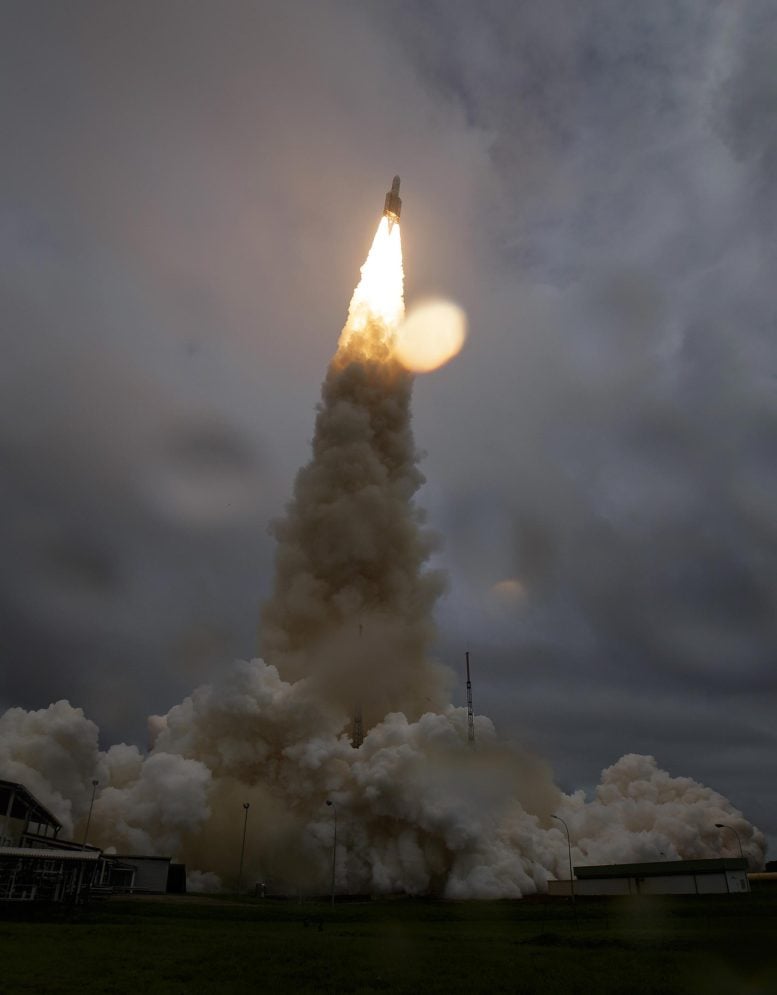

Arianespace’s Ariane 5 rocket launches with NASA’s James Webb House Telescope onboard December 25, 2021, from the ELA-3 Launch Zone of Europe’s Spaceport on the Guiana House Centre in Kourou, French Guiana. The James Webb House Telescope (generally known as JWST or Webb) will research each section of cosmic historical past—from inside our photo voltaic system to probably the most distant observable galaxies within the early universe. Credit score: NASA/Invoice Ingalls
On December 25, the biggest and strongest area telescope ever constructed by NASA was efficiently launched from Earth.
With unprecedented know-how, the James Webb House Telescope (JWST) will peer each close to and much, from the planets and our bodies in our photo voltaic system to the deepest reaches of area, the place the primary stars and galaxies fashioned greater than 13 billion years in the past. JWST has a mirror that's 21.3 toes (6.5 meters) throughout, making it bodily a lot bigger than the Hubble House Telescope and Hubble’s infrared sister telescope, the Spitzer House Telescope, operated by Caltech’s IPAC; it additionally has state-of-the-art photon detectors that register a wider vary of wavelengths and allow deeper and extra detailed views than Spitzer.
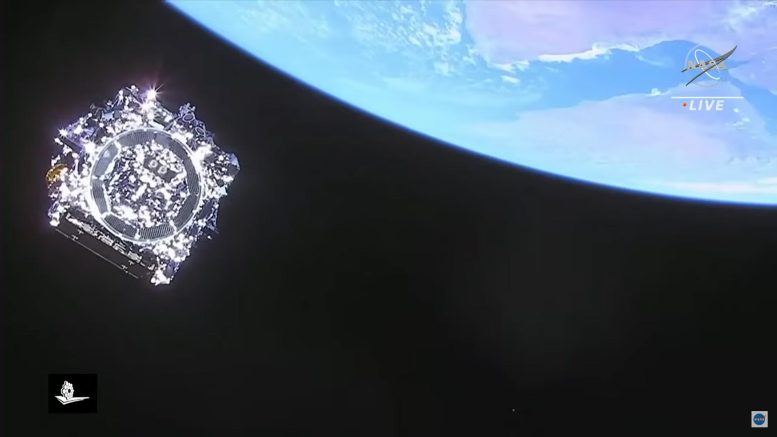

This picture was captured by the cameras on board the rocket’s higher stage because the telescope separated from it. Credit score: NASA
The launch represents a significant milestone for the challenge, which started development again in 2004. After launch, the telescope started a one-month odyssey to its observing perch past the moon, an orbital location in area known as the second Lagrange level or L2, which is about 1 million miles from Earth. As soon as there, JWST will full a six-month means of post-launch commissioning: it would unfold its mirrors, sun-shield, and different programs, and funky down, align, and calibrate.
