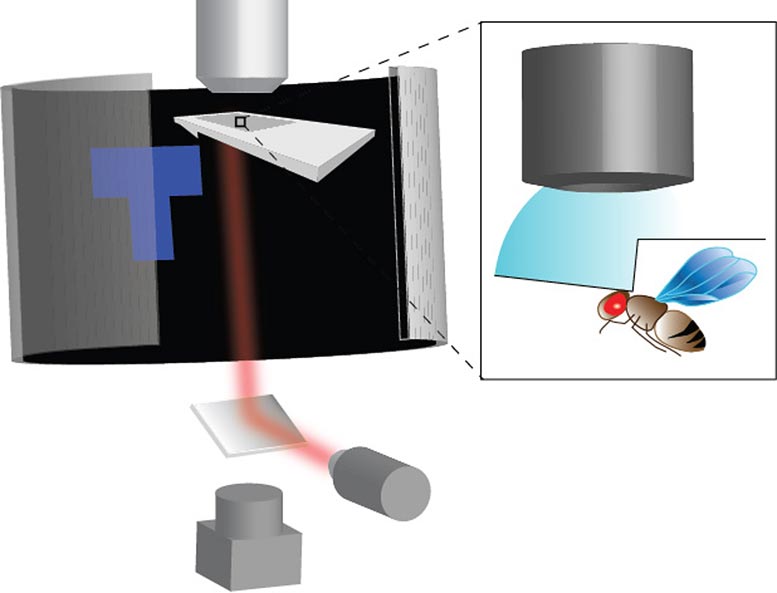
A digital actuality enviornment was coupled with in vivo fluorescence mind exercise imaging to look at the neural dynamics of mind buildings implicated in studying and reminiscence formation throughout conditioning. Credit score: Dhruv Grover, UC San Diego KIBM
Immersive digital actuality and real-time mind exercise imaging showcase Drosophila’s capabilities of consideration, working reminiscence, and consciousness.
As they annoyingly buzz round a batch of bananas in our kitchens, fruit flies seem to have little in widespread with mammals. However as a mannequin species for science, researchers are discovering rising similarities between us and the minuscule fruit-loving bugs.
In a brand new examine, researchers on the College of California San Diego’s Kavli Institute for Mind and Thoughts (KIBM) have discovered that fruit flies (Drosophila melanogaster) have extra superior cognitive talents than beforehand believed. Utilizing a custom-built immersive digital actuality setting, neurogenetic manipulations and in vivo real-time brain-activity imaging, the scientists introduced new proof on February 16, 2022, within the journal Nature of the exceptional hyperlinks between the cognitive talents of flies and mammals.

Researchers created a panoramic digital actuality enviornment the place flies had been conditioned to affiliate the picture of an upright “T” with a destructive warmth stimulus and an inverted “T” with out warmth. Credit score: Dhruv Grover, UC San Diego KIBM
The multi-tiered method of their investigations discovered consideration, working reminiscence, and acutely aware awareness-like capabilities in fruit flies, cognitive talents usually solely examined in mammals. The researchers had been capable of watch the formation, distractibility, and eventual fading of a reminiscence hint of their tiny brains.
“Regardless of an absence of apparent anatomical similarity, this analysis speaks to our on a regular basis cognitive functioning—what we take note of and the way we do it,” mentioned examine senior creator Ralph Greenspan, a professor within the UC San Diego Division of Organic Sciences and affiliate director of KIBM. “Since all brains developed from a typical ancestor, we will draw correspondences between fly and mammalian mind areas based mostly on molecular traits and the way we retailer our recollections.”
