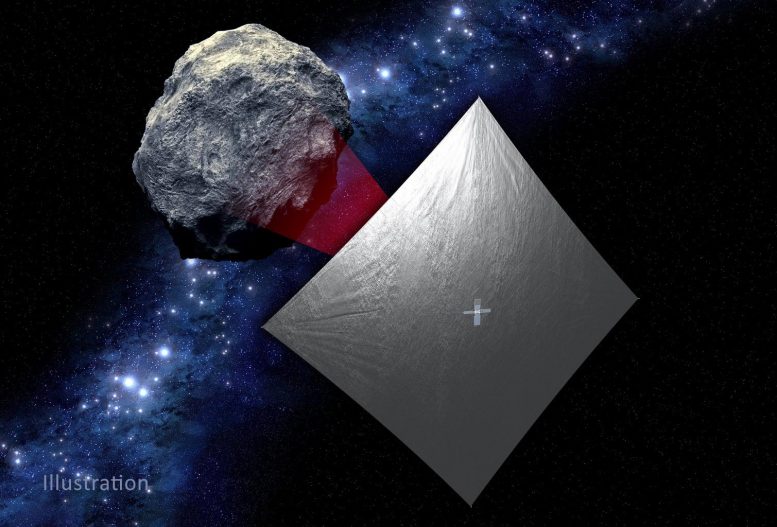
Illustration of NASA’s NEA Scout with the photo voltaic sail deployed because it flies by its asteroid vacation spot. Credit score: NASA
NEA Scout will go to an asteroid estimated to be smaller than a college bus – the smallest asteroid ever to be studied by a spacecraft.
Launching with the Artemis I uncrewed take a look at flight, NASA’s shoebox-size Close to-Earth Asteroid Scout will chase down what is going to turn into the smallest asteroid ever to be visited by a spacecraft. It's going to get there by unfurling a photo voltaic sail to harness photo voltaic radiation for propulsion, making this the company’s first deep house mission of its type.
The goal is 2020 GE, a near-Earth asteroid (NEA) that's lower than 60 ft (18 meters) in measurement. Asteroids smaller than 330 ft (100 meters) throughout have by no means been explored up shut earlier than. The spacecraft will use its science digicam to get a more in-depth look, measuring the article’s measurement, form, rotation, and floor properties whereas searching for any mud and particles that may encompass 2020 GE.
As a result of the digicam has a decision of lower than 4 inches (10 centimeters) per pixel, the mission’s science workforce will have the ability to decide whether or not 2020 GE is strong – like a boulder – or if it’s composed of smaller rocks and dirt clumped collectively like a few of its bigger asteroid cousins, similar to asteroid Bennu.
“Because of the discoveries of NEAs by Earth-based observatories, a number of targets had been recognized for NEA Scout, all inside the 16-to-100-foot [5-to-30-meter] measurement vary,” mentioned Julie Castillo-Rogez, the mission’s principal science investigator at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. “2020 GE represents a category of asteroid that we at the moment know little or no about.”
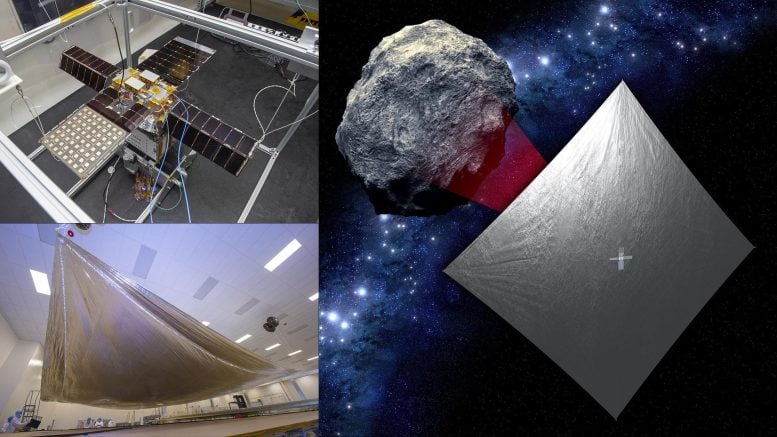
NEA Scout consists of a small, shoebox-sized CubeSat (high left) and a skinny, aluminum-coated photo voltaic sail concerning the measurement of a racquetball court docket (backside left). After the spacecraft launches aboard Artemis I, the sail will use daylight to propel the CubeSat to a small asteroid (as depicted in an illustration, proper). Credit score: NASA
2020 GE was first noticed on March 12, 2020, by the College of Arizona’s Catalina Sky Survey as a part of its seek for near-Earth objects for NASA’s Planetary Protection Coordination Workplace.