“With the Mars missions, they've one thing they name the ‘seven minutes of terror’—the time window during which all the things has to occur exactly for the touchdown,” says Charles Beichman, senior college affiliate in astronomy and director of the NASA Exoplanet Science Institute at Caltech. “For JWST, it’s a type of 29 days of tension for all the things to occur completely.”
Beichman, whose major analysis focus is planets outdoors our photo voltaic system, or exoplanets, is a member of the science workforce for one among JWST’s devices, the Close to Infrared Digital camera (NIRCam). NIRCam will detect mild from the earliest stars and galaxies as they're within the means of formation in addition to from populations of stars in close by galaxies; younger stars in our Milky Approach galaxy; planets orbiting close by stars; and Kuiper Belt objects on the fringes of our photo voltaic system. Utilizing a set of coronagraphic masks developed on the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), which Caltech manages for NASA, to dam the brilliant glare of host stars, Beichman and the NIRCam workforce will seek for Saturn-sized exoplanets orbiting shiny, close by stars together with epsilon Eri and Vega.
NASA’s James Webb House Telescope. Credit score: NASA’s Goddard House Flight Middle Conceptual Picture Lab
NIRCam is one among 4 main JWST devices to look at the sky in numerous wavelengths. The opposite three are the Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI), which can observe the sunshine of distant galaxies, newly forming stars, and faintly seen comets in addition to objects within the Kuiper Belt; the Close to InfraRed Spectrograph (NIRSpec), which can carry out high-resolution spectroscopic observations of 100 cosmic objects concurrently; and the Advantageous Steering Sensor/Close to Infrared Imager and Slitless Spectrograph (FGS/NIRISS), which can conduct lower-resolution spectroscopic measurements to characterize the sunshine from the universe’s first stars in addition to exoplanets. The MIRI instrument was co-developed by JPL and the European House Company.
As soon as the telescope has completed its setup, Caltech researchers are already amongst these accepted to conduct observations. In collaboration with Professor of Astronomy Dimitri Mawet, who can be a JPL analysis scientist, and Caltech postdoctoral scholar Jorge Llop Sayson, Beichman and a global workforce of scientists have acquired approval to look at Alpha Centauri, the closest sun-like star to the earth, and decide if it has a planet orbiting round it—particularly, a fuel planet across the measurement of Jupiter. Future telescopes could possibly search for even smaller planets. Alpha Centauri is barely 4.3 light-years away from Earth.
One other main purpose of the telescope can be to characterize the composition and bodily properties of exoplanets. Together with a workforce led by graduate pupil Michael Zhang (MS ’18), Caltech Professor of Planetary Science Heather Knutson will use the MIRI instrument to review an ultra-hot planet smaller than the earth whipping round a close-by star in an eight-hour orbit.
Different observers are planning to make use of the MIRI instrument to look at Earth-sized planets within the TRAPPIST-1 system explored by the Spitzer House Telescope to characterize the atmospheric compositions of doubtless liveable Earth-like planets for the primary time. Total, Caltech and JPL exoplanet researchers, together with postdoctoral scholar Jessica Spake, visiting affiliate Renyu Hu, additionally of JPL, and JPL researcher Tiffany Kataria, have been collectively profitable at receiving JWST time to review exoplanets. Along with exoplanet research, Caltech scientists will use JWST to make cosmological measurements and research distant galaxies.
For instance, IPAC Employees Scientist Andreas Faisst and his workforce will use the NIRCam and MIRI devices to review a patch of sky nicknamed COSMOS. Few stars and no clouds of fuel in our galaxy block our view of this space; it was famously imaged by Hubble and Spitzer, and follow-up information from the Keck telescopes and different ground-based observatories have been obtained, to review how galaxies are influenced by each their basic bodily properties and the setting that surrounds them—a form of research of nature and nurture in galactic growth.
“JWST is anticipated to broaden on that work by offering imaging information at unprecedented spatial decision to review the construction of far-away galaxies and native locations of star formation in them, and to seek out and characterize the very first galaxies in our universe from greater than 13.5 billion years prior to now,” says Faisst. “As well as, it would revolutionize our understanding of the universe’s most large galaxies, and particularly reply the query why a few of them have stopped forming stars.”
Beichman emphasizes that JWST is transformative in its capabilities to review a variety of objects close to and much, from these in our photo voltaic system to probably the most distant elements of the universe. “It should serve the whole astronomical and photo voltaic system communities with unprecedented capabilities,” he says. “In comparison with any earlier telescope, ground- or space-based, JWST has a revolutionary capability to take each photos and spectra at infrared wavelengths.”
Post a Comment