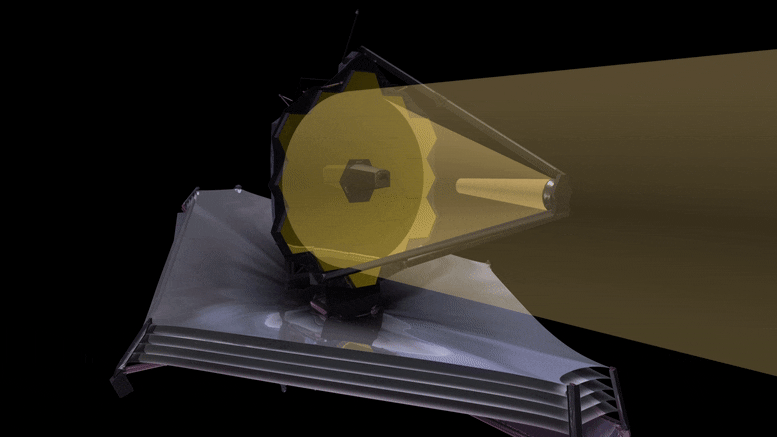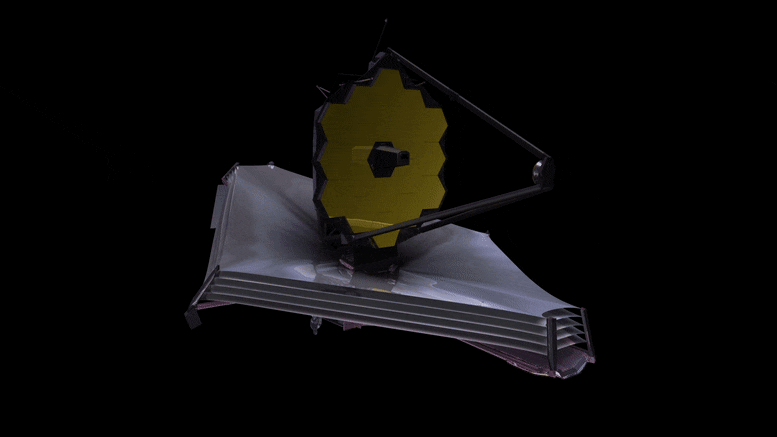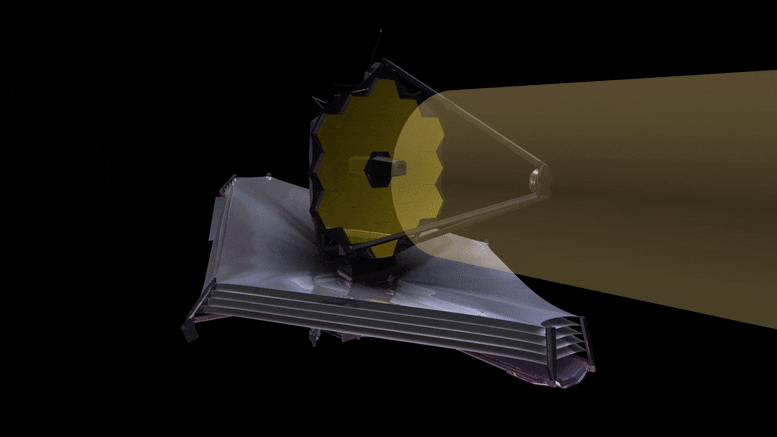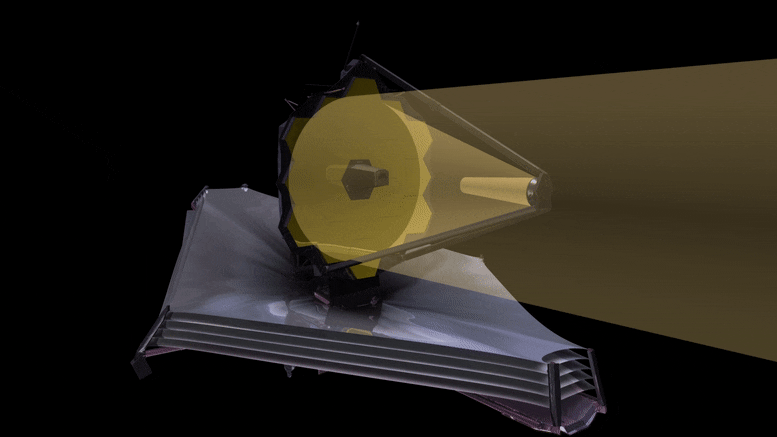
This animation reveals the trail gentle will observe because it hits the first James Webb Area Telescope (JWST) mirror, and is mirrored to the secondary, after which in by way of the aft optics meeting the place the tertiary and fantastic steering mirrors are. The sunshine is then mirrored and break up and directed to the science devices by pick-off mirrors. JWST is a three-mirror anastigmat telescope. Credit score: NASA, ESA, and G. Bacon (STScI)
This week, the three-month technique of aligning the telescope started – and over the past day, Webb staff members noticed the primary photons of starlight that traveled by way of all the telescope and have been detected by the Close to Infrared Digital camera (NIRCam) instrument. This milestone marks the primary of many steps to seize photos which might be at first unfocused and use them to slowly fine-tune the telescope. That is the very starting of the method, however to date the preliminary outcomes match expectations and simulations.
A staff of engineers and scientists from Ball Aerospace, Area Telescope Science Institute, and NASA’s Goddard Area Flight Middle will now use information taken with NIRCam to progressively align the telescope. The staff developed and demonstrated the algorithms utilizing a 1/sixth scale mannequin telescope testbed. They've simulated and rehearsed the method many instances and are actually prepared to do that with Webb. The method will happen in seven phases over the subsequent three months, culminating in a completely aligned telescope prepared for instrument commissioning. The photographs taken by Webb throughout this era is not going to be “fairly” photos like the brand new views of the universe Webb will unveil later this summer time. They strictly serve the aim of getting ready the telescope for science.
