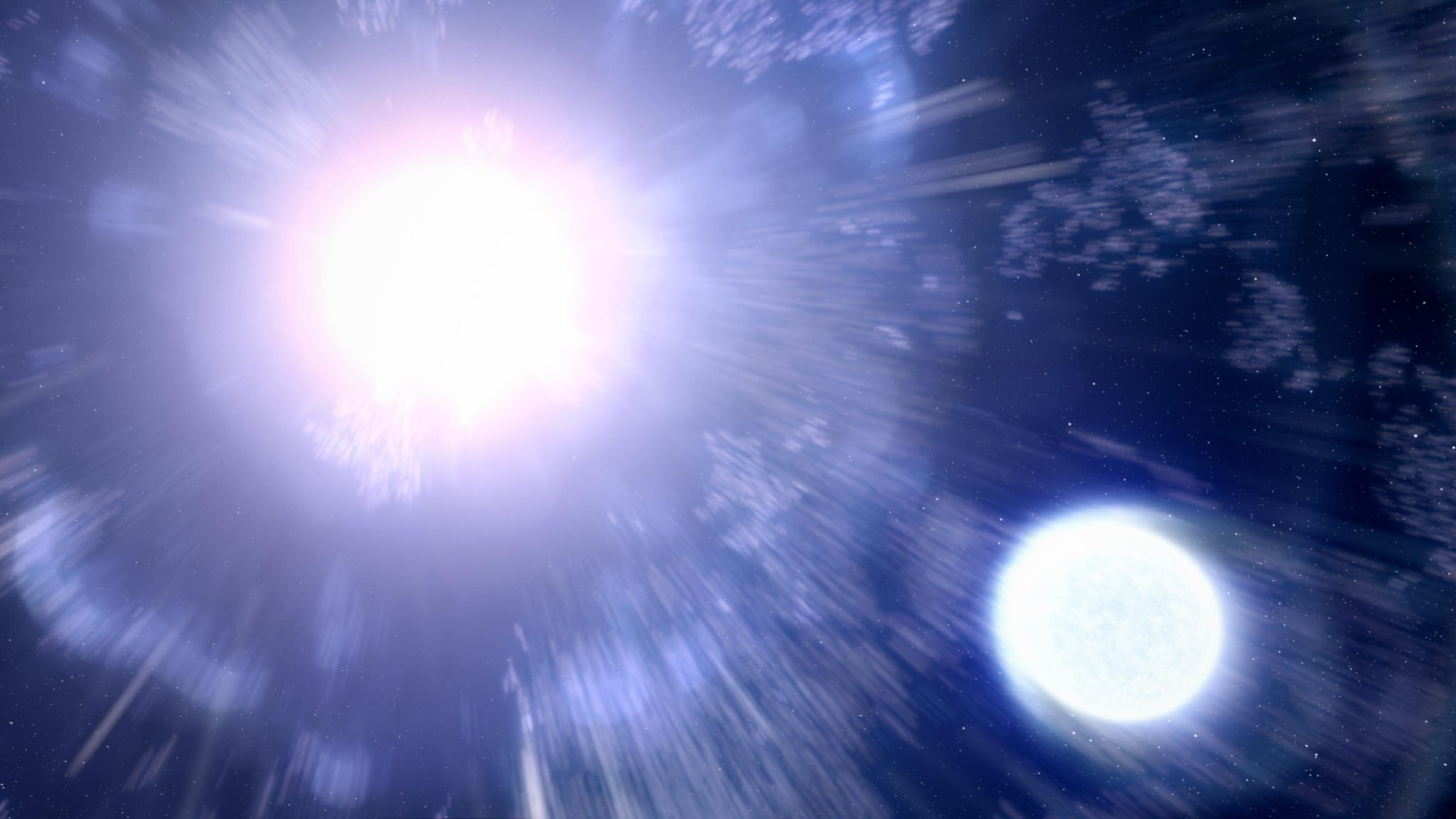

This artist’s illustration reveals supernova 2013ge, with its companion star on the decrease proper. The companion star is impacted by the blast wave from the supernova, however not destroyed. Over time astronomers noticed the ultraviolet (UV) gentle of the supernova fading, revealing a close-by second supply of UV gentle that maintained brightness. The idea is that the 2 large stars developed collectively as a binary pair, and that the present survivor siphoned off its associate’s outer hydrogen fuel shell earlier than it exploded. Finally, the companion star may even go supernova. Credit score: NASA, ESA, Leah Hustak (STScI)
The invention helps clarify the puzzle of hydrogen loss pre-supernova, and helps the speculation that the majority large stars are paired.
