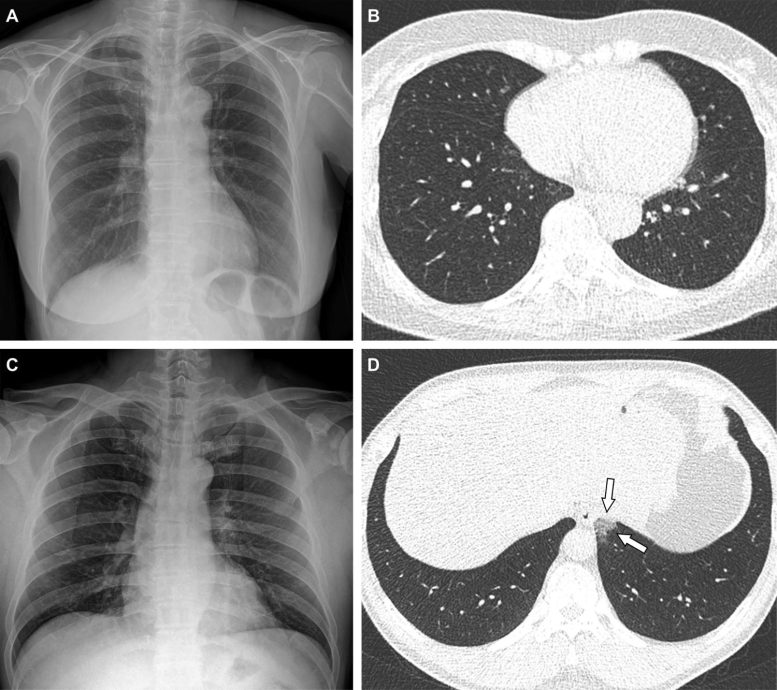
Consultant instances exhibiting pneumonia extents and patterns on chest X-ray (CXR) and CT photos. (A and B) A 65-year-old feminine with breakthrough an infection 2 months after a second dose of the Pfizer vaccine (totally vaccinated). The affected person had a historical past of hypertension. (A) CXR obtained at admission exhibiting no irregular opacification in each lung zones. The CXR extent of pneumonia was scored as 0 (no proof of pneumonia). (B) Axial chest CT picture on the decrease lobe degree (obtained on the identical day) exhibiting negatively for pneumonia; CT extent of pneumonia was scored as 0 (no proof of pneumonia). (C and D) A 48-year-old male with 1 month after a primary dose of the AstraZeneca vaccine (partially vaccinated). The affected person had no historical past of comorbidity. (C) CXR obtained at admission exhibiting no irregular opacification in each lung zones. The CXR extent of pneumonia was scored as 0 (no proof of pneumonia). (D) Axial chest CT picture obtained on the identical day exhibiting unilateral ground-glass opacity with a non-rounded morphology within the left decrease lobe (arrows). CT extent of pneumonia was scored as 1 (1-25% involvement) and this case was categorised as indeterminate look of COVID-19 in response to the RSNA chest CT classification system. Credit score: Radiological Society of North America
The scientific and imaging traits of COVID-19 breakthrough infections in totally vaccinated sufferers are typically milder than these of partially vaccinated or unvaccinated sufferers, in response to a brand new multicenter research revealed within the journal Radiology.
The variety of confirmed COVID-19 instances worldwide now exceeds 270 million with an total mortality fee of roughly 2%.
COVID-19 vaccines are efficient and demanding instruments for bringing the pandemic underneath management. Nevertheless, vaccines are usually not 100% efficient at stopping sickness. Breakthrough infections are outlined because the detection of extreme acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) ribonucleic acid (RNA) or antigen in a respiratory specimen collected from an individual 14 days or extra after receiving all really helpful doses of COVID-19 vaccines.
Breakthrough instances are on the rise with the extremely transmissible Omicron variant. Due to this fact, it is very important know the way vaccination impacts not solely COVID-19 illness severity but in addition scientific information and medical imaging outcomes.
“Though the chance of an infection is way decrease amongst vaccinated people, and vaccination reduces the severity of sickness, scientific and imaging information of COVID-19 breakthrough infections haven't been reported intimately,” stated the research’s senior creator, Yeon Joo Jeong, M.D., Ph.D., from the Division of Radiology and Biomedical Analysis Institute at Pusan Nationwide College Hospital in Busan, South Korea. “The aim of this research was to doc the scientific and imaging options of COVID-19 breakthrough infections and evaluate them with these of infections in unvaccinated sufferers.”