To work collectively as a single mirror, the telescope’s 18 major mirror segments must match one another to a fraction of a wavelength of sunshine – roughly 50 nanometers. To place this in perspective, if the Webb major mirror have been the dimensions of the US, every section can be the dimensions of Texas, and the staff would wish to line the peak of these Texas-sized segments up with one another to an accuracy of about 1.5 inches.
Scott Acton and Chanda Walker of Ball Aerospace, together with Lee Feinberg of NASA Goddard, stroll by way of the fundamental steps beneath:
“With deployment of the mirror segments now full, and the devices turned on, the staff has begun the quite a few steps required to organize and calibrate the telescope to do its job. The telescope commissioning course of will take for much longer than earlier area telescopes as a result of Webb’s major mirror consists of 18 particular person mirror segments that must work collectively as a single high-precision optical floor. The steps within the commissioning course of embody:
- Phase Picture Identification
- Phase Alignment
- Picture Stacking
- Coarse Phasing
- High quality Phasing
- Telescope Alignment Over Instrument Fields of View
- Iterate Alignment for Last Correction
1. Phase Picture Identification
First, we have to align the telescope relative to the spacecraft. The spacecraft is able to making extraordinarily exact pointing strikes, utilizing “star trackers.” Consider star trackers as a GPS for spacecraft. At first, the place of the spacecraft from the star trackers doesn't match the place of every of the mirror segments.
We're pointing the telescope at a shiny, remoted star (HD 84406) to seize a collection of photos which might be then stitched collectively to kind an image of that a part of the sky. However keep in mind, we don’t have only one mirror this star; now we have 18 mirrors, every of which is initially tilted in direction of a special a part of the sky. In consequence, we’ll really seize 18 barely shifted copies of the star – each out of focus and uniquely distorted. We refer to those preliminary star-copies as “section photos.” In actual fact, relying on the beginning positions of the mirrors, it might take a number of iterations to find all 18 segments in a single picture.

