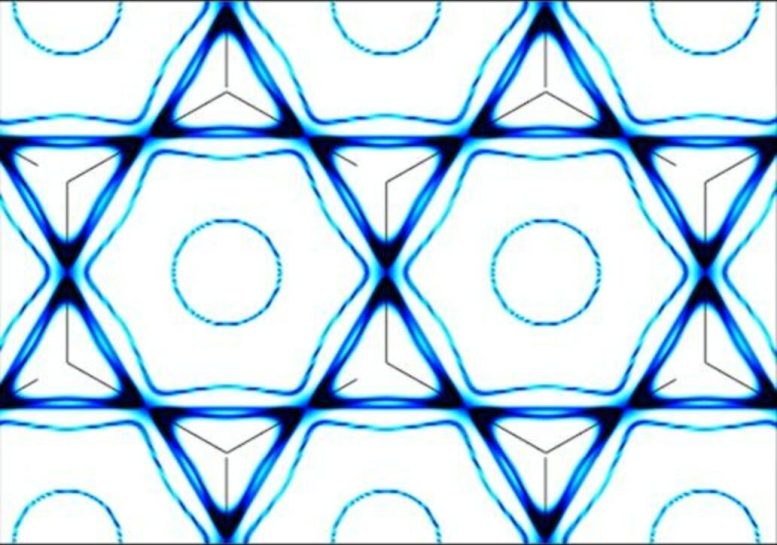
A visualization of the zero-energy digital states – also called a ‘Fermi floor’ – from the kagome materials studied by MIT’s Riccardo Comin and colleagues. Credit score: Comin Laboratory, MIT
Work will assist design of different uncommon quantum supplies with many potential functions.
MIT physicists and colleagues have found the “secret sauce” behind a number of the unique properties of a brand new quantum materials that has transfixed physicists attributable to these properties, which embrace superconductivity. Though theorists had predicted the explanation for the weird properties of the fabric, often known as a kagome steel, that is the primary time that the phenomenon behind these properties has been noticed within the laboratory.
“The hope is that our new understanding of the digital construction of a kagome steel will assist us construct a wealthy platform for locating different quantum supplies,” says Riccardo Comin, the Class of 1947 Profession Improvement Assistant Professor of Physics at MIT, whose group led the examine. That, in flip, may result in a brand new class of superconductors, new approaches to quantum computing, and different quantum applied sciences.
The work is reported within the January 13, 2022, on-line difficulty of the journal Nature Physics.
Classical physics can be utilized to clarify any variety of phenomena that underlie our world—till issues get exquisitely small. Sub-atomic particles like electrons and quarks behave in a different way, in methods which are nonetheless not totally understood. Enter quantum mechanics, the sphere that tries to clarify their habits and ensuing results.
The kagome steel on the coronary heart of the present work is a brand new quantum materials, or one which manifests the unique properties of quantum mechanics at a macroscopic scale. In 2018 Comin and Joseph Checkelsky, MIT’s Mitsui Profession Improvement Affiliate Professor of Physics, led the primary examine on the digital construction of kagome metals, spurring curiosity into this household of supplies. Members of the kagome steel household are composed of layers of atoms organized in repeating models much like a Star of David or sheriff’s badge. The sample can also be widespread in Japanese tradition, notably as a basketweaving motif.
“This new household of supplies has attracted numerous consideration as a wealthy new playground for quantum matter that may exhibit unique properties corresponding to unconventional superconductivity, nematicity, and charge-density waves,” says Comin.
Uncommon Properties
Superconductivity and hints of cost density wave order within the new household of kagome metals studied by Comin and colleagues have been found within the laboratory of Professor Stephen Wilson on the College of California, Santa Barbara, the place single crystals have been additionally synthesized (Wilson is a coauthor of the Nature Physics paper). The precise kagome materials explored within the present work is manufactured from solely three parts (cesium, vanadium, and antimony) and has the chemical system CsV3Sb5.
The researchers targeted on two of the unique properties that a kagome steel exhibits when cooled beneath room temperatures. At these temperatures, electrons within the materials start to exhibit collective habits. “They discuss to one another, versus shifting independently,” says Comin.

MIT graduate pupil Seongyong Lee? hundreds a pattern on the ARPES beamline of the Pohang Mild Supply in Korea, the place a key set of measurements have been taken for a examine of a kagome steel. Credit score: Seongyong Lee
One of many ensuing properties is superconductivity, which permits a fabric to conduct electrical energy extraordinarily effectively. In a daily steel, electrons behave very like individuals dancing individually in a room. In a kagome superconductor, when the fabric is cooled to three Kelvin (~-454 Fahrenheit) the electrons start to maneuver in pairs, like couples at a dance. “And all these pairs are shifting in unison, as in the event that they have been a part of a quantum choreography,” says Comin.
At 100 Kelvin, the kagome materials studied by Comin and collaborators displays one more unusual type of habits often known as cost density waves. On this case, the electrons prepare themselves within the form of ripples, very like these in a sand dune. “They’re not going wherever; they’re caught in place,” Comin says. A peak within the ripple represents a area that's wealthy in electrons. A valley is electron-poor. “Cost density waves are very completely different from a superconductor, however they’re nonetheless a state of matter the place the electrons have to rearrange in a collective, extremely organized trend. They type, once more, a choreography, however they’re not dancing anymore. Now they type a static sample.”
