
A high-definition picture of the Mars Australe lava plain on the Moon taken by Japan’s Kaguya lunar orbiter in November 2007. Credit score: JAXA/NHK
The Moon is ready to realize yet another crater. A leftover SpaceX Falcon 9 higher stage will impression the lunar floor in early March, marking the primary time that a human-made particles merchandise unintentionally reaches our pure satellite tv for pc.
In 2015 the Falcon 9 positioned NOAA’s DSCOVR local weather observatory across the L1 Lagrange level, one in every of 5 such gravitationally-stable factors between Earth and the Solar. Having reached L1, round 1.5 million km from Earth, the mission’s higher stage ended up pointed away from Earth into interplanetary area.
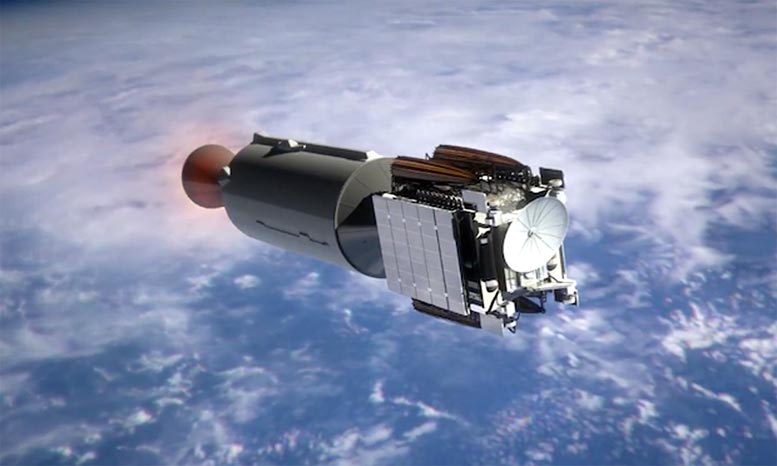

Artist’s impression of DSCOVR on the best way to L1 on its Falcon 9 higher stage in 2015. Credit score: SpaceX
This rendered a deorbit burn to eliminate it in our planet’s environment impractical, whereas the higher stage additionally lacked adequate velocity to flee the Earth-Moon system. As a substitute, it was left in a chaotic Solar-orbiting orbit close to the 2 our bodies.
Now credible public estimates forecast its impression with the Moon on March 4, 2022, at 12:25:39 UTC at some extent on the lunar far facet close to the equator. Observe-up observations ought to sharpen the accuracy of the forecast, however the roughly 3 ton, 15 m lengthy by 3 m vast higher stage is at the moment projected to hit at a pace about 2.58 km/s.
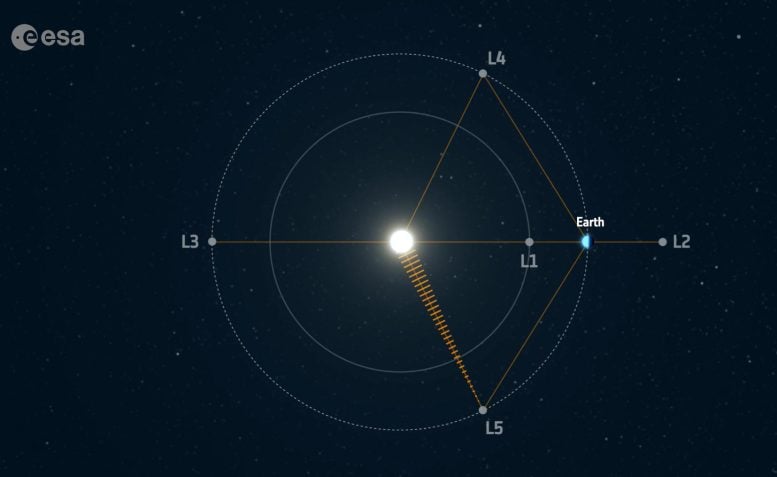
There are areas round a planet’s orbit the place the gravitational forces and the orbital movement of the Solar and planet work together to create a secure location, from the place a spacecraft can reside with little effort from the operators on the bottom to maintain it in place. These factors are referred to as Lagrangian or ‘L’ factors, after the 18th century Italian astronomer and mathematician Joseph-Louis Lagrange (born Giuseppe Luigi Lagrancia). Credit score: ESA
Scientifically important factors in area
The European Ariane 5 that lately delivered the James Webb Area Telescope to its observing level flew a mirror trajectory to that of the Falcon 9 – however the excellent news is that its higher stage has already evaded a comparable destiny because of a particularly developed and certified maneuver.
