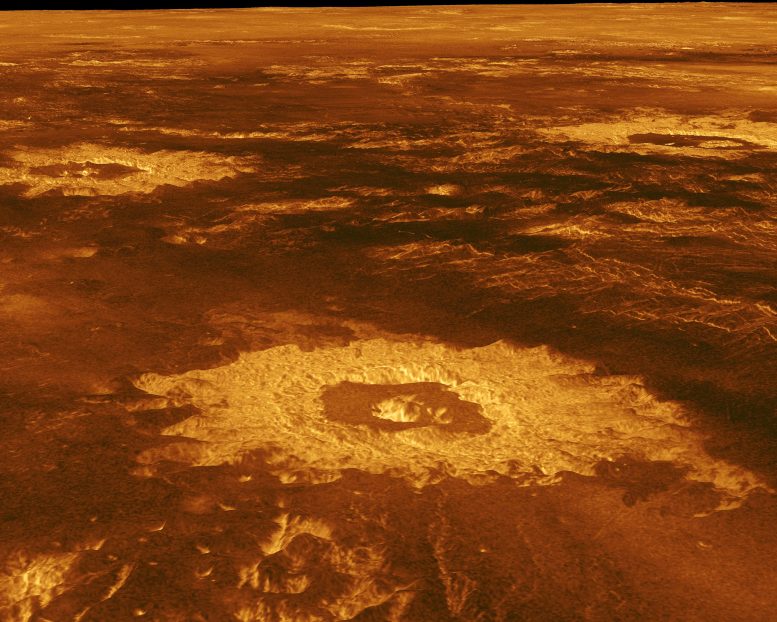

Floor of Venus, noticed by NASA’s Magellan (Magalhães) spacecraft, which mapped the complete floor of the planet utilizing radar within the early Nineties. Proof of volcanic exercise and affect craters is noticed. Credit score: NASA/JPL
Regardless of being near Earth and having almost the identical measurement, Venus is one other world. Beneath its thick mantle of acid sulfuric clouds, on the floor 460 levels Celsius are the rule. This temperature is saved by the greenhouse impact of a nearly carbon dioxide solely environment. Seventy kilometers above, one has to face up to a perpetual wind storm, the product of the so known as Venus superrotation.[1] A workforce of researchers led by the Instituto de Astrofísica e Ciências do Espaço (IAstro[2]) is even nearer to explaining the hyperlink between these infernal options.
A examine revealed within the journal Ambiance, led by Pedro Machado, of IAstro and Faculdade de Ciências da Universidade de Lisboa (Ciências ULisboa), presents essentially the most detailed and full set of measurements ever fabricated from the velocity of the wind in Venus parallel to the equator (zonal wind) and on the altitude of the underside of the cloud deck. One of many novel outcomes was the simultaneous measurement of the velocity of the wind at two completely different heights 20 kilometers aside. The workforce registered a distinction in wind velocity of about 150 kilometers per hour sooner on the prime of the clouds, which reinforces the speculation that power is being transferred from the warmth of the decrease layers to the final circulation of the environment.
“Winds speed up as we transfer upward to growing altitudes, however we don’t know but why,” says Pedro Machado. “This examine throws a lot mild on this, as a result of we managed to check the vertical element of the wind for the primary time, that's, how the power from the decrease and warmer layers is carried as much as the highest of the clouds, the place it results in the acceleration of the winds.”
The temperature on the floor stage reaches 460 levels Celsius and produces infrared radiation (named thermal emission), which heats the air and makes it transfer up. This radiation passes by essentially the most clear areas of the underside of the clouds, at roughly 48 kilometers above the floor. When Venus is noticed in infrared, we see this mild radiate from the warmth of the floor, and the silhouettes of the clouds, opaque and darkish, grow to be seen.
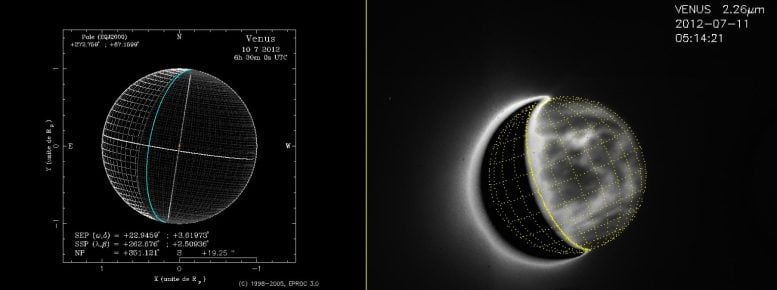
Georeferencing system utilized in observations of Venus from the bottom, the identical system utilized by house probes orbiting Venus. On the precise, this technique is utilized to an remark of the evening aspect of Venus (the day aspect on the left is masked in black). This method permits every pixel of the picture to be assigned a latitude and longitude with excessive precision. Credit score: Pedro Machado, et al. 2022
Observing and following the clouds at one hour intervals, and utilizing a monitoring approach improved by Javier Peralta, of Universidad de Sevilla and co-author of this examine, the researchers not directly computed the velocity of the wind pushing these clouds. This velocity is round 216 kilometers per hour on the backside of the cloud deck and at medium latitudes, reducing to half nearer to the poles.
