Webb House Telescope adjusting orientation. Credit score: NASA’s Goddard House Flight Middle
Webb’s science objectives cowl a really broad vary of themes, and can sort out many open questions in astronomy. They are often divided into 4 primary areas:
Different worlds
Key questions: The place and the way do planetary methods kind and evolve?
Due to the quickly evolving area of exoplanet research – planets past our Photo voltaic System – Webb will have the ability to contribute to key questions resembling: is Earth distinctive? Do different planetary methods just like ours exist? Are we alone within the Universe?
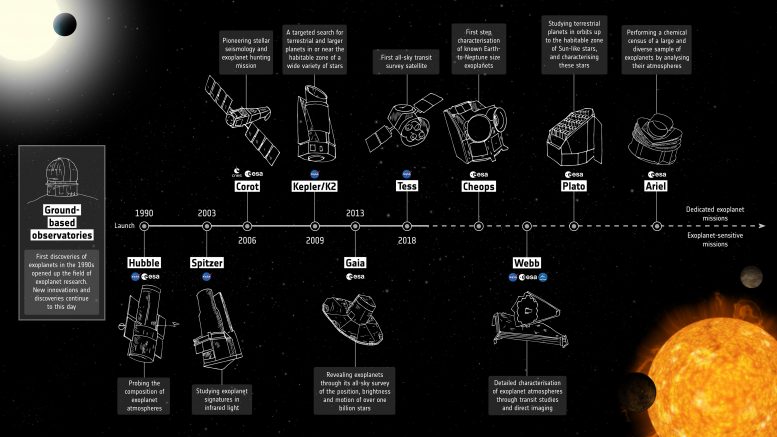
Exoplanet mission timeline. The primary discoveries of exoplanets within the Nineties, by ground-based observatories, fully modified our perspective of the Photo voltaic System and opened up new areas of analysis that continues right now. This infographic highlights the primary space-based contributors to the sphere, together with not solely exoplanet-dedicated missions, but in addition exoplanet-sensitive missions, previous, current, and future. Credit score: ESA
Webb will examine intimately the atmospheres of a large range of exoplanets. It's going to seek for atmospheres just like Earth’s, and for the signatures of key substances resembling methane, water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and sophisticated natural molecules, within the thrilling hope of discovering the constructing blocks of life. On this manner, Webb will complement ESA’s Atmospheric Distant-sensing Infrared Exoplanet Giant-survey (Ariel), an area telescope that can examine what exoplanets are fabricated from, how they shaped, and the way they evolve.
Nearer to dwelling, Webb will even examine the outer planets in our personal Photo voltaic System. Many exoplanets resemble Neptune and Uranus, thus finding out planets in our personal photo voltaic neighborhood can present new insights for higher understanding planetary formation on the whole.
The lifecycle of stars
Key questions: How and the place do stars kind? What determines what number of of them kind and their particular person plenty? How do stars die and the way does their demise affect the encompassing medium?
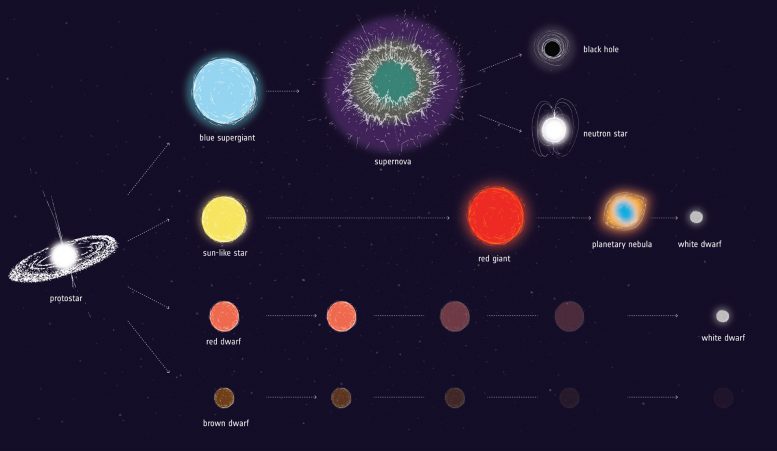
Artist impression of some attainable evolutionary pathways for stars of various preliminary plenty. Some proto-stars, brown dwarfs, by no means really get sizzling sufficient to ignite into fully-fledged stars, and easily cool off and fade away. Crimson dwarfs, the most typical kind of star, preserve burning till they've remodeled all their hydrogen into helium, turning right into a white dwarf. Solar-like stars swell into crimson giants earlier than puffing away their outer shells into colourful nebula whereas their cores collapse right into a white dwarf. Essentially the most huge stars collapse abruptly as soon as they've burned by way of their gas, triggering a supernova explosion or gamma-ray burst, and abandoning a neutron star or black gap. Credit score: ESA
Stars remodel the Universe’s easy components into heavier components and, by way of supernova explosions, unfold them all through the cosmos. Observing within the infrared a part of the spectrum, Webb shall be able to peering by way of the dusty envelopes round new-born stars. Its very good sensitivity will even enable astronomers to straight examine faint protostellar cores — the earliest phases of star start.
Webb will examine brown dwarfs, dim objects with plenty in between these of a planet and a star that aren't themselves huge sufficient to start out thermonuclear reactions and develop into absolutely fledged stars. Webb will decide how and why clouds of mud and fuel collapse into stars, or develop into fuel large planets or brown dwarfs.
Webb will even see probably the most huge stars explode as supernovae and go away behind extra clouds of mud and fuel, together with the dear heavy metals that enrich the cosmos to kind new generations of stars.