Europe’s Ariane 5 delivered the James Webb Area Telescope to L2, the second Solar-Earth Lagrange level – ‘behind’ as a substitute of in ‘entrance of’ our planet – however after separating from Webb the higher stage used all its remaining gas to flee the Earth-Moon system solely, placing it right into a secure heliocentric orbit.
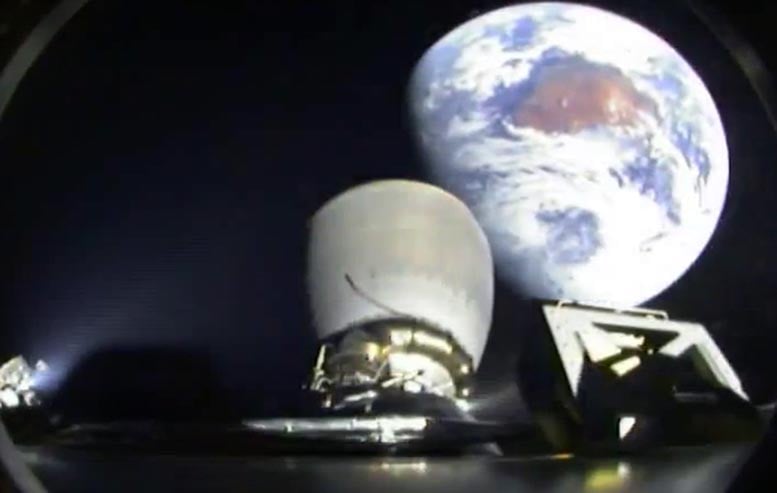

Trying again to Earth from DSCOVR’s Falcon 9 higher stage on the best way to L1. Simply earlier than sundown at 6:03pm ET on February 11, 2015, Falcon 9 lifted off from SpaceX’s Launch Complicated 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Drive Station, Florida, carrying the Deep Area Local weather Observatory (DSCOVR) satellite tv for pc on SpaceX’s first deep-space mission. Credit score: SpaceX
A short historical past of human-made Moon impacts
Human-made objects have deliberately impacted the Moon earlier than, beginning as early because the Nineteen Fifties, together with Apollo higher levels used to induce ‘moonquakes’ for floor seismometers.
In 2009 NASA crashed its LCROSS mission into the Moon, revealing water within the ensuing particles plume, with the LADEE spacecraft doing the identical on the lunar farside in 2013. ESA’s Good-1 spacecraft was crashed into the Moon in 2006, the topic of a worldwide observing marketing campaign.
