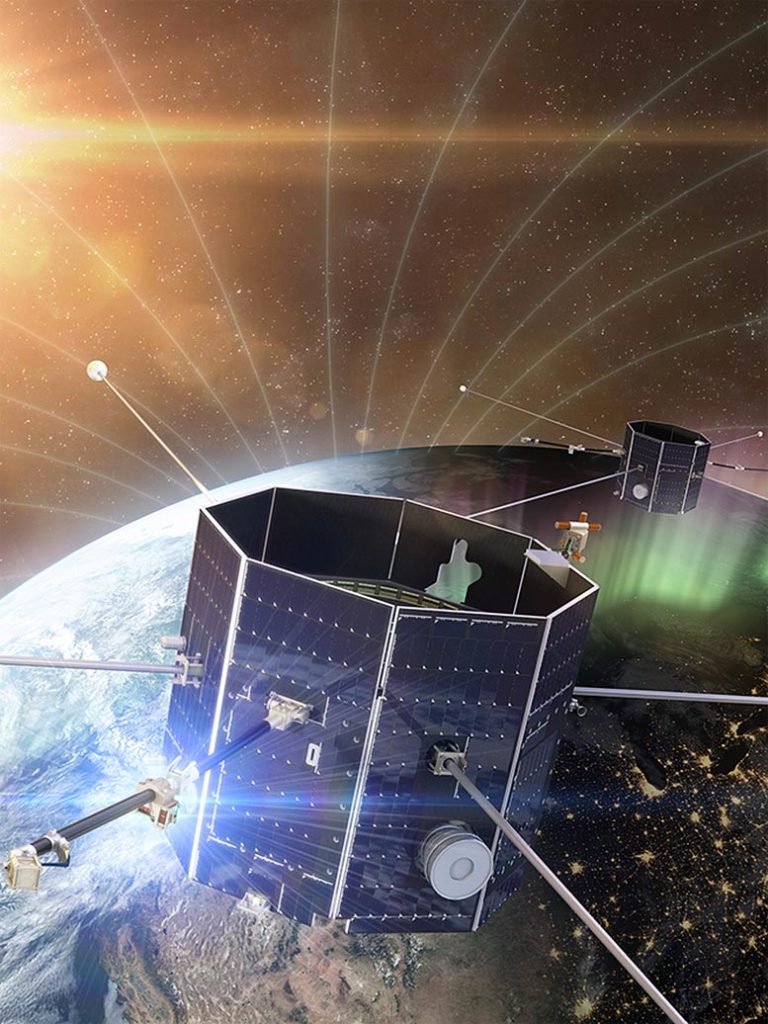

Illustration of the TRACERS satellites in area. TRACERS will fly by the Earth’s magnetic cusp to review magnetic interactions between Earth and the photo voltaic wind. Credit score: NASA
NASA’s Tandem Reconnection and Cusp Electrodynamics Reconnaissance Satellites mission, or TRACERS mission, has handed a important mission evaluate on March 31, 2022. The mission now strikes into its subsequent part, advancing in the direction of its goal launch readiness date of July 27, 2024.
“We’re excited to move this main milestone and get one step nearer to launch,” stated Prof. Craig Kletzing, area physicist on the College of Iowa in Iowa Metropolis and the mission’s principal investigator.
The evaluate, Key Determination Level C, evaluated the mission’s preliminary design and program plan to attain launch by its goal launch readiness. With the profitable evaluate, TRACERS now strikes into Part C, which incorporates the ultimate design of the mission and constructing of the 2 satellites.
“TRACERS might be an necessary addition to our heliophysics fleet,” stated Washito Sasamoto, program government for the mission at NASA Headquarters in Washington, D.C. “The mission is concentrating on long-standing questions important to understanding the Solar-Earth system.”
TRACERS is a pair of satellites that may examine how the photo voltaic wind, the continual stream of ionized particles escaping the Solar and pouring out the area, interacts with Earth’s magnetosphere, the area round Earth dominated by our planet’s magnetic discipline. The linchpin of that interplay is the phenomenon of magnetic reconnection, an explosive switch of power that may occur when two magnetic fields meet.
Magnetic reconnection occurs all all through area however is of particular relevance the place the photo voltaic wind first meets Earth’s magnetosphere, a area generally known as the magnetopause. A reconnection occasion can shoot photo voltaic wind particles, usually diverted round our planet, immediately into our ambiance at excessive speeds. These particles ignite the attractive northern and southern lights but in addition create doubtlessly hazardous circumstances for astronauts and delicate satellites.
To check magnetic reconnection at Earth’s magnetopause, TRACERS will fly by the polar cusp, a degree the place Earth’s magnetic discipline dips down towards the bottom. There, particles funnel by the cusp right into a concentrated a part of our ambiance.
