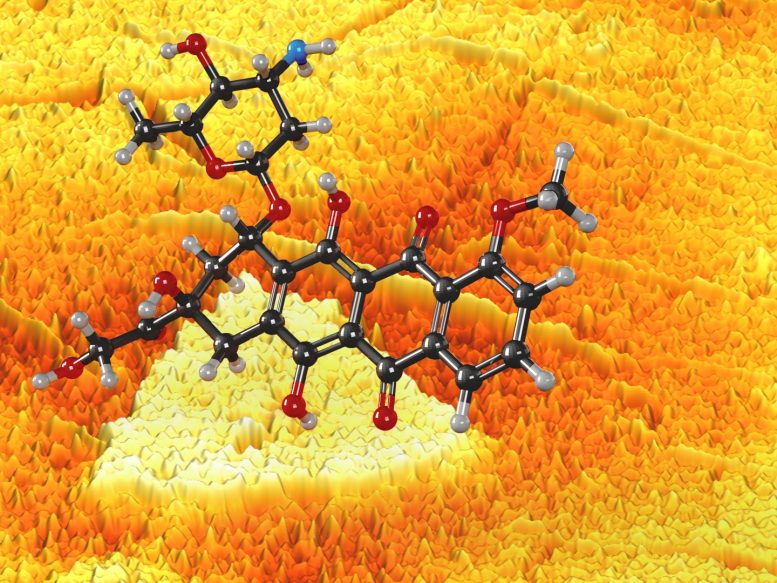
A molecule of the most cancers treatment doxorubicin (foreground), detected utilizing the van der Waals vertical heterostructure biosensor (background). The background is an precise nanoscale scattering scanning near-field optical microscopy picture (sSNOM) of the heterostructure and the big triangle is a single-layer MoS2 island (ca. 3.7 micron vast), the smaller triangle is a partially oxidized MoOS island, and the entire pattern is roofed with the monolayer graphene, with a number of wrinkles clearly seen within the map. The darker graphene space corresponds to the area of additional cost doping. Credit score: Elizabeth Flores-Gomez Murray/Jennifer McCann/Slava Rotkin, Penn state
A novel and higher strategy at detecting non-uniformities within the optical properties of two-dimensional supplies may probably open the door to new makes use of for these supplies, equivalent to for drug detection, in line with a group of researchers.
“The Two-Dimensional Crystal Consortium (2DCC) is a world chief in 2D supplies analysis and my lab usually works with the 2DCC doing supplies characterization for novel 2D supplies,” mentioned Slava V. Rotkin, Frontier Professor of Engineering Science and Mechanics with an appointment within the Supplies Analysis Institute at Penn State. “There's a huge problem in these research: Regularly, optical properties of 2D supplies are usually not uniform in area. Moreover, they could differ at a really small spatial scale, all the way down to a single atom.”
Rotkin and different researchers have been capable of take one step towards a doable answer, which was outlined in ACS Nano. Whereas Rotkin stresses they solely gave an indication of the precept within the research, the answer they suggest was used for van der Waals heterostructures which may allow sensors made with 2D supplies, supplies which are one to some atoms thick.
Sensors might be developed that allow sensing of bio-, chemical and/or medical analytes of curiosity. Analytes are particular chemical substances focused for measurement or evaluation. sensor detects these analytes with minimal pattern preparation, in an abbreviated timeframe, with low detection limits, and utilizing samples containing substances apart from the important thing analyte.
Figuring out and understanding variability of properties in supplies might be extraordinarily essential for functions of 2D supplies as sensors. The sensor materials sometimes can solely work together with the analyte on the floor. Thus, the fabric’s floor is an energetic space, whereas materials’s quantity isn't. The bigger the ratio of floor to quantity, the decrease the fraction of fabric which can't be used. Such atomically skinny supplies have the last word surface-to-volume ratio for sensor use and should possess floor non-uniformities on the nanometer scale. This consists of atomic impurities, adsorbates, defects, wrinkles, ruptures, and so forth. Such options can modulate the optical properties.
“Regardless of this being crucial for effectiveness in sure utility of 2D supplies, there may be at present no actually efficient strategy to detect these variabilities,” Rotkin mentioned. “Because of their being so tiny, they're undetectable by optical instruments and non-optical instruments can not resolve optical distinction.”
The researchers performed experiments utilizing a heterostructure materials made from graphene, the 2D materials model of graphite, and the inorganic compound molybdenum disulfide. The molybdenum disulfide provides a photoluminescence sign that detects the quantity of cost switch between the graphene and the molybdenum disulfide layers. Subsequently, it will probably detect adjustments as a result of bio analyte, which on this case is the most cancers therapy drug doxorubicin, that may have an effect on the cost.
