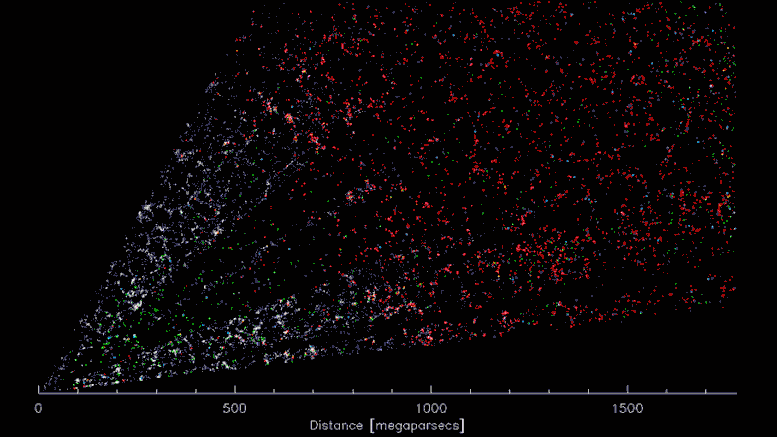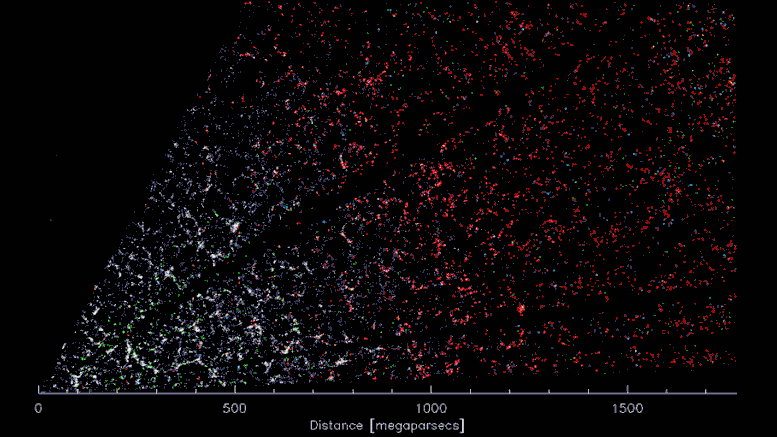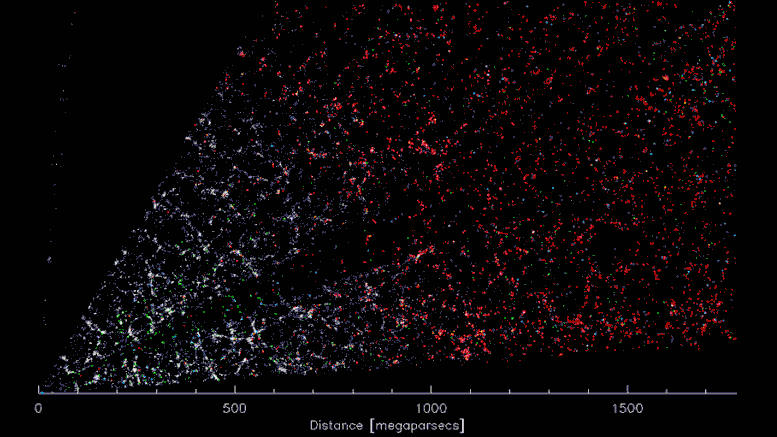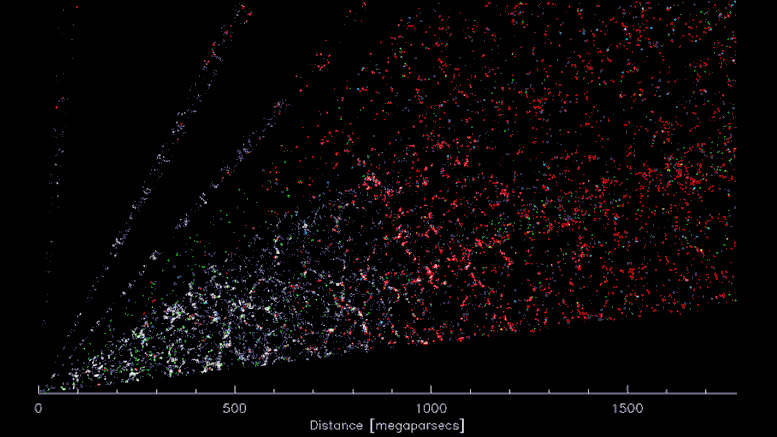
DESI’s three-dimensional “CT scan” of the Universe. The earth is within the decrease left, searching over 5 billion mild years within the course of the constellation Virgo. Because the video progresses, the attitude sweeps towards the constellation Bootes. Every coloured level represents a galaxy, which in flip consists of a whole lot of billions of stars. Gravity has pulled the galaxies right into a “cosmic internet” of dense clusters, filaments and voids. Credit score: D. Schlegel/Berkeley Lab utilizing knowledge from DESI
The Darkish Vitality Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) has capped off the primary seven months of its survey run by smashing by way of all earlier information for three-dimensional galaxy surveys, creating the biggest and most detailed map of the universe ever. But it’s solely about 10% of the way in which by way of its five-year mission. As soon as accomplished, that phenomenally detailed 3D map will yield a greater understanding of darkish vitality, and thereby give physicists and astronomers a greater understanding of the previous – and future – of the universe. In the meantime, the spectacular technical efficiency and actually cosmic achievements of the survey so far are serving to scientists reveal the secrets and techniques of essentially the most highly effective sources of sunshine within the universe.