It’s not exceptional to discover a surviving star on the scene of an enormous supernova explosion, which might be anticipated to obliterate all the things round it, however the newest analysis from the Hubble House Telescope has offered a long-awaited clue to a particular kind of stellar loss of life. In some supernova instances, astronomers discover no hint of the previous star’s outermost layer of hydrogen.
What occurred to the hydrogen?
Suspicions that companion stars are guilty—siphoning away their companions’ outer shells earlier than their loss of life—are supported by Hubble’s identification of a surviving companion star on the scene of supernova 2013ge. The invention additionally lends credence to the speculation that the majority large stars kind and evolve as binary methods. It may be the prequel to a different cosmic drama: In time, the surviving, large companion star may even bear a supernova, and if each the celebrities’ remnant cores aren't flung from the system, they are going to finally merge and produce gravitational waves, shaking the material of area itself.

This infographic reveals the evolution astronomers suggest for supernova (SN) 2013ge. Panels 1-3 present what has already occurred, and panels 4-6 present what could happen sooner or later. 1) A binary pair of large stars orbit each other. 2) One star ages into its pink big stage, getting a puffy outer envelope of hydrogen that its companion star siphons off with gravity. Astronomers suggest for this reason Hubble discovered no hint of hydrogen within the supernova particles. 3) The stripped-envelope star goes supernova (SN 2013ge), jostling however not destroying its companion star. After the supernova, the dense core of the previous large star stays both as a neutron star or a black gap. 4) Finally the companion star additionally ages right into a pink big, sustaining its outer envelope, a few of which got here from its companion. 5) The companion star additionally undergoes a supernova. 6) If the celebrities have been shut sufficient to one another to not be flung from their orbits by the supernova blast wave, the remnant cores will proceed to orbit each other and finally merge, creating gravitational waves within the course of. Credit score: NASA, ESA, Leah Hustak (STScI)
NASA’s Hubble House Telescope has uncovered a witness on the scene of a star’s explosive loss of life: a companion star beforehand hidden within the glare of its associate’s supernova. The invention is a primary for a specific kind of supernova—one through which the star was stripped of its complete outer fuel envelope earlier than exploding.
The discovering supplies essential perception into the binary nature of large stars, in addition to the potential prequel to the final word merger of the companion stars that will rattle throughout the universe as gravitational waves, ripples within the material of spacetime itself.
Astronomers detect the signature of varied components in supernova explosions. These components are layered like an onion pre-supernova. Hydrogen is discovered within the outermost layer of a star, and if no hydrogen is detected within the aftermath of the supernova, which means it was stripped away earlier than the explosion occurred.