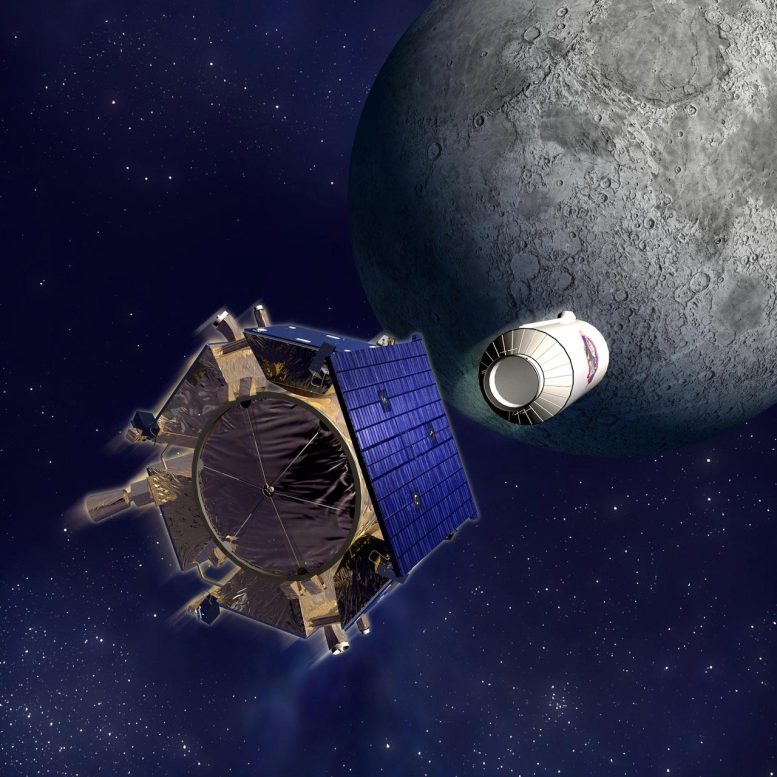

In 2009 NASA’s LCROSS mission deployed a Centaur higher stage to deliberately impression the Moon earlier than occurring to crash into the lunar floor itself. The ensuing particles plumes have been noticed from Earth, revealing water ice and different volatiles. Credit score: NASA
“This forthcoming Falcon 9 impression is slightly past our ordinary space of curiosity, as a result of we're primarily targeted on the particles inhabitants in highly-trafficked low-Earth orbits, as much as 2000 km altitude, in addition to geosynchronous orbits round 35 000 km away,” explains Tim Flohrer of ESA’s Area Particles Workplace.
“Our colleagues within the ESA Planetary Defence Workplace peer additional into area, nevertheless. They use telescopes across the globe to trace Close to-Earth asteroids, and generally observe human-made objects as effectively. Extending our personal remit into the ‘cislunar’ area between Earth and the Moon has been mentioned, because of the rising use of the scientifically important Solar-Earth Lagrange factors in coming years.”
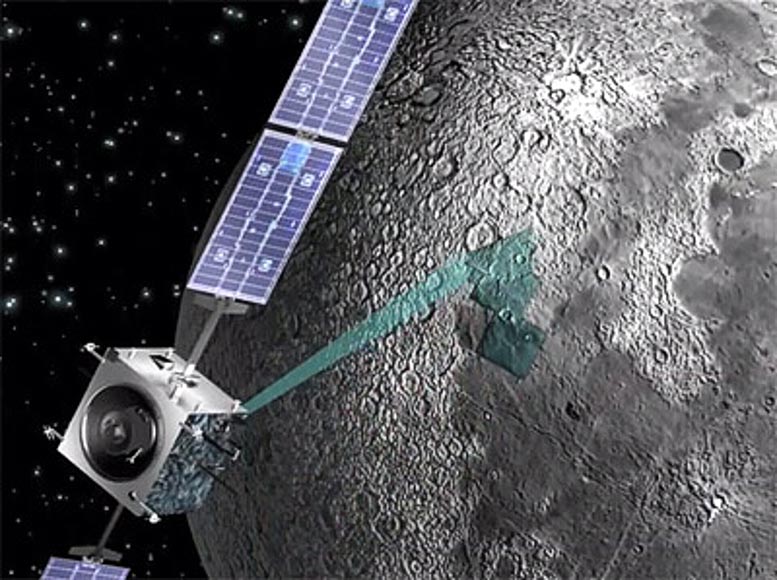

This illustration reveals ESA’s SMART-1 spacecraft making scientific observations in orbit across the Moon. SMART-1 was launched in September 2003 and can conclude its mission by a small lunar impression on September 3, 2006. Credit score: ESA – C. Carreau
Detlef Koschny, heading ESA’s Planetary Defence Workplace, provides: “We use telescopic observations to pinpoint the orbits, primarily of pure objects within the area surrounding Earth. Sometimes, we additionally choose up man-made objects far-off from the Earth, akin to lunar exploration spacecraft remnants, and objects coming back from Lagrange factors.”
