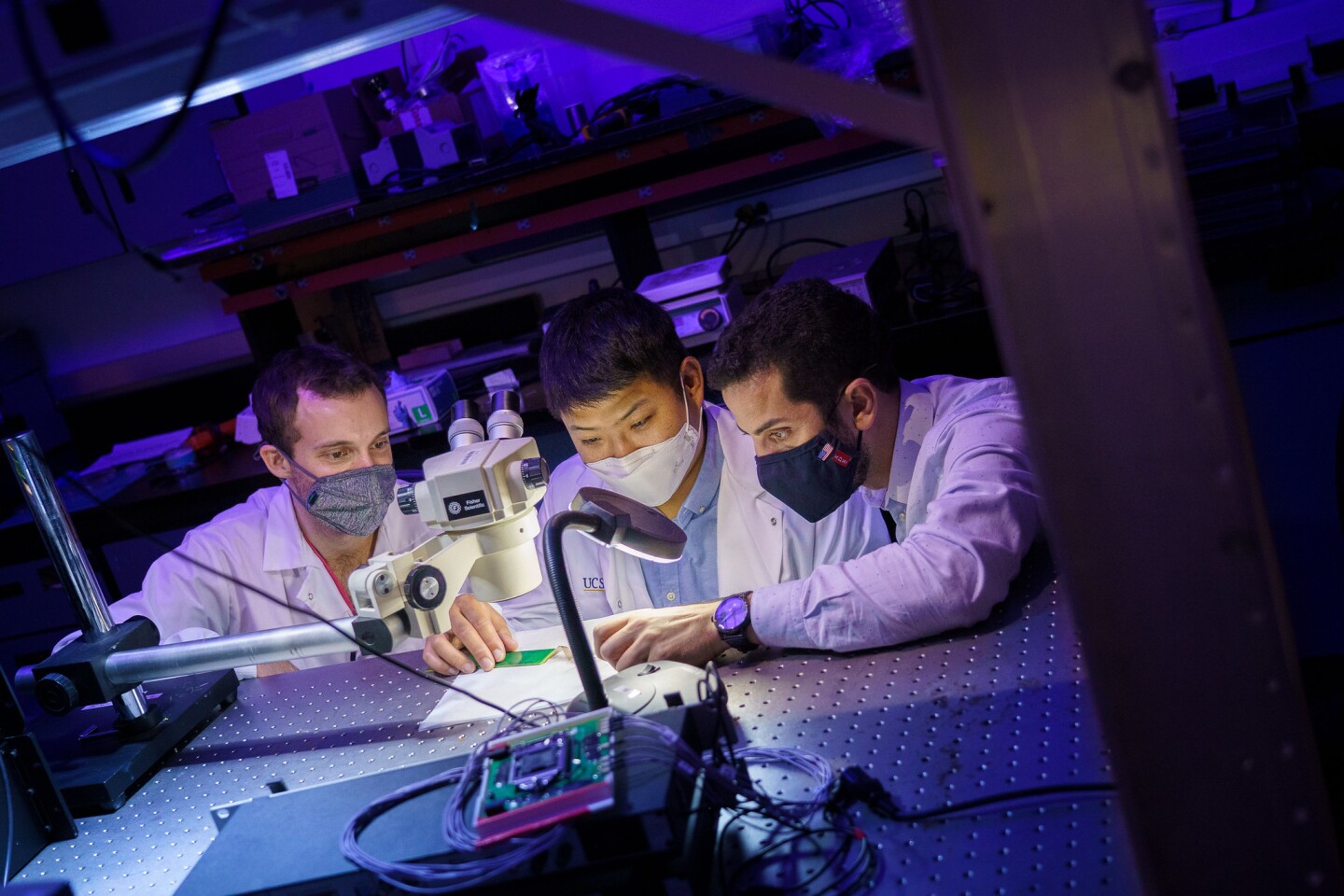
Scientists have developed a complicated new mind sensor that guarantees to take the security and effectivity of most cancers and epilepsy remedy into new terrain. The groundbreaking system is ready to document electrical alerts from the mind's floor in record-breaking decision, which may help neurosurgeons higher distinguish between wholesome and diseased tissue, and likewise deepen our understanding of how the human mind features.
The novel system is the handiwork of engineers on the College of California (UC) San Diego, and is what is called an electrocorticography (ECoG) sensor. These sensors are generally positioned on the uncovered mind cortex throughout surgical procedure to document the emanating electrical alerts, and reveal which areas of the mind tissue are lively. This could in flip allow neurosurgeons to securely take away mind tumors or sections of tissue the place epileptic seizures are originating, whereas leaving wholesome tissue untouched.