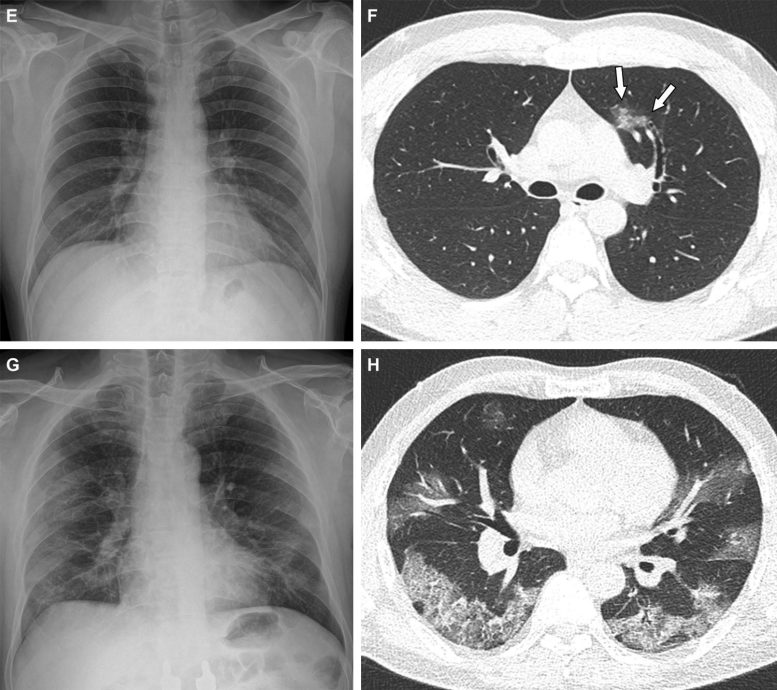
Consultant instances exhibiting pneumonia extents and patterns on chest X-ray (CXRs) and CT photos. (E and F) A 36-year-old male with no historical past of vaccination for COVID- 19. The affected person had no historical past of comorbidity. (E) CXR obtained at admission exhibiting no irregular opacification in both lung zone. CXR extent of pneumonia was scored as 0 (no proof of pneumonia). (F) Axial chest CT picture obtained on the identical day exhibiting unilateral ground-glass opacity with a nonrounded morphology and non-peripheral distribution within the left higher lobe (arrows). CT extent of pneumonia was scored as 1 (1-25% involvement) and this case was categorised as indeterminate look of COVID-19 in response to the RSNA chest CT classification system. (G and H) A 58-year-old male with no historical past of COVID-19 vaccination. The affected person had a historical past of hypertension and diabetes. He required supplemental oxygen on admission and was admitted to intensive care unit someday later. (G) CXR at admission exhibiting patchy ground-glass opacities in each middle- to lower-lung zones. CXR extent of pneumonia was scored as 2 (>25% involvement). (H) Axial chest CT picture obtained on the identical day exhibiting multifocal ground-glass opacities with a crazy-paving look in bilateral lungs. CT extent of pneumonia was scored as 2 (>25% involvement) and was categorised as typical look of COVID-19 in response to the RSNA chest CT classification system. Credit score: Radiological Society of North America
On this retrospective multicenter cohort research, Dr. Jeong and colleagues analyzed information from grownup sufferers registered in an open information repository for COVID-19—Korean Imaging Cohort for COVID-19 (KICC-19)—between June and August 2021. Hospitalized sufferers with baseline chest X-rays had been divided into three teams, in response to their vaccination standing. The researchers evaluated variations between scientific and imaging options and analyzed associations between scientific components—together with vaccination standing—and scientific outcomes.
Of the 761 hospitalized sufferers with COVID-19, the imply age was 47 years, and 385 (51%) had been ladies. Forty-seven sufferers (6.2%) had been totally vaccinated (breakthrough an infection), 127 had been partially vaccinated (17%), and 587 (77%) had been unvaccinated. Chest CT scans had been carried out on 412 (54%) of the sufferers throughout hospitalization. Of sufferers present process CT, the proportion of CT scans with out pneumonia was 22% (71/326) of unvaccinated sufferers, 30% (19/64) of partially vaccinated sufferers, and 59% (13/22) of totally vaccinated sufferers. Totally vaccinated standing was related to a decrease danger of requiring supplemental oxygen than unvaccinated standing, in addition to decrease danger of intensive care unit (ICU) admission.
The outcomes additionally confirmed associations between the chance of extreme illness and scientific traits reminiscent of larger age, historical past of diabetes, lymphocytopenia, thrombocytopenia, elevated LDH (lactate dehydrogenase), and elevated CRP (C-reactive protein). Notably, age was additionally discovered to be an essential predictor of extra extreme illness in COVID-19 sufferers, even in these with a breakthrough an infection.
The researchers famous that noticed variations in scientific traits might mirror variations in vaccination priorities based mostly on underlying comorbidities. Throughout the research interval, high-risk teams, reminiscent of people over 65 years outdated, well being care staff and other people with disabilities had been precedence targets for COVID-19 vaccination. Due to this fact, aged sufferers and sufferers with at the least one comorbidity had been extra widespread within the vaccinated group than in unvaccinated group within the research.
“Regardless of these variations, mechanical air flow and in-hospital demise occurred solely within the unvaccinated group,” Dr. Jeong stated. “Moreover, after adjusting for baseline scientific traits, evaluation confirmed that totally vaccinated sufferers had been at considerably decrease danger of requiring supplemental oxygen and of ICU admission than unvaccinated sufferers.”
Though further analysis will probably be wanted as totally different variants emerge, this research sheds mild on the scientific effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccination within the context of breakthrough infections.
Reference: “Imaging and Medical Options of COVID-19 Breakthrough Infections: A Multicenter Examine” 1 February 2022, Radiology.
Collaborating with Dr. Jeong had been Jong Eun Lee, M.D., Minhee Hwang, M.D., Yun-Hyeon Kim, M.D., Ph.D., Myung Jin Chung, M.D., Ph.D., Byeong Hak Sim, M.D., Kum Ju Chae, M.D., and Jin Younger Yoo, M.D.
Post a Comment