
Chromium defects in silicon carbide might present a brand new platform for quantum data.
Quantum computer systems could possibly remedy science issues which can be inconceivable for at the moment’s quickest typical supercomputers. Quantum sensors could possibly measure alerts that can't be measured by at the moment’s most delicate sensors. Quantum bits (qubits) are the constructing blocks for these units. Scientists are investigating a number of quantum techniques for quantum computing and sensing purposes. One system, spin qubits, relies on the management of the orientation of an electron’s spin on the websites of defects within the semiconductor supplies that make up qubits. Defects can embody small quantities of supplies which can be completely different from the primary materials a semiconductor is manufactured from. Researchers just lately demonstrated how one can make top quality spin qubits based mostly on chromium defects in silicon carbide.
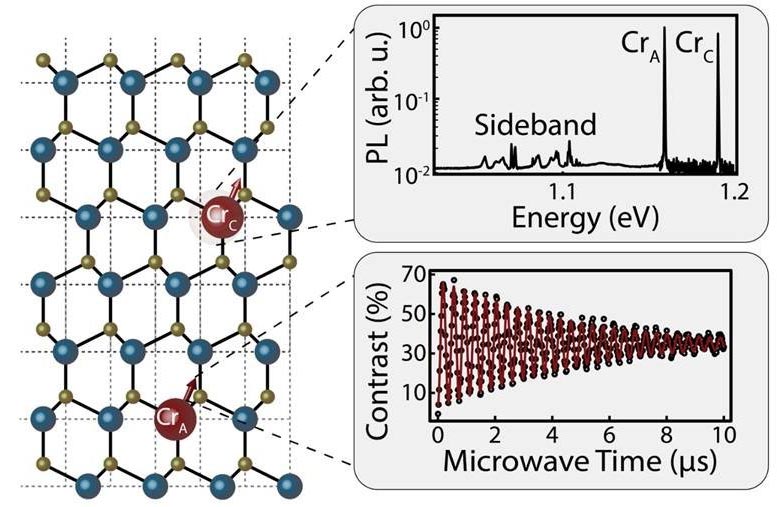
Chromium atoms implanted into silicon carbide function spin qubits. The atoms occupy two websites within the lattice, which emit mild at completely different wavelengths (prime proper). Oscillation in mild emission from these atoms is a quantum property (backside proper). Credit score: Picture courtesy of the College of Chicago
The Affect
Researchers are exploring chromium defects in silicon carbide as potential spin qubits. One benefit of those spin qubits is that they emit mild at wavelengths which can be suitable with telecommunications optical fibers. This implies they're probably helpful for quantum networks that make use of optical fiber to attach qubits. Sadly, points with the standard of supplies have restricted these spin qubits’ viability. Researchers just lately investigated new methods to make chromium defects in silicon carbide. They implanted chromium ions into silicon carbide then heated them to greater than 1600 levels Centigrade. This produced a cloth with spin defects which have a a lot increased qubit high quality. This end result might result in quantum communications that use at the moment’s semiconductor and fiber optic applied sciences.
Abstract
A rising variety of makes an attempt to commercialize quantum computer systems and quantum sensors have invested closely in particular sorts of qubits. Nonetheless, researchers should overcome various challenges to comprehend sensible quantum computing, communication, and sensing. For one, they want an improved understanding of the basic limits of assorted sorts of qubits. Spin qubits are significantly fascinating as a result of the digital spin can retailer data for a very long time in contrast with many different sorts of qubits. Furthermore, these qubits might be operated at room temperature, and they are often managed and skim utilizing optics. Optical interfaces will likely be necessary for the event of this expertise because the photons can carry quantum data lengthy distances utilizing present telecommunications fiber networks.
The analysis reported right here confirmed that chromium ions implanted in commercially accessible silicon carbide substrates, after which annealed at excessive temperature, produced single spin defects that can be utilized for spin qubits. The identical methodology might be used to create vanadium or molybdenum defects as researchers proceed the seek for the perfect qubit.
Reference: “Coherent management and high-fidelity readout of chromium ions in industrial silicon carbide” by Berk Diler, Samuel J. Whiteley, Christopher P. Anderson, Gary Wolfowicz, Marie E. Wesson, Edward S. Bielejec, F. Joseph Heremans and David D. Awschalom, 29 January 2020, npj Quantum Data.
DOI: 10.1038/s41534-020-0247-7
This mission was supported by the Division of Power (DOE) Workplace of Science, Primary Power Sciences, Supplies Sciences and Engineering Division. This work was carried out, partly, on the Middle for Built-in Nanotechnologies, a DOE Workplace of Science Person Facility.
Post a Comment