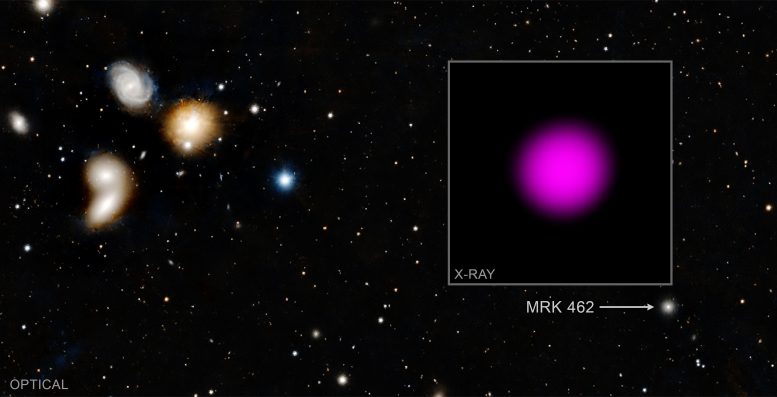
Chandra has detected X-rays from the dwarf galaxy Mrk 462, which reveals the presence of a rising supermassive black gap. This black gap incorporates about 200,000 instances the mass of the Solar and supplies info to astronomers about how a number of the earliest black holes within the Universe might have fashioned and grown billions of years in the past. The optical picture is from the Pan-STARRS telescope in Hawaii, with a number of galaxies from the HCG068 galaxy group on the left-hand aspect and the a lot smaller Mrk 462 to the decrease proper. Astronomers will proceed to attempt to decide the proportion of dwarf galaxies which have supermassive black holes. Credit score: X-ray: NASA/CXC/Dartmouth Coll./J. Parker & R. Hickox; Optical/IR: Pan-STARRS
The invention of a supermassive black gap in a comparatively small galaxy may assist astronomers unravel the thriller surrounding how the very greatest black holes develop.
Researchers used NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory to establish a black gap containing about 200,000 instances the mass of the Solar buried in gasoline and mud within the galaxy Mrk 462.
Mrk 462 incorporates solely a number of hundred million stars, making it a dwarf galaxy. In contrast, our Milky Means is house to some hundred billion stars. This is among the first instances that a closely buried, or “obscured,” supermassive black gap has been present in a dwarf galaxy.
“This black gap in Mrk 462 is among the many smallest of the supermassive, or monster, black holes,” mentioned Jack Parker of Dartmouth School in New Hampshire, who led the research with colleague Ryan Hickox, additionally from Dartmouth. “Black holes like this are notoriously onerous to seek out.”
In bigger galaxies, astronomers usually discover black holes by in search of the speedy motions of stars within the facilities of galaxies. Nevertheless, dwarf galaxies are too small and dim for many present devices to detect this. One other method is to seek for the signatures of rising black holes, resembling gasoline being heated as much as thousands and thousands of levels and glowing in X-rays because it falls in the direction of a black gap.
The researchers on this research used Chandra to have a look at eight dwarf galaxies that had beforehand proven hints of black gap progress from optical information gathered by the Sloan Digital Sky Survey. Of these eight, solely Mrk 462 confirmed the X-ray signature of a rising black gap.
The unusually massive depth of excessive vitality X-rays in comparison with low vitality X-rays, together with comparisons to information at different wavelengths, signifies that the Mrk 462 black gap is closely obscured by gasoline.
“As a result of buried black holes are even tougher to detect than uncovered ones, discovering this instance may imply there are much more dwarf galaxies on the market with related black holes,” mentioned Hickox. “That is necessary as a result of it may assist handle a serious query in astrophysics: How did black holes get so large so early within the universe?”
Earlier analysis has proven that black holes can develop to a billion photo voltaic lots by the point the universe is lower than a billion years previous, a small fraction of its present age. One concept is that these big objects had been created when huge stars collapsed to kind black holes that weighed solely about 100 instances the mass of the Solar. Theoretical work, nonetheless, struggles to clarify how they may pack on weight shortly sufficient to achieve the sizes seen within the early universe.
An alternate rationalization is that the early universe was seeded with black holes containing tens of hundreds of photo voltaic lots once they had been created — maybe from the collapse of gigantic clouds of gasoline and mud.
A big fraction of dwarf galaxies with supermassive black holes favors the concept that small black gap seeds from the earliest technology of stars grew astonishingly shortly to kind the billion photo voltaic mass objects within the early universe. A smaller fraction would tip the scales to favor the concept that black holes started life weighing tens of hundreds of Suns.
These expectations apply as a result of the situations essential for the direct collapse from an enormous cloud to a medium-sized black gap ought to be uncommon, so it's not anticipated that a big fraction of dwarf galaxies would comprise supermassive black holes. Stellar-mass black holes, however, are anticipated in each galaxy.
“We will’t make sturdy conclusions from one instance, however this consequence ought to encourage far more intensive searches for buried black holes in dwarf galaxies,” mentioned Parker. “We’re enthusiastic about what we would study.”
For extra on this analysis, see “Mini” Monster Black Gap Discovery Could Present Clues to Astonishing Supermassive Development.
These outcomes had been scheduled to be offered on the 239th assembly of the American Astronomical Society assembly in Salt Lake Metropolis, and had been a part of a digital press briefing held on Monday, January tenth.
NASA’s Marshall Area Flight Heart manages the Chandra program. The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory’s Chandra X-ray Heart controls science operations from Cambridge, Massachusetts, and flight operations from Burlington, Massachusetts.
Post a Comment