Simulated instance of a doable preliminary deployment displaying 18 section photos. Credit score: NASA
One after the other, we'll transfer the 18 mirror segments to find out which section creates which section picture. After matching the mirror segments to their respective photos, we will tilt the mirrors to carry all the photographs close to a typical level for additional evaluation. We name this association an “picture array.”
2. Phase Alignment
After now we have the picture array, we will carry out Phase Alignment, which corrects many of the giant positioning errors of the mirror segments.
We start by defocusing the section photos by transferring the secondary mirror barely. Mathematical evaluation, referred to as Section Retrieval, is utilized to the defocused photos to find out the exact positioning errors of the segments. Changes of the segments then lead to 18 well-corrected “telescopes.” Nevertheless, the segments nonetheless don’t work collectively as a single mirror.
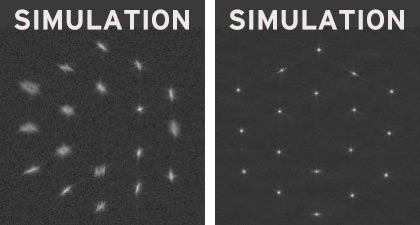
(Left) Earlier than: Simulated preliminary array of photos. (Proper) After: Simulated array of 18 corrected segments. Credit score: NASA
3. Picture Stacking
To place the entire gentle in a single place, every section picture should be stacked on high of each other. Within the Picture Stacking step, we transfer the person section photos in order that they fall exactly on the middle of the sector to supply one unified picture. This course of prepares the telescope for Coarse Phasing.
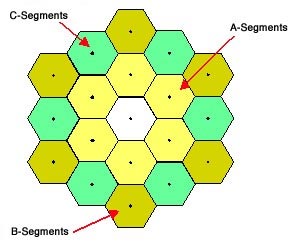
The stacking is carried out sequentially in three teams (A-segments, B-segments, and C-segments).
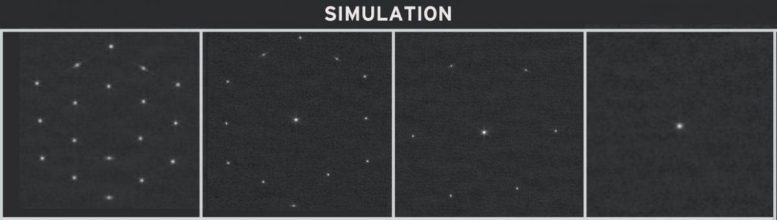
Simulation of picture stacking. First panel: Preliminary picture mosaic. Second panel: A-segments stacked. Third panel: A- and B-segments stacked. Fourth panel: A-, B-, and C-segments stacked. Credit score: NASA
4. Coarse Phasing
Though Picture Stacking places all the sunshine in a single place on the detector, the segments are nonetheless performing as 18 small telescopes reasonably than one massive one. The segments must be lined up with one another with an accuracy smaller than the wavelength of the sunshine.
Performed 3 times through the commissioning course of, Coarse Phasing measures and corrects the vertical displacement (piston distinction) of the mirror segments. Utilizing a expertise often called Dispersed Fringe Sensing, we use NIRCam to seize gentle spectra from 20 separate pairings of mirror segments. The spectrum will resemble a barber pole sample with a slope (or angle) decided by the piston distinction of the 2 segments within the pairing.