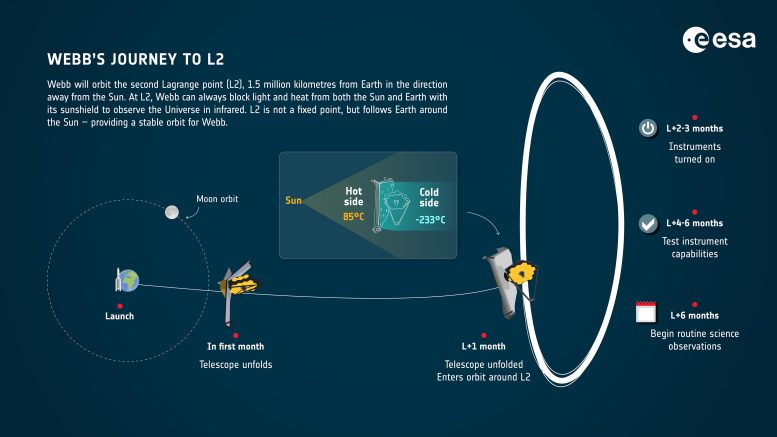
Webb will orbit the second Lagrange level (L2), 1.5 million kilometers from Earth within the path away from the Solar. There, its sunshield can all the time block mild and warmth from each the Solar and Earth from reaching its telescope and devices. L2 isn't a hard and fast level, however follows Earth across the Solar. Credit score: ESA
For worldwide spacefarers, no clear pointers exist in the mean time to manage the disposal at finish of life for spacecraft or spent higher levels despatched to Lagrange factors. Doubtlessly crashing into the Moon or returning and burning up in Earth’s environment have up to now been probably the most simple default choices.
“The upcoming Falcon 9 lunar impression illustrates effectively the necessity for a complete regulatory regime in area, not just for the economically essential orbits round Earth but additionally making use of to the Moon,” says Holger Krag, Head of ESA’s Area Security Program.
“It could take worldwide consensus to ascertain efficient rules, however Europe can actually paved the way.”
All of the launchers developed by ESA over the last decade – Vega, Ariane 6 and Vega C – incorporate a built-in reignition functionality, which ensures the protected return to Earth for atmospheric burn-up of their higher levels.

Since March 2017, the NELIOTA undertaking has been monitoring the darkish facet of the Moon for flashes of sunshine attributable to tiny items of rock hanging the Moon’s floor. This sequence of 12 consecutive frames reveals a brilliant flash detected on 4 frames throughout observations on 1 March 2017. The crimson arrows level to the situation of the impression flash, close to the sting of the body. Credit score: NELIOTA undertaking
Assessing lunar impression danger
Area rocks hit the Moon on a regular basis. Researchers are taken with quantifying the frequency of those pure lunar impacts. Utilizing a system developed by an ESA contract, the Greek NELIOTA undertaking (Close to-Earth object Lunar Impacts and Optical TrAnsients) detects flashes of sunshine attributable to small our bodies hanging the Moon’s floor, significantly throughout its shadowed face. NELIOTA can decide the temperature of those impression flashes in addition to their brightness. From this, the impacting mass might be estimated.
ESA’s Area Security program is on this analysis as a manner of assessing the variety of incoming objects ranging in measurement from tens of centimeters to meters throughout. That is helpful as a result of the exact variety of objects on this vary isn't recognized very effectively.
This analysis may also be beneficial for future lunar colonists. One of many risks they could face is small meteoroids doing harm to their infrastructure – NELIOTA outcomes are serving to to quantify the hazard. With out an environment to expend such our bodies, it's probably that future everlasting lunar constructions can be underground, to supply shielding in opposition to impacts in addition to area radiation.


Post a Comment