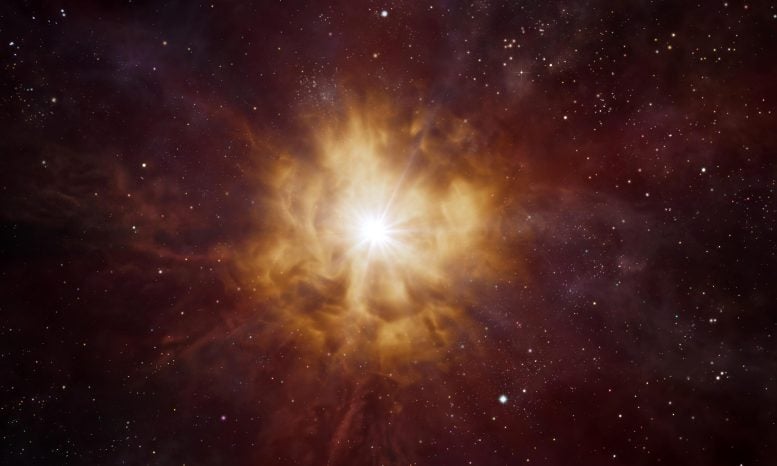

Picture of a Wolf Rayet star – probably earlier than collapsing right into a black gap. Credit score: ESO/L. Calçada
Astronomers are more and more drawing again the curtains on black holes. Prior to now few years, now we have lastly captured precise pictures of those fearsome creatures and measured the gravitational waves – ripples in spacetime – that they create when colliding. However there’s nonetheless loads we don’t learn about black holes. One of many greatest enigmas is precisely how they kind within the first place.
My colleagues and I now consider now we have noticed this course of, offering a number of the greatest indications but of precisely what occurs when a black gap varieties. Our outcomes are revealed in two papers in Nature and the Astrophysical Journal.
Astronomers consider, on each observational and theoretical grounds, that almost all black holes kind when the middle of an enormous star collapses on the finish of its life. The star’s core usually supplies stress, or help, utilizing warmth from intense nuclear reactions. However as soon as such a star’s gas is exhausted and nuclear reactions cease, the interior layers of the star collapse inward underneath gravity, crushing right down to extraordinary densities.
More often than not, this catastrophic collapse is halted when the star’s core condenses right into a strong sphere of matter, wealthy in particles referred to as neutrons. This results in a strong rebound explosion that destroys the star (a supernova), and leaves behind an unique object often called a neutron star. However fashions of dying stars present that if the unique star is huge sufficient (40-50 instances the mass of the Solar), the collapse will merely proceed unabated till the star is crushed down right into a gravitational singularity – a black gap.
Explosive theories
Whereas stars collapsing to kind neutron stars are actually routinely noticed all through the universe (supernova surveys discover dozens of recent ones each night time), astronomers aren't but completely positive what occurs throughout the collapse to a black gap. Some pessimistic fashions recommend all the star can be swallowed up with out a lot of a hint. Others suggest that the collapse to a black gap would produce another sort of explosion.
For instance, if the star is rotating on the time of collapse, a number of the infalling materials could also be targeted into jets that escape the star at excessive velocity. Whereas these jets wouldn’t include a lot mass, they’d pack a giant punch: in the event that they slammed into one thing, the consequences is perhaps fairly dramatic by way of the power launched.
Up till now, the perfect candidate for an explosion from the beginning of a black gap has been the unusual phenomenon often called long-duration gamma-ray bursts. First found within the Sixties by army satellites, these occasions have been hypothesized to end result from jets accelerated to mindboggling speeds by newly shaped black holes in collapsing stars. Nevertheless, a longstanding downside with this situation is that gamma-ray bursts additionally expel considerable radioactive particles that continues to shine for months. This implies a lot of the star exploded outward into house (as in an bizarre supernova), as a substitute of collapsing inward to a black gap.
Whereas this doesn’t imply a black gap can’t have been shaped in such an explosion, some have concluded that different fashions present a extra pure clarification for gamma ray bursts than a black gap forming. For instance, a super-magnetized neutron star might kind in such an explosion and produce highly effective jets of its personal.
Thriller solved?
My colleagues and I, nevertheless, just lately uncovered a brand new and (in our view) significantly better candidate occasion for making a black gap. On two separate events prior to now three years – as soon as in 2019 and as soon as in 2021 – we witnessed an exceptionally quick and fleeting kind of explosion that, very similar to in gamma-ray bursts, originated from a small quantity of very fast-moving materials slamming into gasoline in its speedy setting.
Through the use of spectroscopy – a method that breaks down gentle into completely different wavelengths – we might infer the composition of the star that exploded for every of those occasions. We found that the spectrum was similar to so-called “Wolf-Rayet stars” – a really huge and highly-evolved kind of star, named after the 2 astronomers, Charles Wolf and Georges Rayet, that first detected them. Excitingly, we had been even in a position to rule out a “regular” supernova explosion. As quickly because the collision between the quick materials and its setting ceased, the supply virtually vanished – quite than glowing for a very long time.
That is precisely what you'd count on if, throughout the collapse of its core, the star ejected solely a small quantity of fabric with the remainder of the thing collapsing downward into an infinite black gap.
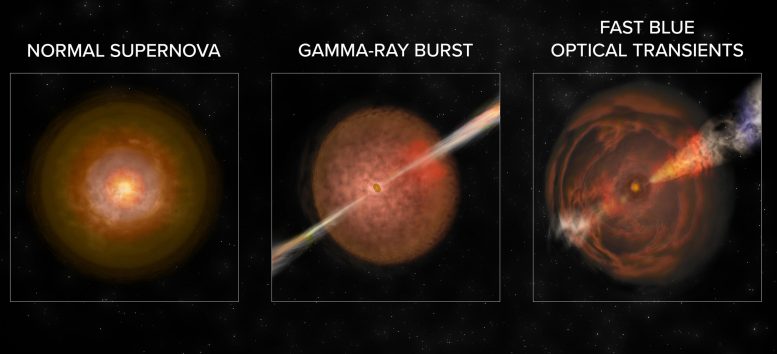
The brand new research noticed two occasions that will belong to 3rd kind of explosion, lasting solely a short while. Credit score: Invoice Saxton, NRAO/AUI/NSF
Whereas that is our favoured interpretation, it’s not the one chance. Essentially the most prosaic one is that it was a standard supernova explosion, however that a huge shell of mud shaped within the collision, concealing the radioactive particles from view. It’s additionally doable that the explosion is of a brand new and unfamiliar kind, originating from a star we’re not accustomed to.
To reply these questions, we might want to seek for extra such objects. Till now these sorts of explosions have been tough to review as a result of they're fleeting and exhausting to search out. We had to make use of a number of observatories collectively in fast succession to characterize these explosions: the Zwicky Transient Facility to find them, the Liverpool Telescope and the Nordic Optical Telescope to verify their nature, and enormous high-resolution observatories (the Hubble House Telescope, Gemini Observatory, and the Very Massive Telescope) to research their composition.
Whereas we didn’t initially know precisely what we had been seeing once we first found these occasions, we now have a transparent speculation: the beginning of a black gap.
Extra knowledge from comparable occasions could quickly be capable to assist us confirm or falsify this speculation and set up the hyperlink to different kinds of uncommon, quick explosions that our group and others have been discovering. Both means, it appears this really is the last decade we crack the mysteries of black holes.
Written by Daniel Perley, Reader of Astrophysics, Liverpool John Moores College.
This text was first revealed in The Dialog.![]()

Post a Comment