These adjustments are additionally detectable in graphene through evaluation by Raman spectroscopy, which discovers distinctive vibrations in molecules. A Raman microscope picks up shifts within the frequency of photons within the laser mild beam brought on by these vibrations.
“The 2 channels collectively permit a greater calibration of the 2 indicators towards analyte focus and the kind of analyte,” Rotkin mentioned. “And moreover, graphene enhances the Raman sign of the analyte itself to the extent one can ‘see’ a sign from only a few molecules.”
The researchers used doxorubicin as their analyte as a result of it's a widespread most cancers drug utilized in chemotherapy, and there may be an acute want for biosensors to detect it to assist regulate dosage and scale back unwanted effects. There are two sorts of biosensors that work for this function, label-free biosensors, which can be utilized to detect quite a lot of medication, and label-based biosensors, which may detect solely a selected drug. The researchers used label-free biosensing within the research.
“The label-based biosensor is sort of a lock that may be opened with just one key, however the label-free biosensor is sort of a lock with many alternative keys,” Rotkin mentioned. “We didn't invent label-free multimodal biosensing, this strategy has been in different research. However an precise demonstration with a selected materials is new and nonetheless essential by itself.”
This might result in steps for fixing varied well being care challenges.
“Retaining in thoughts that there's a hole between elementary analysis and its functions, I'd say we contributed a brick to constructing a big set of nanotechnology/nanomaterials for biosensing and different functions,” Rotkin mentioned. “Label-free detection lays the groundwork for good and built-in sensors, new bio-threat security methods, and extra individualized medication and coverings, amongst others advantages.”
That is additionally important as a result of making a label-free biosensor is tougher than creating a label-based biosensor.
“We make it work by merging a number of sensors in a single system, take into consideration the lock and key analogy as three locks on one chain,” Rotkin mentioned “Particularly, we apply the doxorubicin to our 2D materials, which produces three completely different optical indicators, constituting a multimodal sensing. By measuring three indicators without delay as a substitute of only one like in a traditional sensor, this permits us to detect doxorubicin utilizing label-free biosensing.”
Together with the biosensing prospects, there are additionally extra fast advantages to this analysis, in line with Rotkin.
“This work provides us deeper information of general optical properties of 2D supplies,” Rotkin mentioned. “We uncovered among the mechanisms for one particular construction, graphene and MoS2. However our nanoimaging methodology is relevant to many others, if to not all. Additionally, we hope to draw extra consideration to the physics of 2D materials heterostructures equivalent to our composite materials which mixed the properties of graphene and MoS2 single-layer supplies.”
The following steps for this analysis will embrace making use of the supplies part of their work to different initiatives on the 2DCC and at Penn State’s Nationwide Science Basis Supplies Analysis Science and Engineering Heart, the Heart for Nanoscale Science. This would come with initiatives involving quantum plasmonics and 2D non-linear optics. As well as, the analysis group will likely be on the lookout for companions to analysis sensible functions.
“Since label-free detection is common, we aren't restricted by a sort of analyte, utility nor drawback,” Rotkin mentioned. “Nonetheless, there must be somebody with an actual drawback to use the strategy. We're on the lookout for collaborators from the world of medication for some thrilling new joint analysis.”
Reference: “Multidimensional Imaging Reveals Mechanisms Controlling Multimodal Label-Free Biosensing in Vertical 2DM-Heterostructures” by Tetyana Ignatova, Sajedeh Pourianejad, Xinyi Li, Kirby Schmidt, Frederick Aryeetey, Shyam Aravamudhan and Slava V. Rotkin, 21 January 2022, ACS Nano.
DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.1c09335
Together with Rotkin, who was a co-presenting writer of the research, different authors embrace: from the College of North Carolina Greensboro, co-presenting writer Tetyana Ignatova, assistant professor of nanoscience; Sajedeh Pourianejad and Kirby Schmidt, doctoral college students in nanoscience. From Penn State, a further writer of the research is Xinyi Li, doctoral candidate in engineering science. From North Carolina A & T State College, extra authors of the research embrace Frederick Aryeetey, doctoral candidate on the time of the research, and Shyam Aravamudhan, director of core services at Joint Faculty of Nanoscience and Nanoengineering and affiliate professor of nanoengineering.
The Nationwide Science Basis supported this analysis.
Post a Comment