
New technique from Clemson College researcher, enabled by Frontera supercomputer, helps clarify position of phonons in copper-based superconductivity.
Researchers have recognized about high-temperature superconducting copper-based supplies, or cuprates, because the Eighties. Beneath a sure temperature (roughly -130 diploma Celsius), electrical resistance vanishes from these supplies and magnetic flux fields are expelled. Nevertheless, the premise for that superconductivity continues to be debated and explored.
“It has been broadly accepted that conventional superconductors outcome from electrons interacting with phonons, the place the phonons pair two electrons as an entity and the latter can run in a cloth with out resistance,” stated Yao Wang, assistant professor of physics and astronomy at Clemson College.
Nevertheless, in cuprates, sturdy repulsions often called the Coulomb pressure had been discovered between electrons and had been believed to be the reason for this particular and high-temperature superconductivity.
Phonons are the vibrational vitality that come up from oscillating atoms inside a crystal. The conduct and dynamics of phonons are very totally different from these of electrons, and placing these two interacting items of the puzzle collectively has been a problem.
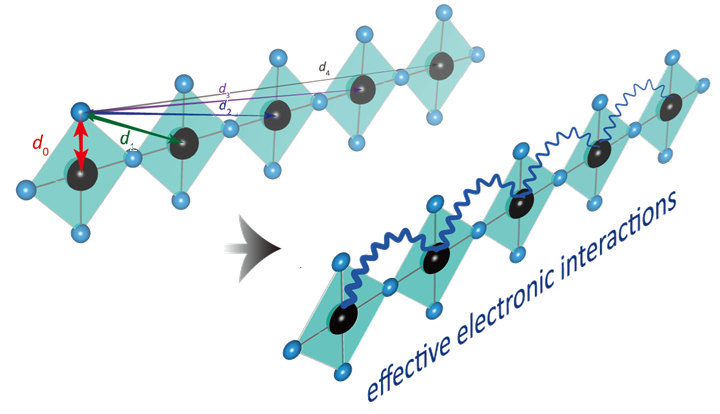
A conceptual illustration of the position of phonons in cuprate superconductivity. Credit score: Yao Wang, Clemson College
In November 2021, writing within the journal Bodily Evaluate Letters, Wang, together with researchers from Stanford College, offered compelling proof that phonons are in actual fact contributing to a key function noticed in cuprates, which can point out their indispensable contribution to superconductivity.
The examine innovatively accounted for the forces of each electrons and phonons collectively. They confirmed that phonons impression not solely electrons of their fast neighborhood, however act on electrons a number of neighbors away.
“An vital discovery on this work is that electron-phonon coupling generates non-local enticing interactions between neighboring electrons in house,” Wang stated. Once they used solely native coupling, they calculated a beautiful pressure an order of magnitude smaller than the experimental outcomes. “This tells us that the longer-range half is dominant and extends as much as 4 unit cells,” or neighboring electrons.
Wang, who led the computational facet of the venture, used the Nationwide Science Basis (NSF)-funded Frontera supercomputer on the Texas Superior Computing Heart (TACC) — the quickest tutorial system on the planet — to copy in simulation experiments carried out on the Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource and offered in Science in September 2021.
The outcomes relied not solely on Frontera’s super-fast parallel computing capabilities, however on a brand new mathematical and algorithmic technique that enables far better accuracy than earlier than.
The tactic, referred to as variational non-Gaussian precise diagonalization, can carry out matrix multiplications on billions of components. “It’s a hybrid technique,” Wang defined. “It treats the electron and phonon by two totally different approaches that may regulate with one another. This technique performs properly and might describe sturdy coupling with excessive precision.” The tactic improvement was additionally supported by a grant from NSF.
The demonstration of phonon-mediated attraction has a major impression even past the scope of superconductors. “Virtually, the outcomes imply we’ve discovered a option to manipulate Coulomb interactions,” Wang stated, referring to the attraction or repulsion of particles or objects due to their electrical cost.
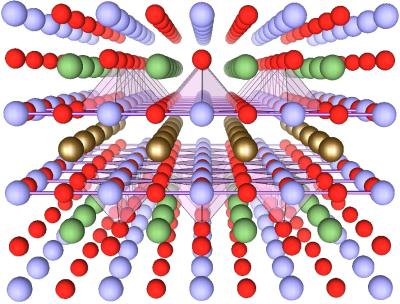
Crystallographic construction of a cuprate Yttrium barium copper oxide, which is a excessive temperature superconductor. Credit score: Julien Bobroff, LPS, Orsay, France
“If superconductivity comes from Coulomb forces solely, we can not simply manipulate this parameter,” he stated. “But when a part of the rationale comes from the phonon, then we are able to do one thing, as an example, placing the pattern on some substrate that may change the electron-phonon interplay. That offers us a path to design a greater superconductor.”
“This analysis provides new insights into the thriller of cuprate superconductivity that will result in increased temperature superconducting supplies and units,” stated Daryl Hess, a program director in Division of Supplies Analysis at NSF. “They might discover their method into future cell telephones and quantum computer systems. A journey began by human creativity, intelligent algorithms, and Frontera.”
Wang and collaborator Cheng-Chien Chen, from the College of Alabama, Birmingham, additionally utilized this new method and highly effective TACC supercomputers to review laser-induced superconductivity. They reported these findings in Bodily Evaluate X in November 2021. And dealing with a group from Harvard, Wang used TACC supercomputers to review the formation of Wigner crystals in work printed in Nature in June 2021.
As is the case in lots of fields of science, supercomputers are the one device that may probe the quantum conduct and clarify the underlying phenomena at play.
“In physics, we've got very lovely frameworks to explain an electron or an atom, however after we’re speaking about actual supplies with 1023 atoms, we don’t know how one can use these lovely frameworks,” Wang stated.
For quantum or correlated supplies particularly, physicists have had a tough time making use of ‘lovely’ idea. “So as a substitute, we use ugly idea – numerical simulation of the supplies. Though we don’t have a well-established quantum pc for now, utilizing classical high-performance computer systems, we are able to push the issue ahead so much. Finally, this can information experiment.”
Wang is presently working with IBM and IonQ to develop quantum algorithms to check on present and future quantum computer systems. “Supercomputing is our first step.”
With regards to huge future developments in know-how, Wang believes computational research, along side experiment, remark, and idea, will assist untangle mysteries and obtain sensible targets, like tunable superconducting supplies.
“A brand new algorithm could make a distinction. Extra numerical precision could make a distinction,” he stated. “Typically we don’t perceive the character of a phenomenon as a result of we didn’t look intently sufficient on the particulars. Solely if you push the simulation and zoom in to the nth digit will some vital facet of nature present up.”

Post a Comment