NASA and China plan to mount crewed missions to Mars within the subsequent decade. Whereas this represents an incredible leap when it comes to house exploration, it additionally presents vital logistical and technological challenges. For starters, missions can solely launch for Mars each 26 months when our two planets are on the closest factors of their orbit to one another (throughout an “Opposition“). Utilizing present expertise, it will take six to 9 months to transit from Earth to Mars.
Even with nuclear-thermal or nuclear-electric propulsion (NTP/NEP), a one-way transit may take 100 days to succeed in Mars. Nonetheless, a workforce of researchers from Montreal’s McGill College assessed the potential of a laser-thermal propulsion system. Based on their examine, a spacecraft that depends on a novel propulsion system – the place lasers are used to warmth hydrogen gas – may scale back transit occasions to Mars to only 45 days!
The analysis was led by Emmanuel Duplay, a McGill graduate and present MSc Aerospace Engineering scholar at TU Delft. He was joined by Affiliate Professor Andrew Higgins and a number of researchers with the Division of Mechanical Engineering at McGill College. Their examine, titled “Design of a fast transit to Mars mission utilizing laser-thermal propulsion,” was lately submitted to the journal Astronomy & Astronomy.

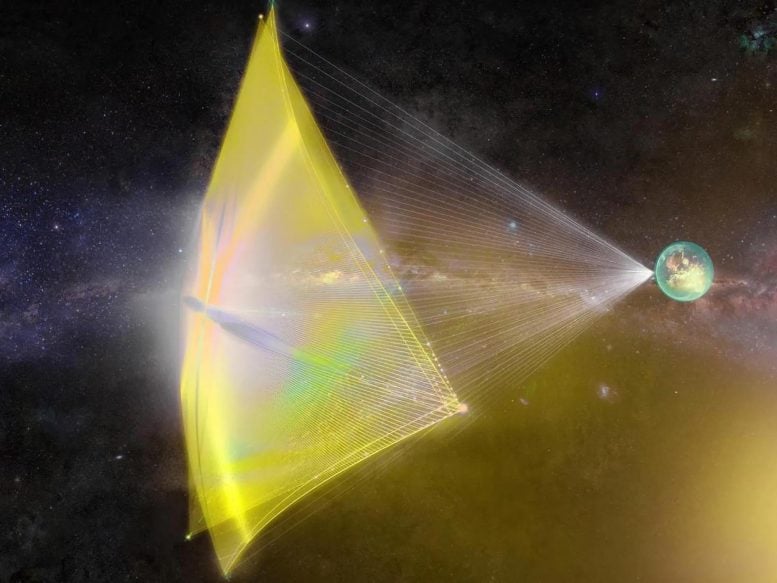
Artist’s impression of a directed-energy propulsion laser sail in motion. Credit score: Q. Zhang/deepspace.ucsb.edu
In recent times, directed-energy (DE) propulsion has been the topic of appreciable analysis and curiosity. Examples embody the Starlight program – often known as the Directed Vitality Propulsion for Interstellar Exploration (DEEP-IN) and Directed Vitality Interstellar Research (DEIS) packages – developed by Prof. Phillip Lubin and the UCSB Experimental Cosmology Group (ECG). As a part of NASA-funded analysis that started in 2009, these packages intention to adapt large-scale DE purposes for interstellar missions.
There’s additionally Breakthrough Starshot and Mission Dragonfly, each of which emerged from a design examine hosted by the Initiative for Interstellar Research (i4iS) in 2013. These ideas name for a gigawatt-power laser array to speed up a lightsail and a small spacecraft to a fraction of the pace of sunshine (aka. relativistic speeds) to succeed in close by star programs in many years, quite than centuries or millennia.
However whereas these ideas are interstellar in focus, Duplay and his colleagues explored the potential for an interplanetary idea. As Duplay defined to Universe In the present day by way of e mail:
“The final word software of directed-energy propulsion could be to propel a lightsail to the celebrities for true interstellar journey, a chance that motivated our workforce that did this examine. We have been eager about how the identical laser expertise may very well be used for fast transit within the photo voltaic system, which is able to hopefully be a nearer-term steppingstone that may exhibit the expertise.”