This work was undertaken nearly from pole to pole on the nightside recovering photos the workforce captured within the infrared with the Telescopio Nazionale Galileo (TNG), in La Palma, Canary Islands, between July 11 and 13, 2012. On those self same days and in a coordinated technique, the Venus Categorical probe, from the European House Company (ESA), then orbiting the planet, noticed in seen mild the highest of the cloud deck, about 20 kilometers above, at 70 kilometers of altitude.
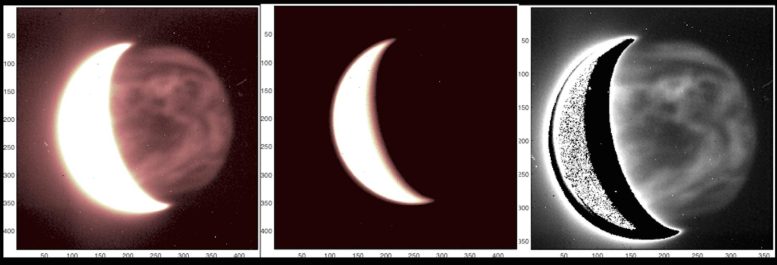
Close to-infrared picture of Venus with the Telescopio Nazionale Galileo, within the Canary Islands. The sequence demonstrates the method of subtracting the brightness of the dayside of Venus with a purpose to analyze the main points of the nightside. The darkish areas on the precise of the primary and third photos are clouds, whereas the sunshine areas are areas of decrease opacity by which thermal radiation (infrared) from the planet’s floor seems. Picture taken on July 11, 2012. Credit score: Pedro Machado, et al. 2022
Additionally monitoring these clouds, the researchers obtained speeds within the order of 360 kilometers per hour. Different research, and pc simulations point out that the velocity of the wind on the backside of the clouds is sort of fixed, with out vital variations between day and evening. The workforce was then capable of assume that the wind velocity registered at evening is identical on the decrease layers of the environment on the dayside.
The researchers thus collected, for the primary time, measurements of variations within the wind velocity between two altitudes from simultaneous observations, concluding that, on the dayside and in solely 20 kilometres, the wind parallel to the equator suffers a lift in velocity of about 150 kilometers per hour extra. The warmth from the floor could be the engine that sustains these cyclonic speeds of the winds on the prime of the clouds.
The precision of the info collected with telescopes on Earth is akin to the infrared cameras on house probes, because of the technique delivered to this examine by Javier Peralta. “We used the identical geographic referencing technique of the photographs obtained with house probes, which was developed by NASA and complemented by the European House Company,” Pedro Machado explains. “It’s as if the telescope right here on the bottom was a spaceship.”
With the success of this method, the workforce will now develop their analysis on the vertical element of the winds with new observations from the bottom coordinated with the probe at the moment within the orbit of Venus, the Akatsuki mission, of the Japanese house company JAXA. This examine demonstrates that the observations carried out from Earth complement the info being collected on the identical time by house missions. Regardless of the decrease spatial decision, because of the distance our planet is from Venus, it is generally potential to have a world view of our neighbor, which house probes, resulting from their orbits, usually are not at all times capable of get.
The subsequent ESA mission devoted to Venus is being deliberate, the EnVision. It is going to examine the floor of the planet and attempt to study its previous. Portugal is concerned within the mission, and Pedro Machado leads the Portuguese consortium, along with being the co-investigator answerable for one of many devices, an infrared spectrograph. “This work reveals the sort of science that might be enabled with the EnVision devices. We're already demonstrating the good relevance of the science that might be potential with this future mission.”
The expertise of IAstro and of the Portuguese researchers within the understanding of the dynamics of the environment of Venus will assist choose the wavelengths of sunshine wherein the EnVision mission will observe, in addition to essentially the most related atmospheric layers from a scientific viewpoint, thus contributing to the design and planning of the mission and its devices.
It's also anticipated that the nationwide participation within the mission will carry onboard the Portuguese trade in one other ESA worldwide undertaking, with the angle of the help of the Portuguese House Company, Portugal House.
- The super-rotation of the Venus’ environment is a phenomenon wherein, because of the winds parallel to the equator, or zonal winds, the environment circles the planet in simply little greater than 4 Earth days, that's, 60 occasions sooner than the rotation interval of the stable globe, which is 243 Earth days. Consequently, the conventional wind velocity relative to the bottom, at 70 kilometres of altitude, is round 360 kilometres per hour.
- The Instituto de Astrofísica e Ciências do Espaço (Institute of Astrophysics and House Sciences – IA) is the reference Portuguese analysis unit on this subject, integrating researchers from the College of Lisbon and the College of Porto, and encompasses a lot of the subject’s nationwide scientific output. It was evaluated as Wonderful within the final analysis of analysis and improvement models undertaken by Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia (FCT). IA’s exercise is funded by nationwide and worldwide funds, together with FCT/MCES (UIDB/04434/2020 and UIDP/04434/2020).
Reference: “Venus’ Cloud-Tracked Winds Utilizing Floor- and House-Primarily based Observations with TNG/NICS and VEx/VIRTIS” by Pedro Machado, Javier Peralta, José E. Silva, Francisco Brasil, Ruben Gonçalves and Miguel Silva, 17 February 2022, Ambiance.
DOI: 10.3390/atmos13020337

Post a Comment