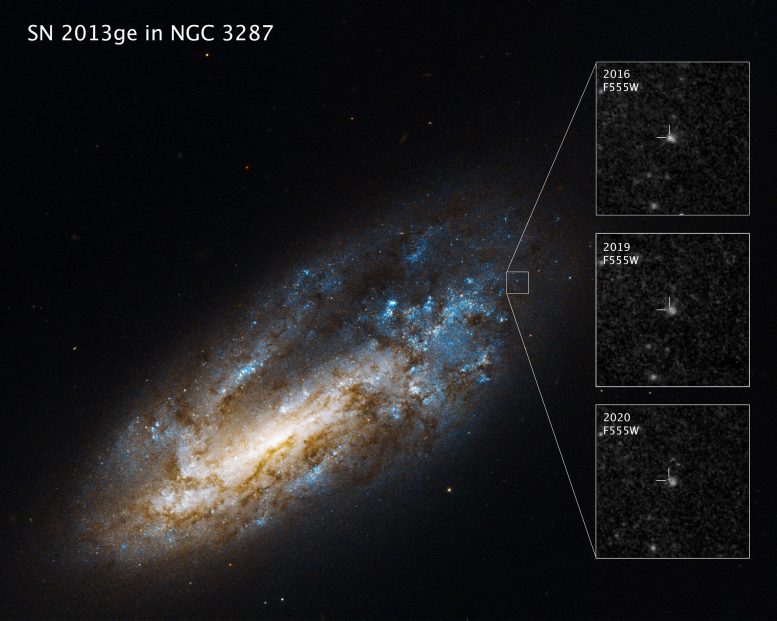

Hubble photographs of galaxy NGC 3287 present supernova 2013ge fading over time, revealing the regular supply of ultraviolet gentle astronomers have recognized as its binary companion star. Credit score: Science: NASA, ESA, Ori Fox (STScI), Picture Processing: Joseph DePasquale (STScI)
The reason for the hydrogen loss had been a thriller, and astronomers have been utilizing Hubble to seek for clues and take a look at theories to elucidate these stripped supernovae. The brand new Hubble observations present the perfect proof but to help the speculation that an unseen companion star siphons off the fuel envelope from its associate star earlier than it explodes.
“This was the second we had been ready for, lastly seeing the proof for a binary system progenitor of a completely stripped supernova,” mentioned astronomer Ori Fox of the House Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore, Maryland, lead investigator on the Hubble analysis program. “The aim is to maneuver this space of research from idea to working with information and seeing what these methods actually appear to be.”
Fox’s crew used Hubble’s Extensive Discipline Digital camera 3 to review the area of supernova (SN) 2013ge in ultraviolet gentle, in addition to earlier Hubble observations within the Barbara A. Mikulski Archive for House Telescopes (MAST). Astronomers noticed the sunshine of the supernova fading over time from 2016 to 2020—however one other close by supply of ultraviolet gentle on the identical place maintained its brightness. This underlying supply of ultraviolet emission is what the crew proposes is the surviving binary companion to SN 2013ge.
Two by two?
Beforehand, scientists theorized that a large progenitor star’s robust winds may blow away its hydrogen fuel envelope, however observational proof didn’t help that. To clarify the disconnect, astronomers developed theories and fashions through which a binary companion siphons off the hydrogen.
“Lately many alternative traces of proof have informed us that stripped supernovae are probably fashioned in binaries, however we had but to truly see the companion. A lot of finding out cosmic explosions is like forensic science—trying to find clues and seeing what theories match. Due to Hubble, we're in a position to see this instantly,” mentioned Maria Drout of the College of Toronto, a member of the Hubble analysis crew.

Hubble picture of galaxy NGC 3287. Credit score: Science: NASA, ESA, Ori Fox (STScI), Picture Processing: Joseph DePasquale (STScI)
In prior observations of SN 2013ge, Hubble noticed two peaks within the ultraviolet gentle, slightly than simply the one sometimes seen in most supernovae. Fox mentioned that one rationalization for this double brightening was that the second peak reveals when the supernova’s shock wave hit a companion star, a risk that now appears more likely. Hubble’s newest observations point out that whereas the companion star was considerably jostled, together with the hydrogen fuel it had siphoned off its associate, it was not destroyed. Fox likens the impact to a jiggling bowl of jelly, which can finally settle again to its authentic kind.
Whereas extra affirmation and comparable supporting discoveries have to be discovered, Fox mentioned that the implications of the invention are nonetheless substantial, lending help to theories that almost all of large stars kind and evolve as binary methods.
One to Watch
Not like supernovae which have a puffy shell of fuel to gentle up, the progenitors of totally stripped-envelope supernovae have confirmed troublesome to establish in pre-explosion photographs. Now that astronomers have been fortunate sufficient to establish the surviving companion star, they will use it to work backward and decide traits of the star that exploded, in addition to the unprecedented alternative to observe the aftermath unfold with the survivor.