DESI is a world science collaboration managed by the Division of Vitality’s Lawrence Berkeley Nationwide Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) with main funding for building and operations from DOE’s Workplace of Science.
DESI scientists are presenting the efficiency of the instrument, and a few early astrophysics outcomes, this week at a Berkeley Lab-hosted webinar referred to as CosmoPalooza, which may even characteristic updates from different main cosmology experiments.
“There may be loads of magnificence to it,” mentioned Berkeley Lab scientist Julien Man, one of many audio system. “Within the distribution of the galaxies within the 3D map, there are big clusters, filaments, and voids. They’re the largest buildings within the universe. However inside them, you discover an imprint of the very early universe, and the historical past of its enlargement since then.”
DESI has come a protracted method to attain this level. Initially proposed over a decade in the past, building on the instrument began in 2015. It was put in on the Nicholas U. Mayall 4-meter telescope at Kitt Peak Nationwide Observatory close to Tucson, Arizona. Kitt Peak Nationwide Observatory is a program of the Nationwide Science Basis’s (NSF) NOIRLab, which the Division of Vitality contracts with to function the Mayall Telescope for the DESI survey. The instrument noticed first mild in late 2019. Then, throughout its validation part, the coronavirus pandemic hit, shutting down the telescope for a number of months, although some work continued remotely. In December 2020, DESI turned its eyes to the sky once more, testing out its hardware and software program, and by Might 2021 it was prepared to begin its science survey.
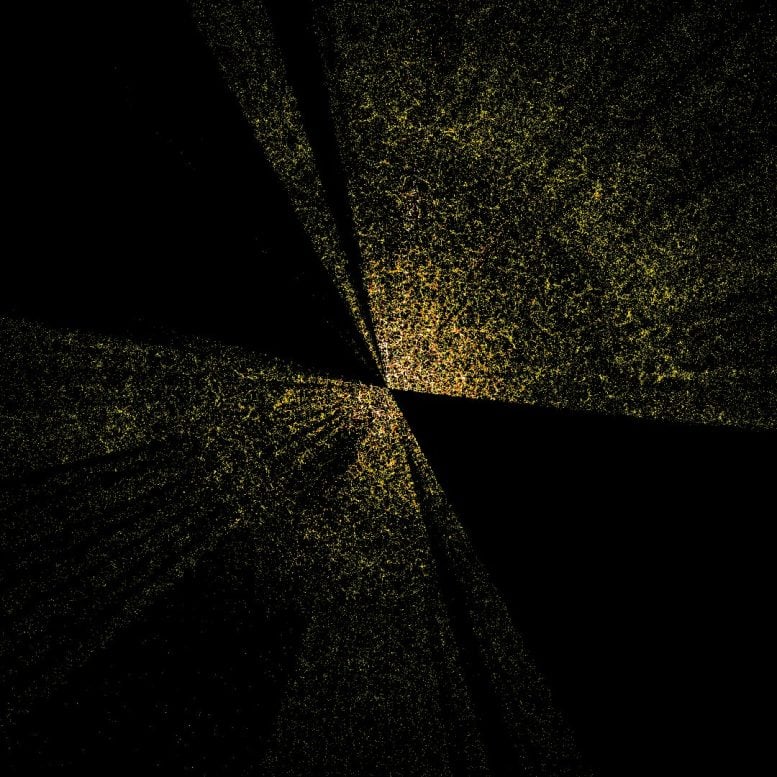

A slice by way of the 3-D map of galaxies from the primary few months of the Darkish Vitality Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI; proper). The earth is on the heart, with the furthest galaxies over 10 billion mild years away. Every level represents one galaxy. This 2D slice of the 3D DESI map reveals solely about 800,000 of the 7.5 million galaxies presently surveyed, which is itself only a fraction of the 35 million galaxies that can be within the closing map. Credit score: D. Schlegel/Berkeley Lab utilizing knowledge from DESI
However work on DESI itself didn’t finish as soon as the survey began. “It’s fixed work that goes on to make this instrument carry out,” mentioned physicist Klaus Honscheid of Ohio State College, co-Instrument Scientist on the undertaking, who will ship the primary paper of the CosmoPalooza DESI session. Honscheid and his staff make sure the instrument runs easily and routinely, ideally with none enter throughout an evening’s observing. “The suggestions I get from the evening observers is that the shifts are boring, which I take as a praise,” he mentioned.
