
An enormous asteroid struck Earth and worn out the dinosaurs 65 million years in the past.
An area safety professional explains NASA’s plans to stop a possible disaster.
The Earth exists in a harmful atmosphere. Cosmic our bodies, like asteroids and comets, are always zooming by way of area and infrequently crash into our planet. Most of those are too small to pose a risk, however some could be trigger for concern.
As a scholar who research area and worldwide safety, it's my job to ask what the chance of an object crashing into the planet actually is – and whether or not governments are spending sufficient cash to stop such an occasion.
To seek out the solutions to those questions, one has to know what near-Earth objects are on the market. Thus far, NASA has tracked solely an estimated 40% of the larger ones. Shock asteroids have visited Earth up to now and can undoubtedly accomplish that sooner or later. After they do seem, how ready will humanity be?
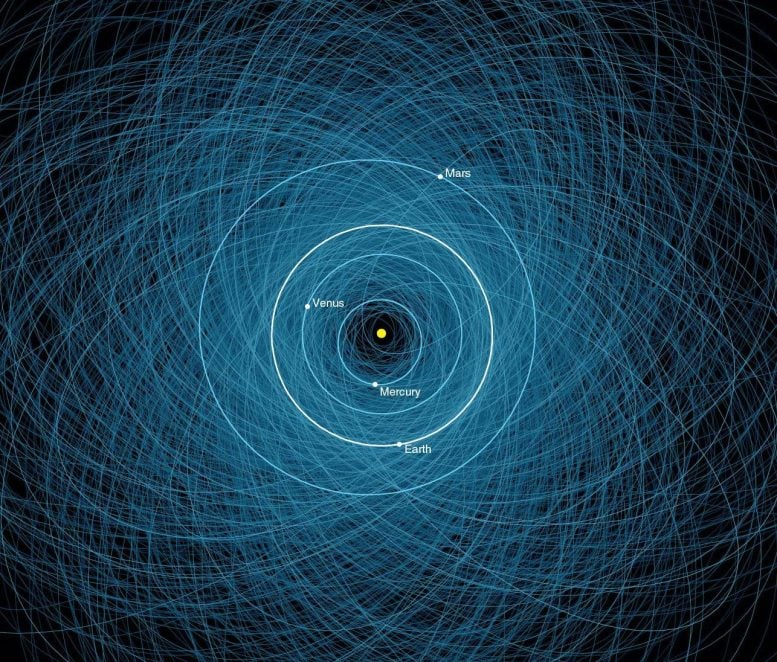

The orbits of 1000's of asteroids (in blue) cross paths with the orbits of planets (in white), together with Earth’s. Credit score: NASA/JPL
The risk from asteroids and comets
Tens of millions of objects of assorted sizes orbit the Solar. Close to-Earth objects embody asteroids and comets whose orbits will convey them inside 120 million miles (193 million kilometers) of the Solar.
Astronomers think about a near-Earth object a risk if it is going to come inside 4.6 million miles (7.4 million km) of the planet and is a minimum of 460 ft (140 meters) in diameter. If a celestial physique of this dimension crashed into Earth, it may destroy a complete metropolis and trigger excessive regional devastation. Bigger objects – 0.6 miles (1 km) or extra – may have international results and even trigger mass extinctions.
Probably the most well-known and damaging affect befell 65 million years in the past when a 6-mile (10-km) diameter asteroid crashed into what's now the Yucatán Peninsula. It worn out most plant and animal species on Earth, together with the dinosaurs.
However smaller objects may trigger vital injury. In 1908, an roughly 164-foot (50-meter) celestial physique exploded over the Tunguska River in Siberia. It leveled greater than 80 million timber over 830 sq. miles (2,100 sq. km). In 2013, an asteroid solely 65 ft (20 meters) throughout burst within the ambiance 20 miles (32 km) above Chelyabinsk, Russia. It launched the equal of 30 Hiroshima bombs value of vitality, injured over 1,100 folks and triggered US$33 million in injury.