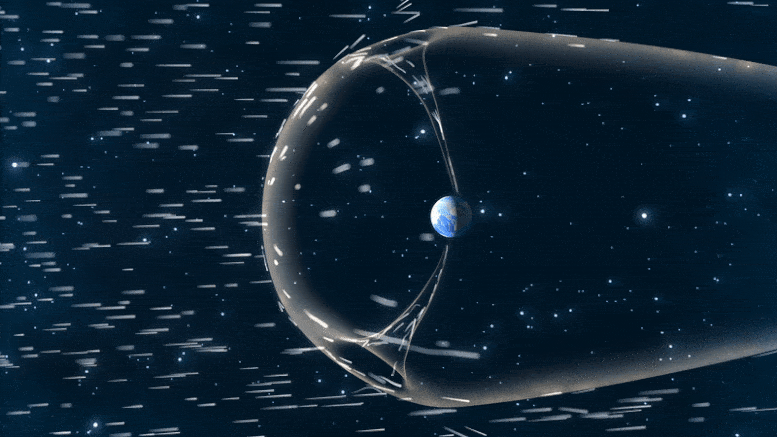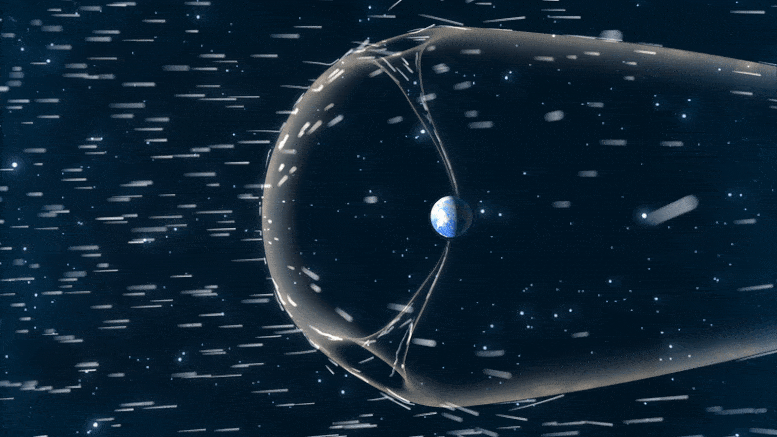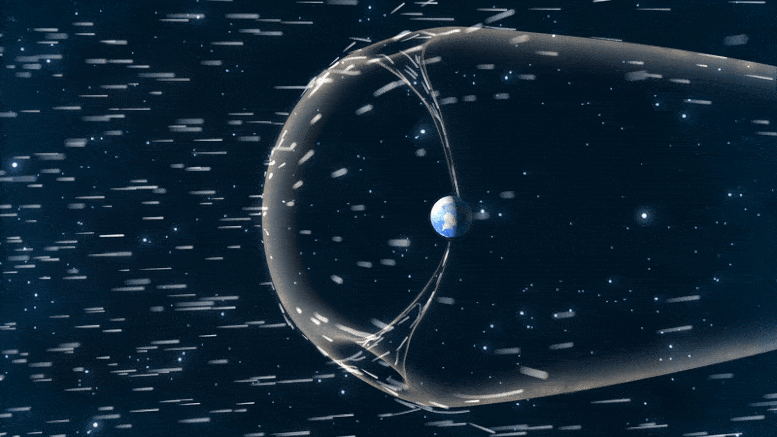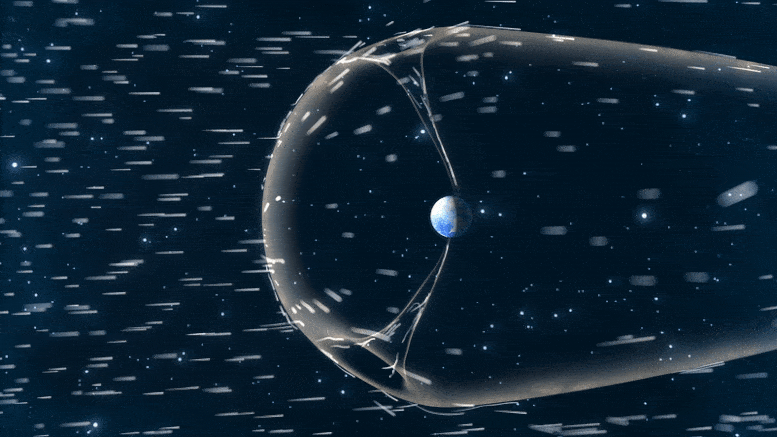
Earth is protected by a large magnetic bubble generally known as our magnetosphere. Nonetheless, the photo voltaic wind can nonetheless impinge on our planet’s ambiance by the polar cusps, two funnels in that magnetic discipline that enable some particles by. The particles that move by the cusp carry signatures of the magnetic interactions that occur the place the photo voltaic wind meets our magnetosphere. Credit score: ASA/CILab/Josh Masters
“Magnetic reconnection can occur in a number of locations within the magnetopause, however it’s laborious to survey such a large search area,” Kletzing stated. “The cusp is one place the place can examine the signatures of reconnection that occur throughout.”
TRACERS will repeatedly fly by the northern polar cusp, one satellite tv for pc behind the opposite, to review the place and the way usually reconnection occurs on the outer edges of Earth’s magnetic discipline. These measurements are important for understanding and ultimately predicting how power from our Solar transfers into our planet.
TRACERS is led by Craig Kletzing on the College of Iowa and managed by the Southwest Analysis Institute in San Antonio, Texas. NASA’s Heliophysics Explorers Program Workplace at NASA’s Goddard Area Flight Middle in Greenbelt, Maryland supplies mission oversight to the challenge for the company’s Heliophysics Division at NASA Headquarters in Washington, D.C.
Post a Comment