Newly Found Neural Community Will get Visible and Motor Circuits in Sync
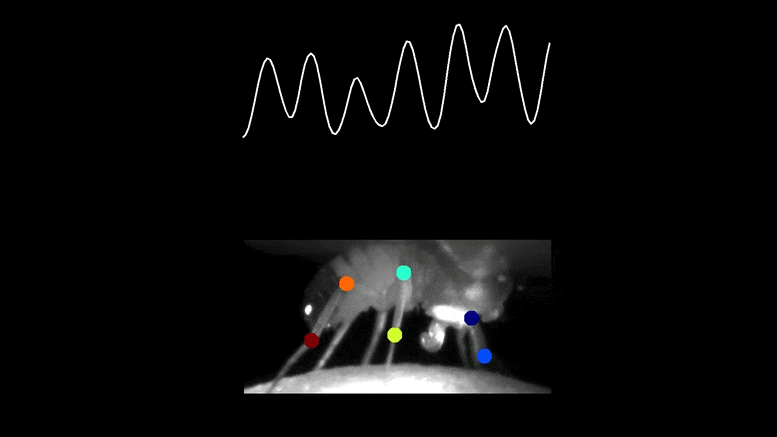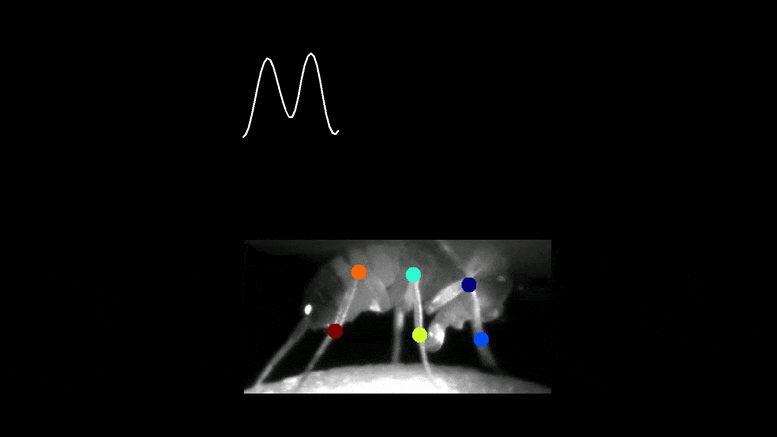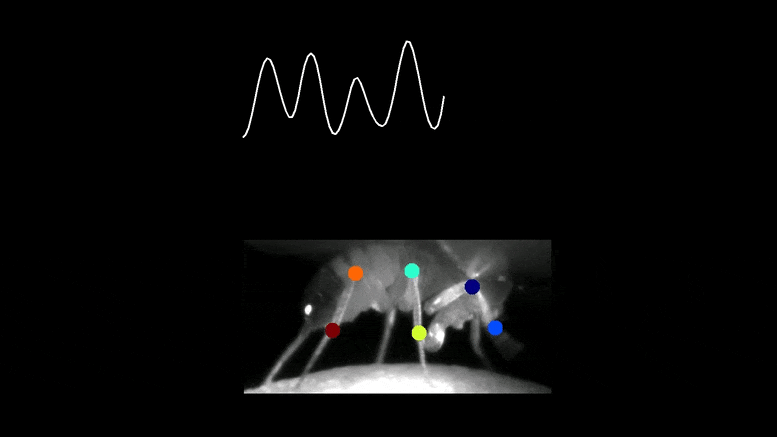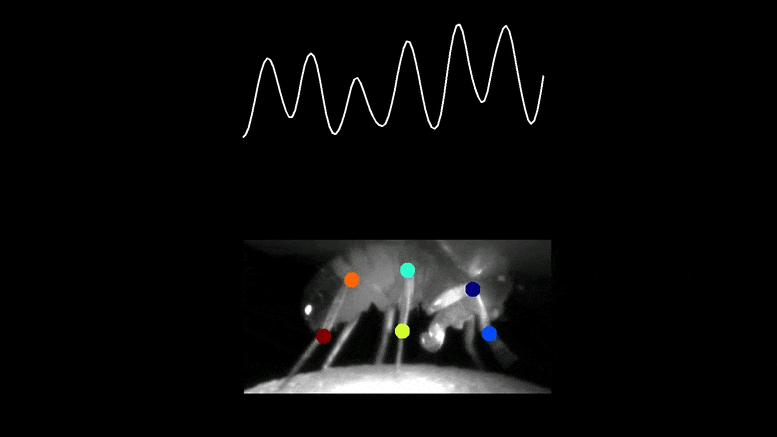
A fruit fly walks on a small styrofoam ball normal right into a floating 3D treadmill. The room is totally darkish, and but, an electrode recording visible neurons within the fly’s mind relays a mysterious stream of neural exercise, rising and falling like a sinusoidal wave.