The following asteroid of considerable dimension to doubtlessly hit Earth is asteroid 2005 ED224. When the 164-foot (50-meter) asteroid passes by on March 11, 2023, there's roughly a 1 in 500,000 probability of affect.
NASA has been steadily discovering and monitoring near-Earth objects because the Nineties. Credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Watching the skies
Whereas the probabilities of a bigger cosmic physique impacting Earth are small, the devastation could be huge.
Congress acknowledged this risk, and in the 1998 Spaceguard Survey, it tasked NASA to search out and observe 90% of near-Earth objects 0.6 miles (1 km) throughout or greater inside 10 years. NASA surpassed the 90% aim in 2011.
In 2005, Congress handed one other invoice requiring NASA to broaden its search and observe a minimum of 90% of all near-Earth objects 460 ft (140 meters) or bigger by the tip of 2020. That yr has come and gone and, largely attributable to an absence of monetary assets, solely 40% of these objects have been mapped.
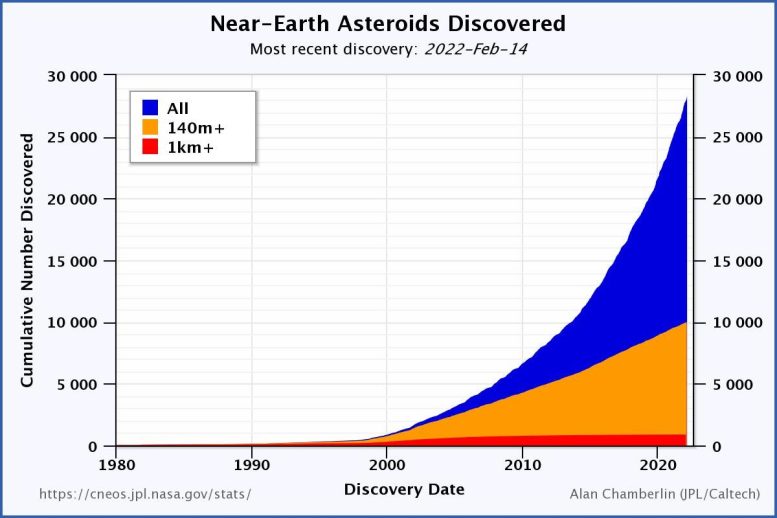
As of Feb. 14, 2022, astronomers have situated 28,266 near-Earth asteroids, of which 10,033 are 460 ft (140 meters) or bigger in diameter and 888 a minimum of 0.6 miles (1 km) throughout. About 30 new objects are added every week.
A brand new mission, funded by Congress in 2018, is scheduled to launch in 2026 an infrared, space-based telescope – NEO Surveyor – devoted to looking for doubtlessly harmful asteroids.
Smaller asteroids, just like the one which exploded over Russia in 2013, can strike Earth with out warning, however bigger, extra harmful objects have stunned astronomers, too.
Cosmic surprises
We are able to solely forestall a catastrophe if we all know it's coming, and asteroids have sneaked up on Earth earlier than.
An asteroid the dimensions of a soccer discipline – dubbed the “Metropolis-killer” – handed lower than 45,000 miles from Earth in 2019. An asteroid the dimensions of a 747 jet got here shut in 2021 as did a 0.6-mile (1-km) vast asteroid in 2012. Every of those was found solely a couple of day earlier than they handed Earth.
Analysis means that one motive could also be that Earth’s rotation creates a blind spot whereby some asteroids stay undetected or seem stationary. This can be an issue, as some shock asteroids don't miss us. In 2008, astronomers noticed a small asteroid solely 19 hours earlier than it crashed into rural Sudan. And the latest discovery of an asteroid 1.2 miles (2 km) in diameter means that there are nonetheless massive objects lurking.
