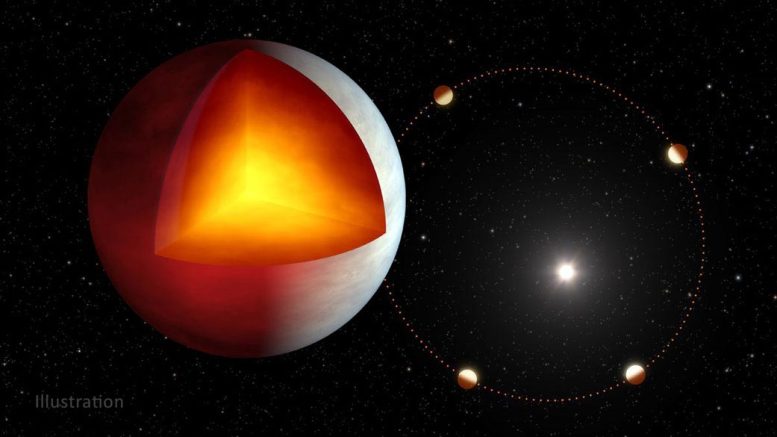
Planet XO-3b has an inside supply of warmth, presumably from tidal heating, which is brought on by the squeezing of the planet’s inside by the gravity of its guardian star. This may very well be elevated by the planet’s barely elliptical orbit (proven on the correct), which means it’s extra oval-shaped than round. Credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech
The infrared observatory could assist reply questions on planets outdoors our photo voltaic system, or exoplanets, together with how they kind and what drives climate of their atmospheres.
Two new research utilizing knowledge from NASA’s retired Spitzer Area Telescope make clear big exoplanets and brown dwarfs, objects that aren’t fairly stars however aren’t fairly planets both. Each research had been the main focus of digital information conferences hosted by the American Astronomical Society on January 13.
One investigation exhibits that the climate on brown dwarfs – which kind like stars however don’t have adequate mass to begin burning hydrogen of their cores as stars do – varies with age. Brown dwarfs and big exoplanets are comparable in diameter, mass, and composition, so understanding the atmospheric properties of 1 can present insights about these of the opposite.
The second research belongs to a physique of labor sizzling Jupiters – gasoline exoplanets that orbit extraordinarily near their guardian stars. How do these huge planets come to be, and will there be subclasses of sizzling Jupiters with totally different formation tales? To search for solutions, the research authors checked out exoplanet XO-3b, a uncommon instance of a sizzling Jupiter noticed whereas migrating nearer to its host star.
Exoplanet Analogs
Age usually brings stability in people, and that seems to be true for cosmic objects as properly. Johanna Vos, an astrophysicist on the American Museum of Pure Historical past in New York, will talk about a Spitzer survey printed within the Astrophysical Journal that discovered greater variability within the climate on younger brown dwarfs in comparison with outdated ones.
With regard to brown dwarfs, the phrase variability refers to short-term adjustments within the depth of various wavelengths of infrared mild coming from the item’s environment. Astronomers suppose these variations are brought on by clouds, which replicate and take in mild within the environment.
Excessive variability would possibly point out a serious atmospheric characteristic, maybe like Jupiter’s Nice Crimson Spot – a storm bigger than Earth that’s been swirling for tons of of years. It will possibly additionally point out a quickly altering environment, which might have a number of causes akin to main temperature variations within the environment or turbulence (typically brought on by highly effective winds).