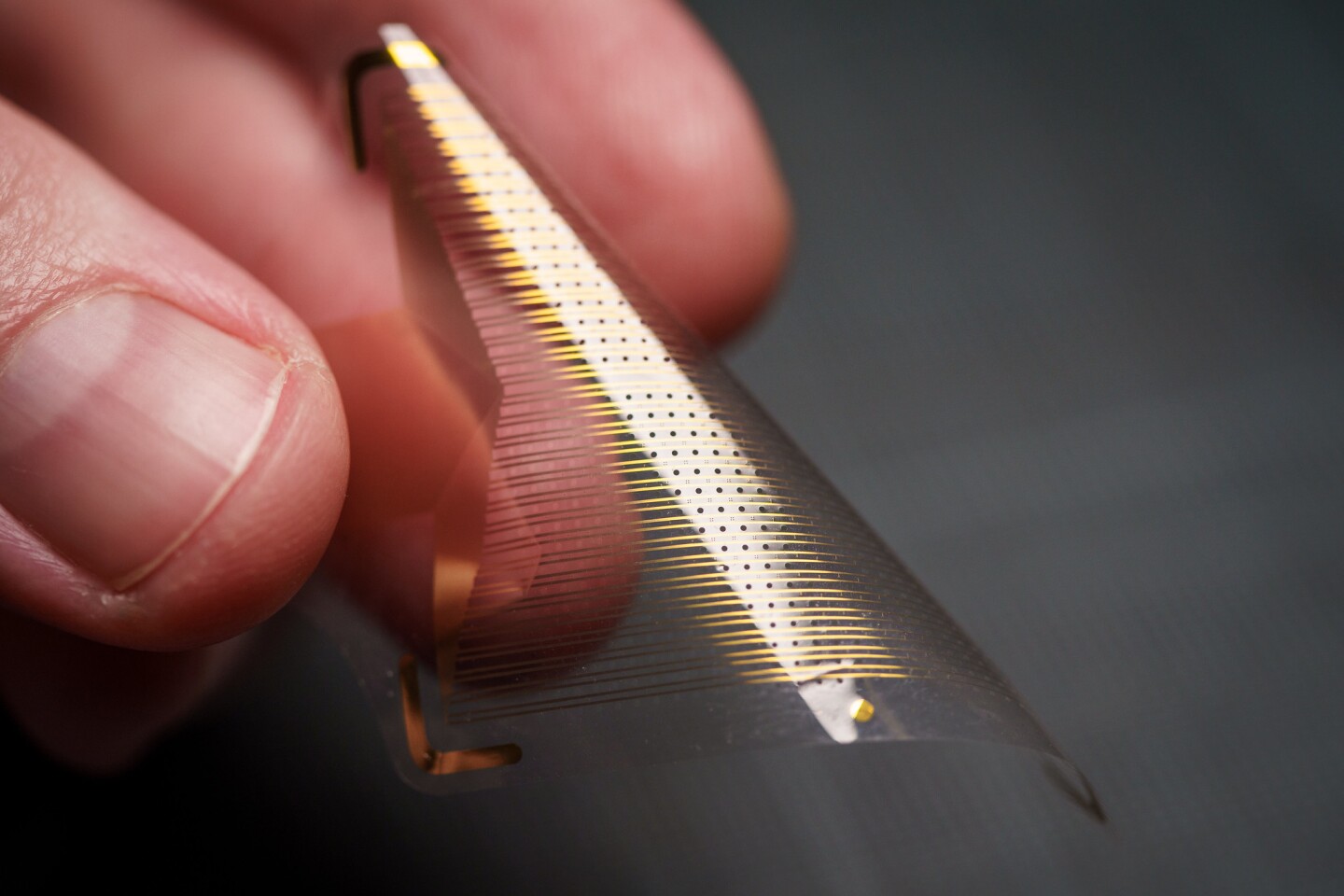
Having the ability to take action with better precision would due to this fact enhance the preservation of wholesome, functioning mind tissue, and that is the aim being pursued by the UC San Diego researchers. The ECoG gadgets in use at the moment are largely comprised of someplace between 16 and 64 sensors, although some research-grade examples can embrace as much as 256. The UC San Diego staff was in a position to produce ECoG grids with both 1,024 or 2,048 sensors, by way of some key engineering breakthroughs.

Clinically permitted ECoG grids characteristic sensors spaced a centimeter (0.4 in) aside, to keep away from problematic interference between them. The staff was in a position to produce grids with a far better density, by utilizing nanoscale platinum rods, which supply a better sensing floor space than the flat platinum sensors used at the moment, and permit for placement of 100 sensors per unit space as a substitute of 1, or 100 instances the spatial decision.
These rods are positioned one millimeter aside on a versatile, biocompatible materials referred to as parylene, with the ensuing sensor grids round 100 instances thinner than these used at the moment, at round 10 micrometers thick or round one tenth the scale of a human hair. This thinness and adaptability permits the sensor grid to higher adhere to the mind throughout refined actions, like these pushed by heartbeats, for instance, enabling nearer connection and clearer readings.
The scientists demonstrated the capabilities of their new sensor grids by way of a collection of experiments, which included utilizing the 1024-sensor model to straight document alerts from mind tissue of 19 sufferers present process surgical procedure. Additionally they used the sensors to map key areas of the mind in 4 totally different topics throughout motor duties, and likewise used them to map the cortical column of a rat mind for the primary time, one thing that had solely been achieved earlier than with a needle and electrical stimulation.
With a view to providing new choices for victims of treatment-resistant epilepsy and mind tumors, the researchers at the moment are working towards scientific approval of the know-how. Amongst their ambitions shifting ahead is the event of a wi-fi model, which could possibly be used for as much as 30 days at a time. As well as, the scientists hope that the know-how can additional our understanding of how the mind works by decoding its electrical alerts as sure duties are undertaken.
Monitoring and interpretation of those mind waves is a extremely lively area of examine that would have wide-ranging ramifications, from enabling thoughts management of prosthetic limbs, to treating reminiscence loss, to interacting with the digital world with out the necessity for smartphones. The staff explored this by utilizing the sensors to observe mind exercise related to finger sensation and hand greedy.
The video under gives an summary of the analysis, which was revealed within the journal Science Translational Drugs.
Supply: College of California San Diego
Post a Comment