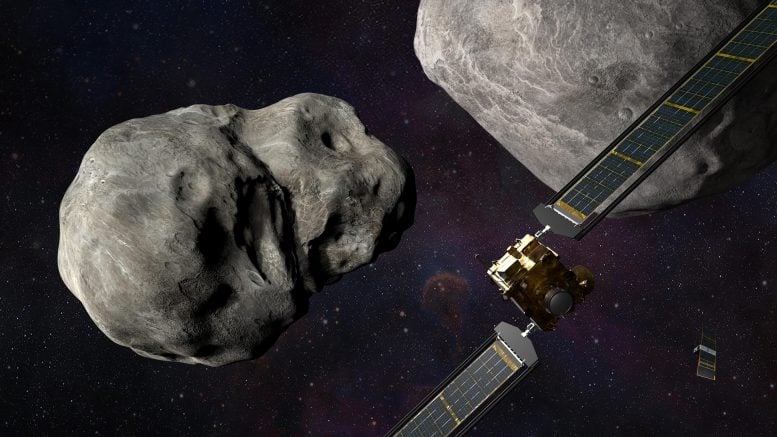

NASA’s DART mission will crash a small spacecraft into the double asteroid Didymos to see if it is going to change the asteroid’s orbit. Credit score: NASA/Johns Hopkins, APL/Steve Gribben
What could be completed?
To guard the planet from cosmic risks, early detection is vital. On the 2021 Planetary Protection Convention, scientists really helpful a minimal of 5 to 10 years’ preparation time to mount a profitable protection in opposition to hazardous asteroids.
If astronomers discover a harmful object, there are 4 methods to mitigate a catastrophe. The primary includes regional first-aid and evacuation measures. A second strategy would contain sending a spacecraft to fly close to a small- or medium-sized asteroid; the gravity of the craft would slowly change the thing’s orbit. To change an even bigger asteroid’s path, we will both crash one thing into it at excessive speeds or detonate a nuclear warhead close by.
These might look like far-fetched concepts, however in November 2021, NASA launched the world’s first full-scale planetary protection mission as a proof of idea: the Double Asteroid Redirection Check, or DART. The massive asteroid Didymos and its small moon at the moment pose no risk to Earth. In September 2022, NASA plans to vary the asteroid’s orbit by crashing a 1,340-pound (610 kg) probe into Didymos’ moon at a pace of roughly 14,000 mph (22,500 kph).
Studying extra about what threatening asteroids are manufactured from can also be vital, as their composition might have an effect on how profitable we're at deflecting them. The asteroid Bennu is 1,620 ft (490 meters) in diameter. Its orbit will convey it dangerously near Earth on Sept. 24, 2182, and there's a 1 in 2,700 probability of a collision. An asteroid of this dimension may wipe out a complete continent, so to study extra about Bennu, NASA launched the OSIRIS-Rex probe in 2016. The spacecraft arrived at Bennu, took footage, collected samples and is because of return to Earth in 2023.
Spending on planetary protection
In 2021, NASA’s planetary protection price range was $158 million. That is simply 0.7% of NASA’s complete price range and simply 0.02% of the roughly $700 billion 2021 U.S. protection price range.
This price range helps a lot of missions, together with the NEO Surveyor at $83 million, DART at $324 million and Osiris Rex at round $1 billion over a number of years.
Is that this the correct amount to put money into monitoring the skies, given the truth that some 60% of all doubtlessly harmful asteroids stay undetected? This is a crucial query to ask when one considers the potential penalties.
Investing in planetary protection is akin to purchasing owners insurance coverage. The chance of experiencing an occasion that destroys your home could be very small, but folks purchase insurance coverage nonetheless.
If even a single object bigger than 460 ft (140 meters) hits the planet, the devastation and lack of life could be excessive. An even bigger affect may fairly actually wipe out most species on Earth. Even when no such physique is anticipated to hit Earth within the subsequent 100 years, the prospect will not be zero. On this low chance versus excessive penalties state of affairs, investing in defending the planet from harmful cosmic objects might give humanity some peace of thoughts and will forestall a disaster.
Written by Svetla Ben-Itzhak, Assistant Professor of Area and Worldwide Relations, West Area Seminar, Air Warfare Faculty, Air College.
This text was first printed in The Dialog.![]()
Post a Comment