When Eugenia Chiappe, a neuroscientist on the Champalimaud Basis in Portugal, first noticed these outcomes, she had a hunch her staff had made an distinctive discovery. They have been recording from visible neurons, however the room was darkish, so there was no visible sign that would drive the neurons in that method.
“That meant that the weird exercise was both an artifact, which was unlikely, or that it was coming from a non-visual supply,” Chiappe recalled. “After the opportunity of interference was investigated and dismissed, I used to be positive: the neurons have been faithfully monitoring the animal’s steps.”
Just a few years and lots of new insights later, Chiappe and her staff now current their discovery within the scientific journal Neuron: a bi-directional neural community connecting the legs and the visible system to form strolling.
“Some of the exceptional points of our discovering is that this community helps strolling on two totally different timescales concurrently,” mentioned Chiappe. “It operates on a quick timescale to observe and proper every step whereas selling the animal’s behavioral purpose.”
The cost of a visible neuron (prime) within the mind of a fruit fly was recorded whereas the animal was strolling freely on prime of a floating 3D treadmill. Monitoring the place of the legs exhibits that the cost is in tune with the fly’s entrance leg. Credit score: Terufumi Fujiwara & Eugenia Chiappe, Champalimaud Basis
Monitoring neural “temper”
“Imaginative and prescient and motion could seem unrelated, however they're really tightly related; simply select a degree on the wall and check out putting your finger on it together with your eyes closed,” mentioned Chiappe. “Nonetheless, little is understood concerning the neural foundation of this hyperlink.”
On this research, the staff centered on a selected kind of visible neuron that's recognized to hook up with motor mind areas. “We needed to establish the alerts that these neurons obtain and perceive if and the way they take part in motion,” defined Terufumi Fujiwara, the primary creator of the research.
To reply these questions, Fujiwara used a robust approach known as whole-cell patch recording that enabled him to faucet into the neurons’ “temper,” which could be both constructive or destructive.
“Neurons talk with one another utilizing electrical currents that alter the general cost of the receiving neuron. When the neuron’s web cost is extra constructive, it's extra prone to develop into lively after which transmit alerts to different neurons. However, if the cost is extra destructive, the neuron is extra inhibited,” Fujiwara defined.
Watching every step
The staff tracked the neurons’ cost and revealed that it was synched to the animal’s steps in a fashion that was optimum for fine-tuning every motion.
“When the foot was up within the air, the neuron was extra constructive, able to ship out adjustment instructions to the motor area if wanted. However, when the foot was on the bottom, making changes inconceivable, the cost was extra destructive, successfully inhibiting the neuron,” mentioned Chiappe.
Preserving the course
When the staff analyzed their outcomes additional, they seen that cost of the neurons was additionally altering on an extended timescale. Particularly, when the fly was strolling quick, the cost turned more and more an increasing number of constructive.
“We consider that this variation helps keep the animal’s behavioral purpose,” mentioned Fujiwara. “The longer the fly has been strolling quick, the upper are the possibilities that it could need assistance to take care of this motion plan. Subsequently, the neurons develop into more and more ‘extra alert’ and able to be recruited for motion management.”
The mind is just not at all times the boss
Many experiments adopted, making a fuller description of the community and demonstrating its direct involvement in strolling. However in response to Chiappe, this research goes even additional than revealing a brand new visual-motor circuit, it additionally gives a contemporary perspective on the neural mechanisms of motion.
“The present view of how conduct is generated could be very ‘top-down’: the mind commanding the physique. However our outcomes present a transparent instance of how alerts originating from the physique contribute to motion management. Although our findings have been made within the fly animal mannequin, we speculate that comparable mechanisms could exist in different organisms. Pace-related representations are crucial throughout exploration, navigation, and spatial notion, features which can be widespread to many animals, together with people,” she concluded.
Reference: “Strolling strides direct fast and versatile recruitment of visible circuits for course management in Drosophila” 6 Could 2022, Neuron.
DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2022.04.008
Post a Comment