However that monotonous productiveness requires extremely detailed management over every of the 5000 cutting-edge robots that place optical fibers on the DESI instrument, making certain their positions are correct to inside 10 microns. “Ten microns is tiny,” mentioned Honscheid. “It’s lower than the thickness of a human hair. And you must place every robotic to gather the sunshine from galaxies billions of light-years away. Each time I take into consideration this method, I'm wondering how may we presumably pull that off? The success of DESI as an instrument is one thing to be very happy with.”
Seeing darkish vitality’s true colours
That stage of accuracy is required to perform the first activity of the survey: accumulating detailed coloration spectrum photographs of hundreds of thousands of galaxies throughout greater than a 3rd of the complete sky. By breaking down the sunshine from every galaxy into its spectrum of colours, DESI can decide how a lot the sunshine has been redshifted – stretched out towards the purple finish of the spectrum by the enlargement of the universe through the billions of years it traveled earlier than reaching Earth. It's these redshifts that allow DESI see the depth of the sky.
The extra redshifted a galaxy’s spectrum is, typically, the farther away it's. With a 3D map of the cosmos in hand, physicists can chart clusters and superclusters of galaxies. These buildings carry echoes of their preliminary formation, after they have been simply ripples within the toddler cosmos. By teasing out these echoes, physicists can use DESI’s knowledge to find out the enlargement historical past of the universe.
A brand new quasar found utilizing DESI provides a glimpse of the universe because it was practically 13 billion years in the past, lower than a billion years after the Large Bang. That is essentially the most distant quasar found with DESI to this point, from a DESI very high-redshift quasar choice. The background reveals this quasar and its environment within the DESI Legacy imaging surveys. Credit score: Jinyi Yang, Steward Observatory/College of Arizona
“Our science purpose is to measure the imprint of waves within the primordial plasma,” mentioned Man. “It’s astounding that we are able to truly detect the impact of those waves billions of years later, and so quickly in our survey.”
Understanding the enlargement historical past is essential, with nothing lower than the destiny of the complete universe at stake. In the present day, about 70% of the content material of the universe is darkish vitality, a mysterious type of vitality driving the enlargement of the universe ever quicker. Because the universe expands, extra darkish vitality pops into existence, which quickens the enlargement extra, in a cycle that's driving the fraction of darkish vitality within the universe ever upwards. Darkish vitality will finally decide the future of the universe: will it increase perpetually? Will it collapse onto itself once more, in a Large Bang in reverse? Or will it rip itself aside? Answering these questions means studying extra about how darkish vitality has behaved up to now – and that’s precisely what DESI is designed to do. And by evaluating the enlargement historical past with the expansion historical past, cosmologists can test whether or not Einstein’s idea of basic relativity holds over these immense spans of house and time.
Black holes and brilliant galaxies
However understanding the destiny of the universe must wait till DESI has accomplished extra of its survey. Within the meantime, DESI is already driving breakthroughs in our understanding of the distant previous, greater than 10 billion years in the past when galaxies have been nonetheless younger.
“It’s fairly superb,” mentioned Ragadeepika Pucha, a graduate scholar in astronomy on the College of Arizona engaged on DESI. “DESI will inform us extra concerning the physics of galaxy formation and evolution.”