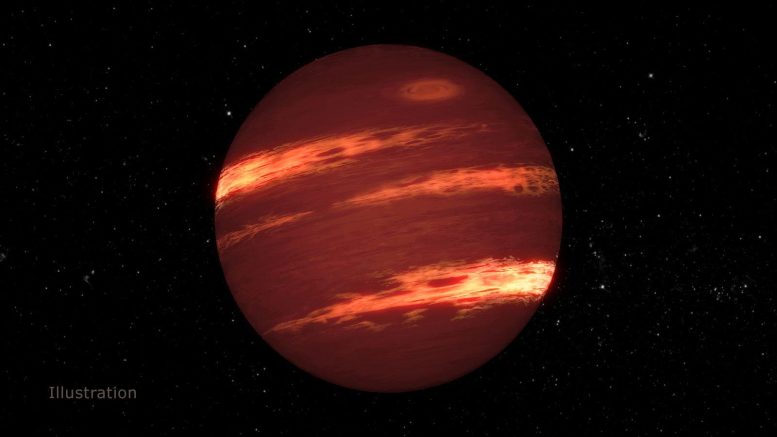

This illustration exhibits what clouds would possibly appear like within the environment of a brown dwarf. Utilizing NASA’s retired Spitzer Area Telescope, scientists had been in a position to detect clouds and different climate options in brown dwarf atmospheres. Credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/IPAC/T. Pyle
Evaluating the younger brown dwarfs to earlier Spitzer observations of older brown dwarfs, the authors discovered that the younger objects usually tend to present atmospheric variation. In addition they discovered that variations are bigger and extra dramatic in youthful brown dwarfs. Vos and her colleagues attribute the distinction to the truth that brown dwarfs are puffier after they’re younger however turn out to be extra compact as they age, which possible makes the environment seem extra uniform.
Younger brown dwarfs are comparable in diameter, mass, and composition to massive exoplanets primarily product of gasoline. However finding out massive exoplanets is sophisticated by the shut presence of their guardian stars: The companion irradiates the planet’s environment, which adjustments the temperature, and even the chemistry, and impacts the climate. The brilliant mild from the star additionally makes seeing the a lot fainter planet tougher.
Brown dwarfs, then again, can act as a form of management group and be noticed in isolation in area. The research’s authors plan to include the brand new discovering into fashions of how brown dwarf and big exoplanet atmospheres evolve with age.
Migrating Giants
Although sizzling Jupiters are probably the most studied kind of exoplanet, main questions stay about how they kind. For instance, do these planets take form removed from their guardian stars – at a distance the place it’s chilly sufficient for molecules akin to water to turn out to be strong – or nearer? The primary state of affairs matches higher with theories about how planets in our personal photo voltaic system are born, however what would drive a majority of these planets emigrate so near their guardian stars stays unclear.
Lisa Dang, an exoplanet scientist at McGill College in Montreal, and her colleagues used Spitzer knowledge to review an exoplanet named XO-3b, which has an eccentric (oval) orbit slightly than the round orbit of just about all different recognized sizzling Jupiters. The eccentric orbit signifies XO-3b could have lately migrated towards its guardian star; if that’s the case, it's going to ultimately settle right into a extra round orbit.
Observations by Gaia, an ESA (European Area Company) area observatory, and Spitzer each counsel the planet produces a few of its personal warmth, however scientists don’t know why. The Spitzer knowledge additionally offers a map of the placessnet’s local weather patterns. It’s attainable that the surplus heat is coming from the planet’s inside, by means of a professional referred to as tidal heating. The star’s gravitational squeeze on the planet oscillates because the irregular orbit takes the planet farther after which nearer to the star. The ensuing adjustments in inside strain produce warmth.
For Dang, an uncommon sizzling Jupiter offers a possibility to check concepts about which formation processes could produce sure traits in these exoplanets. For instance, may tidal heating in different sizzling Jupiters even be an indication of latest migration? XO-3b alone received’t remedy the thriller, however it serves as an essential check for rising concepts about these scorching giants.
Extra Concerning the Mission
Your complete physique of scientific knowledge collected by Spitzer throughout its lifetime is accessible to the general public through the Spitzer knowledge archive, housed on the Infrared Science Archive at IPAC at Caltech in Pasadena, California. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California managed the Spitzer Area Telescope mission for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington.
Science operations had been performed on the Spitzer Science Heart at IPAC. Spacecraft operations had been based mostly at Lockheed Martin Area in Littleton, Colorado.
Post a Comment