Comin notes that kagome metals are of nice curiosity to physicists partly as a result of they will exhibit each superconductivity and cost density waves. “These two unique phenomena are sometimes in competitors with each other, subsequently it's uncommon for a fabric to host each of them.”
The Secret Sauce?
However what's behind the emergence of those two properties? “What causes the electrons to begin speaking to one another, to begin influencing one another? That's the key query,” says first creator Mingu Kang, a graduate pupil within the MIT Division of Physics additionally affiliated with the Max Planck POSTECH Korea Analysis Initiative. That’s what the physicists report in Nature Physics. “By exploring the digital construction of this new materials, we found that the electrons exhibit an intriguing habits often known as an digital singularity,” Kang says. This specific singularity is called for Léon van Hove, the Belgian physicist who first found it.
The van Hove singularity includes the connection between the electrons’ vitality and velocity. Usually, the vitality of a particle in movement is proportional to its velocity squared. “It’s a basic pillar of classical physics that [essentially] means the larger the rate, the larger the vitality,” says Comin. Think about a Purple Sox pitcher hitting you with a quick ball. Then think about a child attempting to do the identical. The pitcher’s ball would damage much more than the child’s, which has much less vitality.
What the Comin group discovered is that in a kagome steel, this rule doesn’t maintain anymore. As a substitute, electrons touring with completely different velocities occur to all have the identical vitality. The result's that the pitcher’s quick ball would have the identical bodily impact as the child’s. “It’s very counterintuitive,” Comin says. He famous that relating the vitality to the rate of electrons in a stable is difficult and requires particular devices at two worldwide synchrotron analysis services: Beamline 4A1 of the Pohang Mild Supply and Beamline 7.0.2 (MAESTRO) of the Superior Mild Supply at Lawrence Berkeley Nationwide Lab.
Feedback Professor Ronny Thomale of the Universität Würzburg (Germany): “Theoretical physicists (together with my group) have predicted the peculiar nature of van Hove singularities on the kagome lattice, a crystal construction manufactured from corner-sharing triangles. Riccardo Comin has now supplied the primary experimental verification of those theoretical options.” Thomale was not concerned within the work.
When many electrons exist directly with the identical vitality in a fabric, they're recognized to work together far more strongly. On account of these interactions, the electrons can pair up and turn into superconducting, or in any other case type cost density waves. “The presence of a van Hove singularity in a fabric that has each makes excellent sense because the widespread supply for these unique phenomena” provides Kang. “Subsequently, the presence of this singularity is the ‘secret sauce’ that allows the quantum habits of kagome metals.”
The group’s new understanding of the connection between vitality and velocities within the kagome materials “can also be vital as a result of it should allow us to ascertain new design rules for the event of latest quantum supplies,” Comin says. Additional, “we now know learn how to discover this singularity in different programs.”
Direct Suggestions
When physicists are analyzing knowledge, more often than not that knowledge should be processed earlier than a transparent development is seen. The kagome system, nevertheless, “gave us direct suggestions on what’s occurring,” says Comin. “The perfect a part of this examine was having the ability to see the singularity proper there within the uncooked knowledge.”
Reference: “Twofold van Hove singularity and origin of cost order in topological kagome superconductor CsV3Sb5” by Mingu Kang, Shiang Fang, Jeong-Kyu Kim, Brenden R. Ortiz, Sae Hee Ryu, Jimin Kim, Jonggyu Yoo, Giorgio Sangiovanni, Domenico Di Sante, Byeong-Gyu Park, Chris Jozwiak, Aaron Bostwick, Eli Rotenberg, Efthimios Kaxiras, Stephen D. Wilson, Jae-Hoon Park and Riccardo Comin, 13 January 2022, Nature Physics.
DOI: 10.1038/s41567-021-01451-5
Further authors of the Nature Physics paper are Shiang Fang of Rutgers College; Jeung-Kyu Kim, Jonggyu Yoo, and Jae-Hoon Park of Max Planck POSTECH/Korea Analysis Initiative and Pohang College of Science and Expertise (Korea); Brenden Ortiz of the College of California, Santa Barbara; Jimin Kim of the Institute for Fundamental Science (Korea); Giorgio Sangiovanni of the Universität Würzburg (Germany); Domenico Di Sante of the College of Bologna (Italy) and the Flatiron Institute; Byeong-Gyu Park of Pohang Mild Supply (Korea); Sae Hee Ryu, Chris Jozwiak, Aaron Bostwick and Eli Rotenberg of Lawrence Berkeley Nationwide Laboratory; and Efthimios Kaxiras of Harvard College.
This work was funded by the Air Drive Workplace of Scientific Analysis, the Nationwide Science Basis, the Nationwide Analysis Basis of Korea, a Samsung Scholarship, a Rutgers Middle for Materials Concept Distinguished Postdoctoral Fellowship, the California NanoSystems Institute, the European Union Horizon 2020 program, the German Analysis Basis, and it used the assets of the Superior Mild Supply, a Division of Power Workplace of Science person facility.
Post a Comment