Pucha and her colleagues are utilizing DESI knowledge to grasp the habits of intermediate-mass black holes in small galaxies. Huge black holes are thought to inhabit the cores of practically each giant galaxy, like our personal Milky Manner. However whether or not small galaxies at all times include their very own (smaller) black holes at their cores remains to be not recognized. Black holes on their very own could be practically unattainable to seek out – but when they appeal to sufficient materials, they turn out to be simpler to identify. When gasoline, mud, and different materials falling into the black gap heats up (to temperatures hotter than the core of a star) on its method in, an energetic galactic nucleus (AGN) is shaped. In giant galaxies, AGNs are among the many brightest objects within the recognized universe. However in smaller galaxies, AGNs could be a lot fainter, and more durable to differentiate from new child stars. The spectra taken by DESI can assist remedy this drawback – and its large attain throughout the sky will yield extra details about the cores of small galaxies than ever earlier than. These cores, in flip, will give scientists clues about how brilliant AGNs shaped within the very early universe.
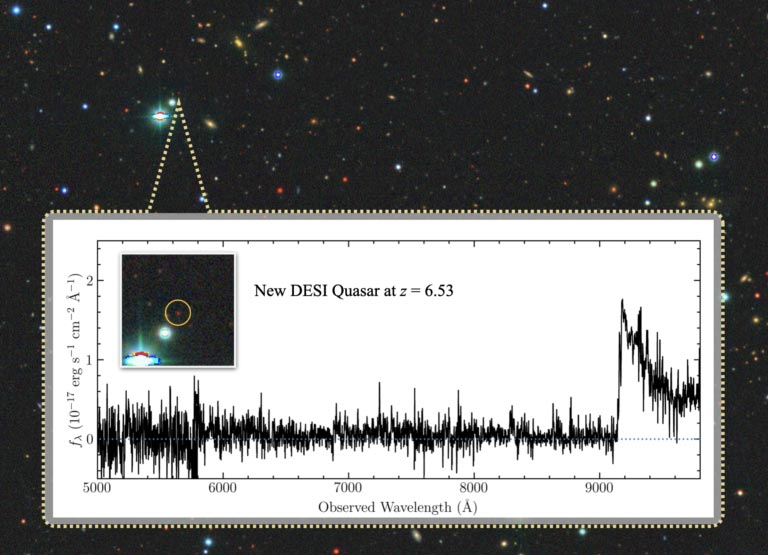
Quasars – a very brilliant number of galaxies – are among the many brightest and most distant objects recognized. “I like to think about them as lampposts, wanting again in time into the historical past of the universe,” mentioned Victoria Fawcett, an astronomy graduate scholar at Durham College within the UK. Quasars are wonderful probes of the early universe due to their sheer energy; DESI’s knowledge will return in time 11 billion years.
Fawcett and her colleagues are utilizing DESI knowledge to grasp the evolution of quasars themselves. It's thought that quasars begin out surrounded by an envelope of mud, which reddens the sunshine they provide off, just like the solar by way of haze. As they age, they drive off this mud and turn out to be bluer. However it has been onerous to check this idea, due to the paucity of information on purple quasars. DESI is altering that, discovering extra quasars than any prior survey, with an estimated 2.4 million quasars anticipated within the closing survey knowledge.
“DESI is absolutely nice as a result of it’s choosing up a lot fainter and far redder objects,” mentioned Fawcett. That, she provides, permits scientists to check concepts about quasar evolution that simply couldn’t be examined earlier than. And this isn’t simply restricted to quasars. “We’re discovering various unique techniques, together with giant samples of uncommon objects that we simply haven’t been capable of examine intimately earlier than,” Fawcett mentioned.
There’s extra to return for DESI. The survey has already cataloged over 7.5 million galaxies and is including extra at a fee of over one million a month. In November 2021 alone, DESI cataloged redshifts from 2.5 million galaxies. By the top of its run in 2026, DESI is predicted to have over 35 million galaxies in its catalog, enabling an unlimited number of cosmology and astrophysics analysis.
“All this knowledge is simply there, and it’s simply ready to be analyzed,” mentioned Pucha. “After which we'll discover a lot superb stuff about galaxies. For me, that’s thrilling.”
DESI is supported by the DOE Workplace of Science and by the Nationwide Vitality Analysis Scientific Computing Middle, a DOE Workplace of Science person facility. Further help for DESI is supplied by the U.S. Nationwide Science Basis, the Science and Applied sciences Amenities Council of the UK, the Gordon and Betty Moore Basis, the Heising-Simons Basis, the French Various Energies and Atomic Vitality Fee (CEA), the Nationwide Council of Science and Expertise of Mexico, the Ministry of Financial system of Spain, and by the DESI member establishments.
The DESI collaboration is honored to be permitted to conduct scientific analysis on Iolkam Du’ag (Kitt Peak), a mountain with specific significance to the Tohono O’odham Nation.

Post a Comment