Developed beneath NASA’s Superior Exploration Programs Division by Marshall House Flight Middle in Huntsville, Alabama, and JPL, NEA Scout is a science and expertise demonstration mission that can improve the company’s understanding of small NEAs. Utilizing a six-unit CubeSat type issue, it can journey as certainly one of 10 secondary payloads aboard the highly effective House Launch System (SLS) rocket, which can launch no sooner than March 2022 at NASA’s Kennedy House Middle in Florida. NEA Scout will then be deployed from a dispenser connected to the adapter ring that connects the rocket and Orion spacecraft.
The mission will act as a nimble scout for future human and robotic missions that will make the most of asteroid assets – and can achieve essential planetary protection insights about this class of NEA.
“Though massive asteroids are of most concern from a planetary protection perspective, objects like 2020 GE are much more widespread and might pose a hazard to our planet, regardless of their smaller measurement,” mentioned Castillo-Rogez. The Chelyabinsk meteor was brought on by a small asteroid about 65 ft (20 meters) in diameter – it exploded over the Russian metropolis on Feb. 15, 2013, making a shockwave that broke home windows everywhere in the metropolis and injured greater than 1,600 folks. That was the identical class of NEA as 2020 GE.
Low Mass, Excessive Efficiency
Studying extra about asteroid 2020 GE is just a part of NEA Scout’s job. It's going to additionally exhibit photo voltaic sail expertise for deep house encounters. When launched from its dispenser after launch, the spacecraft will use stainless-steel alloy booms to unfurl a photo voltaic sail that can increase from a small bundle to a sail concerning the measurement of a racquetball court docket, or 925 sq. ft (86 sq. meters).
Created from plastic-coated aluminum thinner than a human hair, this light-weight, mirror-like sail will generate thrust by reflecting photo voltaic photons – quantum particles of sunshine radiating from the Solar. The sail will present most of NEA Scout’s propulsion, however small cold-gas thrusters with a restricted propellant provide may also help with maneuvers and orientation.
“The genesis of this mission was a query: Can we actually use a tiny spacecraft to do deep house missions and produce helpful science at a low price?” mentioned Les Johnson, the mission’s principal expertise investigator at Marshall. “It is a big problem. For asteroid characterization missions, there’s merely not sufficient room on a CubeSat for big propulsion techniques and the gasoline they require.”
Daylight acts as a relentless drive, so a tiny spacecraft outfitted with a big photo voltaic sail can finally journey many miles per second. Photo voltaic sails are a high-performance propulsion system for low-mass and low-volume spacecraft, in accordance with Johnson. NEA Scout will maneuver by tipping and tilting its sail to alter the angle of daylight, altering the quantity of thrust and course of journey, much like how a ship makes use of the wind to sail.
In September 2023, asteroid 2020 GE will make a detailed method with Earth, and with a gravitational help from the Moon, NEA Scout can have gathered sufficient pace to catch up. Mission navigators will fine-tune NEA Scout’s trajectory earlier than the spacecraft approaches inside a mile of the asteroid.
“NEA Scout will accomplish most likely the slowest flyby of an asteroid ever – at a relative pace of lower than 100 ft [30 meters] per second,” mentioned Castillo-Rogez. “It will give us a couple of hours to assemble invaluable science and permit us to see what asteroids of this class appear like up shut.”
NEA Scout units the stage for future photo voltaic sails: NASA’s Superior Composite Photo voltaic Sail System will exhibit novel, light-weight booms to deploy a photo voltaic sail from a CubeSat following its 2022 launch. After that, Photo voltaic Cruiser, an 18,000-square-foot (almost 1,700-square-meter) photo voltaic sail expertise demonstration, will use daylight to journey towards the Solar in 2025, enabling future missions to raised monitor house climate.
Post a Comment