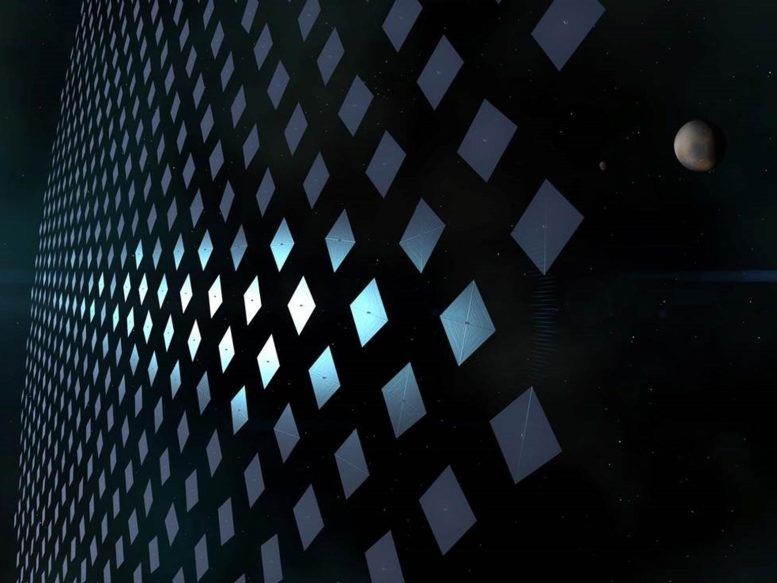
Mission Starshot, an initiative sponsored by the Breakthrough Basis, is meant to be humanity’s first interstellar voyage. Credit score: breakthroughinitiatives.org
Apart from laser sail propulsion, DE is being explored for a number of different house exploration purposes. This consists of energy beaming to and from spacecraft and permanently-shadowed habitats (e.g., the Artemis Program), communications, asteroid protection, and the seek for doable technosignatures. There’s additionally an idea for a laser-electric spacecraft being investigated by NASA and as a part of a collaborative examine between the UCSB ECG and MIT.
For this software, lasers are used to ship energy to photovoltaic arrays on a spacecraft, which is transformed to electrical energy to energy a Corridor-Impact Thruster (ion engine). This concept is much like a nuclear-electric propulsion (NEP) system, the place a laser array takes the place of a nuclear reactor. As Duplay defined, their idea is expounded however completely different:
“Our method is complimentary to those ideas, in that it makes use of the identical phased-array laser idea, however would use a way more intense laser flux on the spacecraft to straight warmth propellant, much like a large steam kettle. This allows the spacecraft to speed up quickly whereas it's nonetheless close to earth, so the laser doesn't must focus as far into house.
“Our spacecraft is sort of a dragster that accelerates in a short time whereas nonetheless close to earth. We consider we will even use the identical laser-powered rocket engine to carry the booster again into earth orbit, after it has thrown the principle automobile to Mars, enabling it to be shortly recycled for the following launch.”
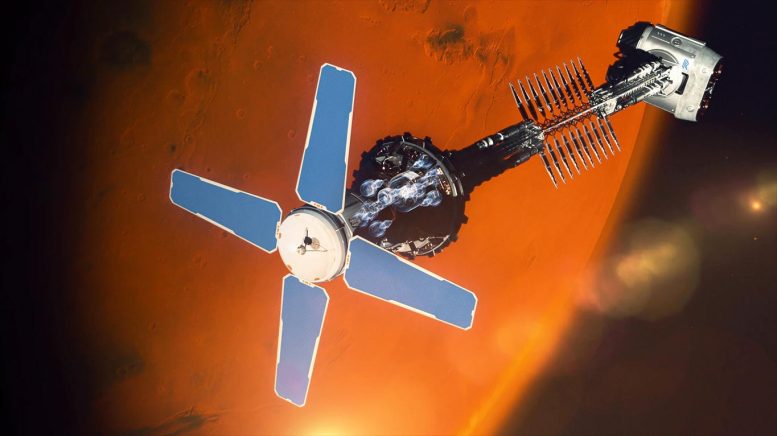

An artist’s idea for a nuclear rocket that might facilitate missions to Mars. Credit score: Rolls-Royce
On this respect, the idea proposed by Duplay and his colleagues is akin to a nuclear-thermal propulsion (NTP) system, the place the laser has taken the place of a nuclear reactor. Along with DE and hydrogen propellant, the mission structure for a laser-thermal spacecraft consists of a number of applied sciences from different architectures. As Duplay indicated, they embody:
“[A]rrays of fiber-optic lasers that act as a single optical component, inflatable house buildings that can be utilized to focus the laser beam when it arrives on the spacecraft into the heating chamber, and the event of high-temperature supplies that permit the spacecraft to interrupt towards the Martian ambiance upon arrival.”
