Utilizing the MeerKAT telescope in South Africa, astronomers have detected essentially the most distant highly effective radio-wave laser, known as a ‘megamaser’ of its variety. That is the primary hydroxyl megamaser of its variety.
Magamasers are normally created after the galactic collision. When galaxies collide, the gasoline they include turns into extraordinarily dense and might set off concentrated mild beams to shoot out.
The sunshine from the megamaser has traveled 58 thousand billion billion (58 adopted by 21 zeros) kilometers to Earth.
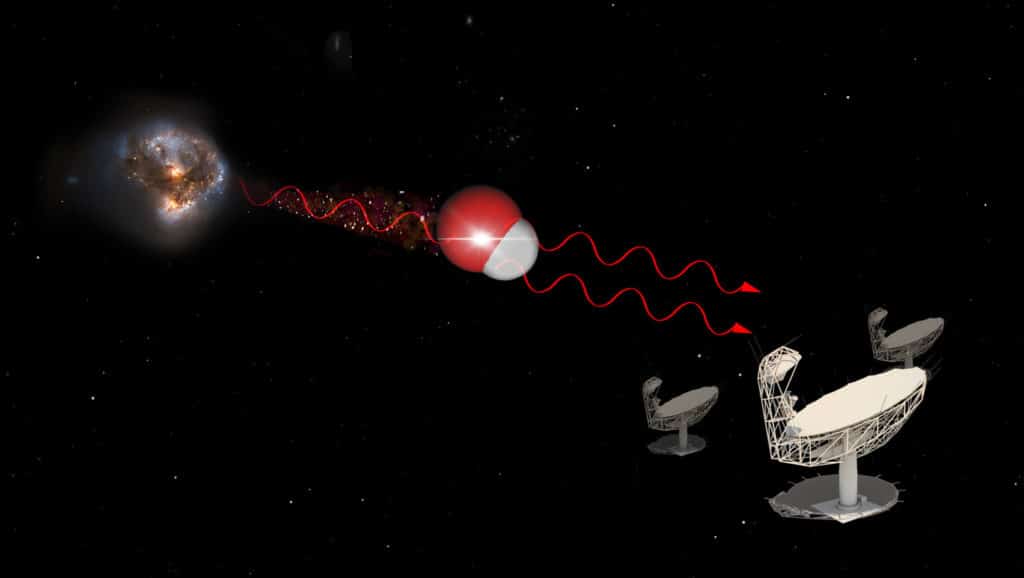
Astronomers named this object Nkalakatha’ [pronounced ng-kuh-la-kuh-tah]. It's an isiZulu phrase that means ‘large boss.’

Dr. Marcin Glowacki, who beforehand labored on the Inter-College Institute for Information-Intensive Astronomy and the College of the Western Cape in South Africa, mentioned, “The megamaser was detected on the primary evening of a survey involving greater than 3000 hours of observations by the MeerKAT telescope.”
“We've follow-up observations of the megamaser deliberate and hope to make many extra discoveries.”
Post a Comment