The early Universe
Key questions: What did the early Universe appear like? When did the primary stars and galaxies emerge?
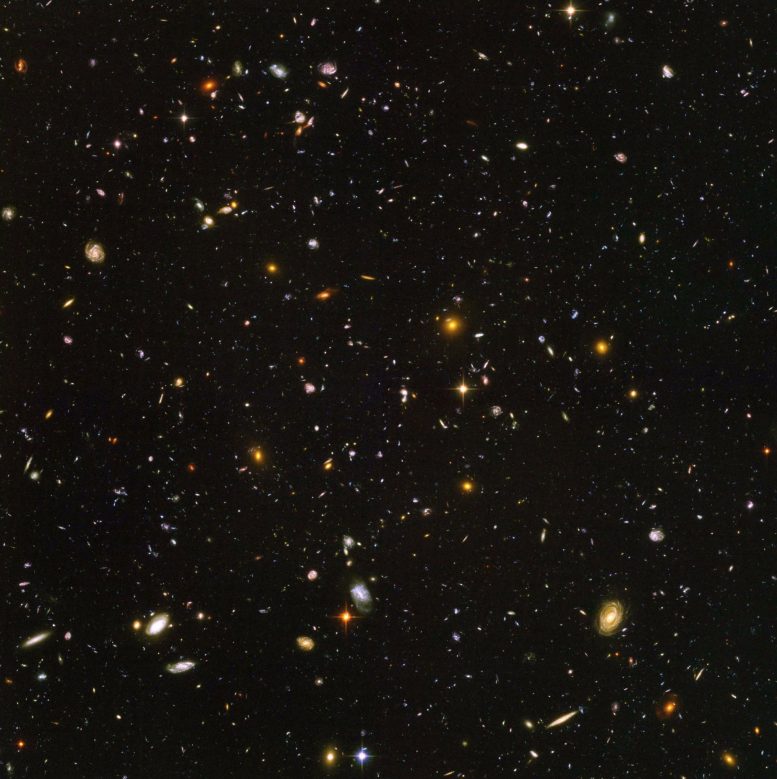

The Hubble Extremely Deep Subject of galaxies. A brand new examine of the star formation exercise in 179 of the galaxies on this picture together with many relationship from about six billion years in the past confirms an earlier puzzling end result: decrease mass galaxies are likely to make stars at a fee barely slower than anticipated. Credit score: NASA, ESA, and S. Beckwith (STScI) and the HUDF Workforce
For the primary time in human historical past we've got the chance to straight observe the primary stars and galaxies forming. Webb’s infrared imaginative and prescient makes it a robust time machine that can peer again over 13.5 billion years, pushing past the bounds of Hubble’s “deep fields” that confirmed us younger galaxies once they had been solely few hundred million years previous and had been small, compact, and irregular. Webb’s infrared sensitivity is not going to solely look again additional in time however will even reveal dramatically extra details about stars and galaxies within the early Universe. Whereas Hubble checked out ‘toddler’ galaxies, Webb will see the ‘child’ part!
Webb’s knowledge will even reply the compelling questions of how black holes shaped and grew early on, and what affect they'd on the formation and evolution of the early Universe.
Galaxies over time
Key questions: How did the primary galaxies evolve over time? What can we study darkish matter and darkish power?
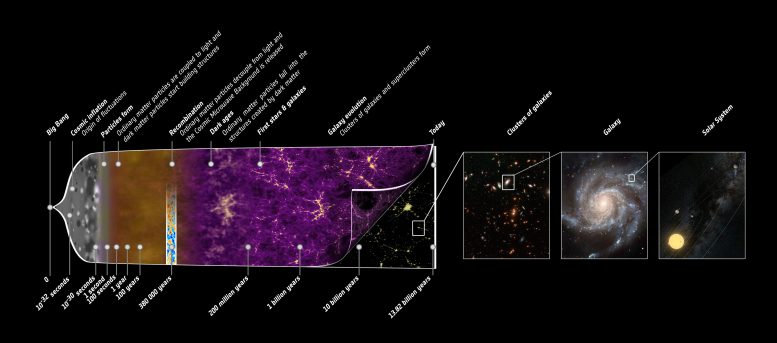
This illustration summarises the just about 14-billion-year lengthy historical past of our Universe. It exhibits the primary occasions that occurred between the preliminary part of the cosmos, the place its properties had been nearly uniform and punctuated solely by tiny fluctuations, to the wealthy number of cosmic buildings that we observe right now: stars and galaxies. The sequence of panels on the suitable facet of the illustration zooms into the cosmic large-scale construction to disclose first a cluster of galaxies, then a spiral galaxy just like our personal Milky Manner Galaxy, and at last, the Photo voltaic System. Credit score: ESA – C. Carreau
Immediately’s Universe is populated by galaxies – cosmic islands fabricated from a whole bunch of billions of stars. Their configurations and dimensions are vastly totally different, holding clues to how they shaped and developed. Within the first few billion years, the Universe was very dynamic, with galaxies present process merging occasions or being ripped aside, and had been peppered by supernova explosions from short-lived, huge stars. Working at infrared wavelengths, Webb can observe the majority of the sunshine from these primordial galaxies and reveal their dust-shrouded star start and matter-absorbing black holes.
Webb will even make clear darkish matter, the fabric that fills the cosmos however shouldn't be straight seen. On this manner, Webb will complement ESA’s Euclid mission that can map the geometry of the Universe and is particularly designed to check darkish power, the drive behind the Universe’s accelerating growth, and darkish matter.
Post a Comment