This final component is crucial provided that there’s no laser array at Mars to decelerate the spacecraft as soon as it reaches Mars. “The inflatable reflector is a key from different directed-energy architectures: designed to be extremely reflective, it could maintain a better laser energy per unit space than a photovoltaic panel, making this mission possible with a modest laser array dimension in comparison with laser-electric propulsion,” added Duplay.
By combining these components, a laser-thermal rocket may allow very quick transits to Mars that might be as quick as six weeks – one thing that was thought-about doable solely with nuclear-powered rocket engines earlier than. Essentially the most rapid profit is that it presents an answer to the hazards of deep-space transits, like extended publicity to radiation and microgravity.
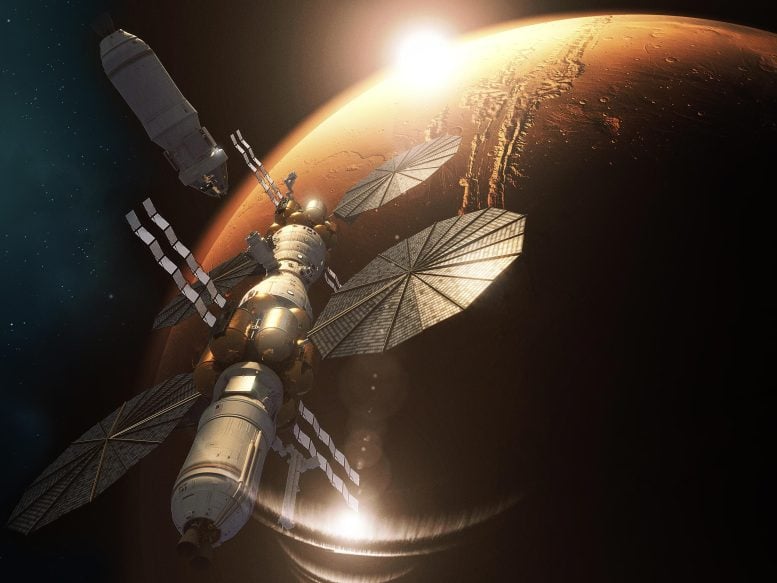

Artist’s impression of the Mars Base Camp in orbit round Mars. When missions to Mars start, one of many best dangers will likely be that posed by house radiation. Credit score: Lockheed Martin
On the identical time, says Duplay, the mission presents some hurdles since lots of the applied sciences concerned are bleeding-edge and haven't been examined simply but:
“The laser heating chamber is probably going essentially the most vital problem: Can we include hydrogen fuel, our propellant, as it's being heated by the laser beam to temperatures better than 10,000 Okay whereas on the identical time holding partitions of the chamber cool? Our fashions say that is possible, however experimental testing at full scale just isn't doable at current as a result of we have now not but constructed the 100 MW lasers wanted.”
Whereas a lot of the expertise on this proposed mission structure – and different related proposals – remains to be within the idea and improvement part, there isn't a doubt about their potential. Lowering the time it takes to get to Mars to a matter of weeks as an alternative of months will deal with two of the largest challenges for Mars missions – logistical and well being concerns.
Moreover, establishing a rapid-transit system between Earth and Mars will pace the creation of infrastructure between Earth and Mars. This might embody a Gateway-like house station in orbit of Mars, just like the Mars Base Camp proposed by Lockheed Martin, in addition to a laser array to decelerate incoming spacecraft. The presence of those services would additionally speed up plans to create a everlasting human presence on the floor. As Professor Higgins concluded:
“The Mars-in-45-days design examine that Emmanuel led was motivated by exploring different, near-term purposes of the phased array laser expertise that Philip Lubin’s group is growing. The flexibility to ship vitality deep into house by way of laser could be a disruptive expertise for propulsion and energy. Our examine examined the laser thermal method, which seems encouraging, however the laser expertise itself is the actual sport changer.”
Initially revealed on Universe In the present day.
Post a Comment