
In keeping with a brand new examine, hunter-gatherers made use of open woodland circumstances within the millennia earlier than Stonehenge monuments have been constructed.
Analysis examine investigates habitat circumstances encountered by first farmers and monument-builders.
Hunter-gatherers made use of open woodland circumstances within the millennia earlier than Stonehenge monuments have been constructed, based on a examine by Samuel Hudson of the College of Southampton, U.Ok., and colleagues that was printed on April 27, 2022, within the open-access journal PLOS ONE.
A lot analysis has explored the Bronze Age and Neolithic historical past of the area surrounding Stonehenge, however much less is understood about earlier instances on this space. This leaves open questions on how historic individuals and wildlife used this space previous to the development of the well-known archaeological monuments. On this new paper, Hudson and colleagues reconstruct environmental circumstances on the website of Blick Mead, a pre-Neolithic hunter-gatherer website on the sting of the Stonehenge World Heritage Web site.
The authors mix pollen, spores, sedimentary DNA, and animal stays to characterize the pre-Neolithic habitat of the location, inferring partially open woodland circumstances, which might have been helpful to massive grazing herbivores like aurochs, in addition to hunter-gatherer communities. This examine helps earlier proof that the Stonehenge area was not lined in closed cover forest right now, as has beforehand been proposed.
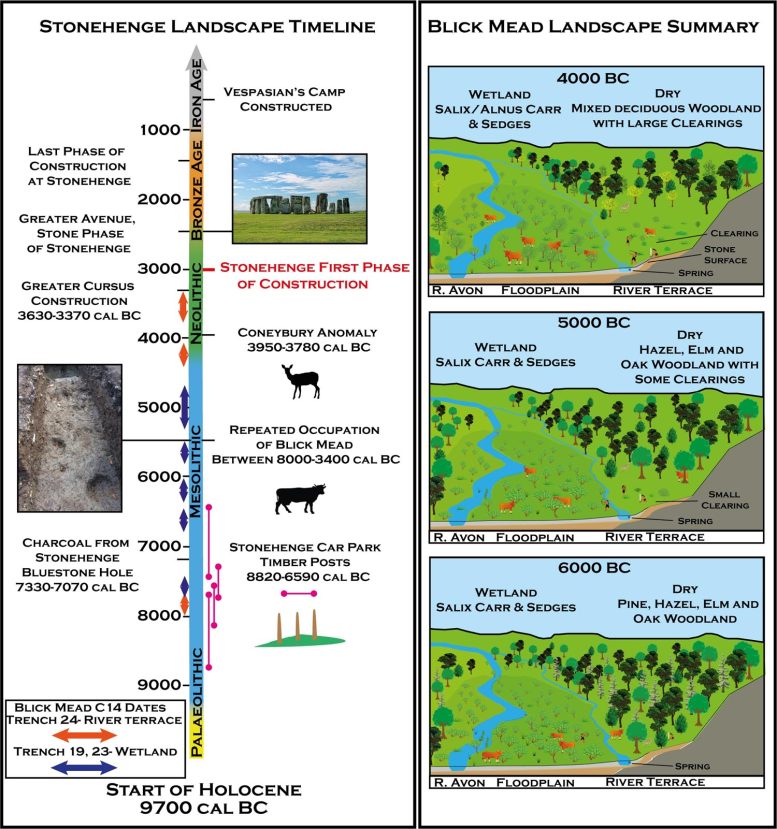
A) Timeline of the Stonehenge panorama, together with radiocarbon dates from Blick Mead and different important Stonehenge World Heritage Archaeological Websites. B) A illustration of the event of vegetation historical past at Blick Mead primarily based on the palaeoenvironmental knowledge. Credit score: Hudson et al., 2022, PLOS ONE, CC-BY 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/)
This examine additionally offers date estimates for human exercise at Blick Mead. Outcomes point out that hunter-gatherers used this website for 4,000 years up till the time of the earliest identified farmers and monument-builders within the area, who would even have benefited from the area offered in open environments. These outcomes point out that the primary farmers and monument-builders within the Stonehenge space encountered open habitats already maintained and utilized by massive grazers and earlier human populations.
Additional examine on related websites will present essential insights into the interactions between hunter-gatherers and early farming communities within the U.Ok. and elsewhere. Moreover, this examine offers strategies for combining sedimentary DNA, different ecological knowledge, and stratigraphic knowledge to interpret the traditional atmosphere at a website the place such data is troublesome to evaluate.
The authors add: “The Stonehenge World Heritage Web site is globally acknowledged for its wealthy Neolithic and Bronze Age monumental panorama, however little is understood of its significance to Mesolithic populations. Environmental analysis at Blick Mead means that hunter-gatherers had already chosen a part of this panorama, an alluvial clearing, as a persistent place for looking and occupation.”
Reference: “Life earlier than Stonehenge: The hunter-gatherer occupation and atmosphere of Blick Mead revealed by sedaDNA, pollen and spores” by Samuel M. Hudson, Ben Pears, David Jacques, Thierry Fonville, Paul Hughes, Inger Alsos, Lisa Snape, Andreas Lang and Antony Brown, 27 April 2022, PLOS ONE.
DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0266789
Funding: The authors acquired no particular funding for this work. Nevertheless, the corresponding creator did obtain funding from the College of Southampton for normal fieldwork prices.
Post a Comment