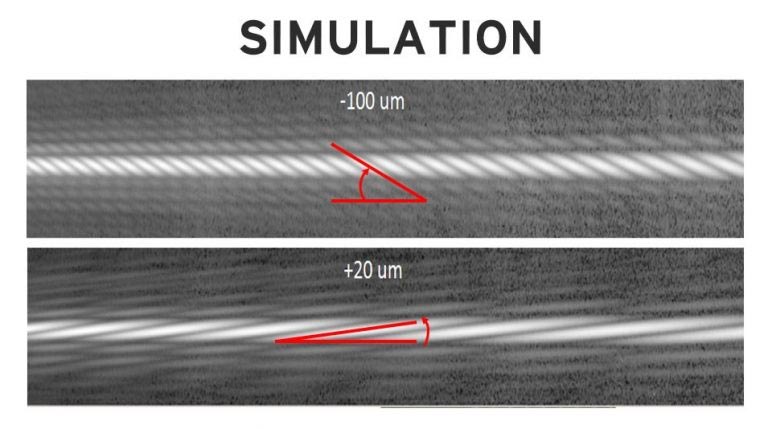
On this simulation, the “Barber pole” patterns are created by the Disperse Fringe Sensor indicating a big piston error (high) or a small piston error (backside). Credit score: NASA
5. High quality Phasing
High quality Phasing can also be performed 3 times, immediately after every spherical of Coarse Phasing, after which routinely all through Webb’s lifespan. These operations measure and proper the remaining alignment errors utilizing the identical defocusing methodology utilized throughout Phase Alignment. Nevertheless, as a substitute of utilizing the secondary mirror, we use particular optical parts contained in the science instrument which introduce various quantities of defocus for every picture (-8, -4, +4, and +8 waves of defocus).
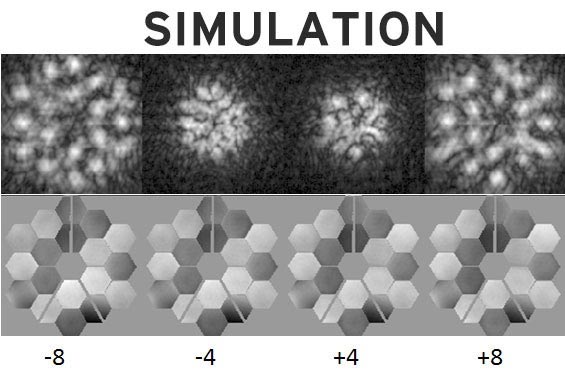
A simulation of the defocused photos utilized in High quality Phasing. The photographs (high) present defocus launched to an nearly aligned telescope. The evaluation (backside) signifies the errors related to every telescope section. Segments with very shiny or darkish colours want bigger corrections. Credit score: NASA
6. Telescope Alignment Over Instrument Fields of View
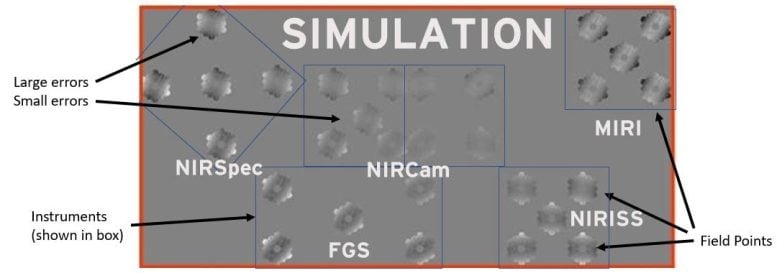
After High quality Phasing, the telescope will probably be properly aligned at one place within the NIRCam subject of view. Now we have to prolong the alignment to the remainder of the devices.
On this part of the commissioning course of, we make measurements at a number of areas, or subject factors, throughout every of the science devices, as proven beneath. Extra variation in depth signifies bigger errors at that subject level. An algorithm calculates the ultimate corrections wanted to attain a well-aligned telescope throughout all science devices.
7. Iterate Alignment for Last Correction
After making use of the Area of View correction, the important thing factor left to deal with is the elimination of any small, residual positioning errors within the major mirror segments. We measure and make corrections utilizing the High quality Phasing course of. We are going to do a ultimate verify of the picture high quality throughout every of the science devices; as soon as that is verified, the wavefront sensing and controls course of will probably be full.
As we undergo the seven steps, we might discover that we have to iterate earlier steps as properly. The method is versatile and modular to permit for iteration. After roughly three months of aligning the telescope, we will probably be able to proceed to commissioning the devices.”
Written by Scott Acton, Webb lead wavefront sensing and management scientist, Ball Aerospace; Chanda Walker, Webb wavefront sensing and management scientist, Ball Aerospace; and Lee Feinberg, Webb optical telescope aspect supervisor, NASA’s Goddard Area Flight Middle.
Post a Comment