As an enormous star itself, SN 2013ge’s companion can be destined to bear a supernova. Its former associate is now probably a compact object, akin to a neutron star or black gap, and the companion will probably go that route as properly.
The closeness of the unique companion stars will decide in the event that they keep collectively. If the space is simply too nice, the companion star can be flung out of the system to wander alone throughout our galaxy, a destiny that might clarify many seemingly solitary supernovae.
Nonetheless, if the celebrities have been shut sufficient to one another pre-supernova, they are going to proceed orbiting one another as black holes or neutron stars. In that case, they might finally spiral towards one another and merge, creating gravitational waves within the course of.
That's an thrilling prospect for astronomers, as gravitational waves are a department of astrophysics that has solely begun to be explored. They're waves or ripples within the material of spacetime itself, predicted by Albert Einstein within the early twentieth century. Gravitational waves have been first instantly noticed by the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO).
“With the surviving companion of SN 2013ge, we may probably be seeing the prequel to a gravitational wave occasion, though such an occasion would nonetheless be a few billion years sooner or later,” Fox mentioned.
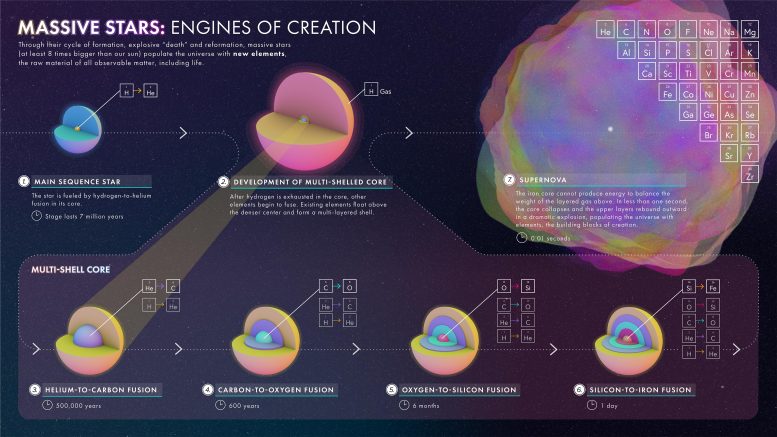
This illustration demonstrates how an enormous star (at the least 8 instances larger than our solar) fuses heavier and heavier components till exploding as a supernova and spreading these components all through area. Credit score: NASA, ESA, and L. Hustak (STScI)
Fox and his collaborators can be working with Hubble to construct up a bigger pattern of surviving companion stars to different supernovae, in impact giving SN 2013ge some firm once more.
“There may be nice potential past simply understanding the supernova itself. Since we now know most large stars within the universe kind in binary pairs, observations of surviving companion stars are crucial to assist perceive the main points behind binary formation, material-swapping, and co-evolutionary growth. It’s an thrilling time to be finding out the celebrities,” Fox mentioned.
“Understanding the lifecycle of large stars is especially necessary to us as a result of all heavy components are solid of their cores and thru their supernovae. These components make up a lot of the observable universe, together with life as we all know it,” added co-author Alex Filippenko of the College of California at Berkeley.
The outcomes are printed in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
Reference: “The Candidate Progenitor Companion Star of the Sort Ib/c SN 2013ge” by Ori D. Fox, Schuyler D. Van Dyk, Benjamin F. Williams, Maria Drout, Emmanouil Zapartas, Nathan Smith, Dan Milisavljevic, Jennifer E. Andrews, Okay. Azalee Bostroem, Alexei V. Filippenko, Sebastian Gomez, Patrick L. Kelly, S. E. de Mink, Justin Pierel, Armin Relaxation, Stuart Ryder, Niharika Sravan, Lou Strolger, Qinan Wang and Kathryn E. Weil, 13 April 2022, The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
DOI: 10.3847/2041-8213/ac5890
The Hubble House Telescope is a challenge of worldwide cooperation between NASA and ESA (European House Company). NASA’s Goddard House Flight Heart in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the telescope. The House Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Maryland, conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Affiliation of Universities for Analysis in Astronomy in Washington, D.C.
Post a Comment