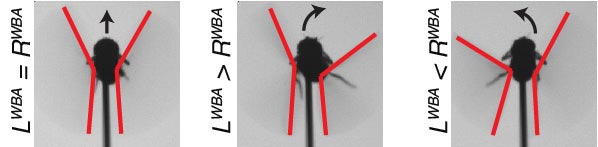
Fly wingbeats had been imaged and analyzed in real-time (200 Hz) to find out in the event that they flew straight (left), turned clockwise (middle), or counter-clockwise (proper). The digital actuality imagery was then rotated to mirror the orientation of the flying fly. Credit score: Dhruv Grover, UC San Diego KIBM
To reach on the coronary heart of their new findings the researchers created an immersive digital actuality setting to check the fly’s conduct by way of visible stimulation and matched the displayed imagery with an infra-red laser as an averse warmth stimulus. The close to 360-degree panoramic enviornment allowed Drosophila to flap their wings freely whereas remaining tethered, and with the digital actuality consistently updating based mostly on their wing motion (analyzed in real-time utilizing high-speed machine-vision cameras) it gave the flies the phantasm of flying freely on the earth. This gave researchers the flexibility to coach and take a look at flies for conditioning duties by permitting the insect to orient away from a picture related to the destructive warmth stimulus and in the direction of a second picture not related to warmth.
They examined two variants of conditioning, one through which flies got visible stimulation overlapping in time with the warmth (delay conditioning), each ending collectively, or a second, hint conditioning, by ready 5 to twenty seconds to ship the warmth after displaying and eradicating the visible stimulation. The period in-between is taken into account the “hint” interval throughout which the fly retains a “hint” of the visible stimulus in its mind, a function indicative of consideration, working reminiscence and acutely aware consciousness in mammals.
The researchers additionally imaged the mind to trace calcium exercise in real-time utilizing a fluorescent molecule they genetically engineered into their mind cells. This allowed the researchers to report the formation and length of the fly’s residing reminiscence since they noticed the hint blinking on and off whereas being held within the fly’s short-term (working) reminiscence. In addition they discovered that a distraction launched throughout coaching—a delicate puff of air—made the visible reminiscence fade extra shortly, marking the primary time researchers have been capable of show such distractedness in flies and implicating an attentional requirement in reminiscence formation in Drosophila.
“This work demonstrates not solely that flies are able to this increased type of hint conditioning, and that the training is distractible similar to in mammals and people, however the neural exercise underlying these attentional and dealing reminiscence processes within the fly present exceptional similarity to these in mammals,” mentioned Dhruv Grover, a UC San Diego KIBM analysis college member and lead creator of the brand new examine. “This work demonstrates that fruit flies might function a robust mannequin for the examine of upper cognitive features. Merely put, the fly continues to amaze in how good it truly is.”
The scientists additionally recognized the world of the fly’s mind the place the reminiscence shaped and light—an space often known as the ellipsoid physique of the fly’s central advanced, a location that corresponds to the cerebral cortex within the human mind.
Additional, the analysis workforce found that the neurochemical dopamine is required for such studying and better cognitive features. The info revealed that dopamine reactions more and more occurred earlier within the studying course of, finally anticipating the approaching warmth stimulus.
The researchers are actually investigating particulars of how consideration is physiologically encoded within the mind. Grover believes the teachings realized from this mannequin system are prone to instantly inform our understanding of human cognition methods and neural problems that disrupt them, but additionally contribute to new engineering approaches that result in efficiency breakthroughs in synthetic intelligence designs.
Reference: “Differential mechanisms underlie hint and delay conditioning in Drosophila” by Dhruv Grover, Jen-Yung Chen, Jiayun Xie, Jinfang Li, Jean-Pierre Changeux and Ralph J. Greenspan, 16 February 2022, Nature.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-04433-6
The coauthors of the examine embody Dhruv Grover, Jen-Yung Chen, Jiayun Xie, Jinfang Li, Jean-Pierre Changeux and Ralph Greenspan (all affiliated with the UC San Diego Kavli Institute for Mind and Thoughts, and J.-P. Changeux additionally a member of the Collège de France).
Supporters of the analysis embody the Air Drive Workplace of Scientific Analysis (FA9550-14-1-0211 and FA9550-19-1-0280); the Mathers Basis (20154167); Nationwide Science Basis (1212778); the European Union’s Horizon 2020 Framework Programme for Analysis and Innovation (grant settlement 945539, Human Mind Venture SGA3); and a Kavli Institute for Mind and Thoughts Worldwide School award.
Post a Comment