Carbon is vital to life, so far as we all know. So anytime we detect a robust carbon signature someplace like Mars, it may point out organic exercise.
Does a robust carbon sign in Martian rocks point out organic processes of some sort?
Any robust carbon sign is intriguing once you’re looking for life. It’s a typical component in all of the types of life we all know of. However there are various kinds of carbon, and carbon can develop into concentrated within the atmosphere for different causes. It doesn’t robotically imply life is concerned in carbon signatures.
Carbon atoms at all times have six protons, however the neutron depend can differ. Carbon atoms with completely different numbers of neutrons are known as isotopes. Three carbon isotopes happen naturally: C12 and C13, that are steady, and C14, a radionuclide. C12 has six neutrons, C13 has seven neutrons, and C14 has eight neutrons.
In the case of carbon isotopes, life prefers C12. They use it in photosynthesis or to metabolize meals. The reason being comparatively easy. C12 has one fewer neutron than C13, which implies that when it bonds with different atoms into molecules, it makes fewer connections than C13 does in the identical state of affairs. Life is actually lazy, and it'll at all times search the simplest option to do issues. C12 is less complicated to make use of as a result of it varieties fewer bonds than C13. It’s simpler to get at than C13, and life by no means takes the arduous means when a neater means is out there.
The Curiosity rover is tough at work in Mars’ Gale crater, trying to find indicators of life. It drills into rock, extracts a pulverized pattern, and locations it into its onboard chemistry laboratory. Curiosity’s lab is named SAM which stands for Pattern Evaluation at Mars. Inside SAM, the rover makes use of pyrolysis to bake the pattern and convert the carbon within the rock into methane. The pyrolysis is completed in a stream of inert helium to forestall any contamination within the course of. Then it probes the fuel with an instrument named the Tunable Laser Spectrometer to search out out what carbon isotopes are within the methane.

The Pattern Evaluation at Mars software is named SAM. SAM is made up of three completely different devices that seek for and measure natural chemical compounds and lightweight components which can be essential components doubtlessly related to life. Credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech
The crew behind Curiosity’s SAM checked out 24 rock samples with this course of and lately found one thing noteworthy. Six of the samples confirmed elevated ratios of C12 to C13. In comparison with an Earth-based reference customary for C12/C13 ratios, the samples from these six websites contained larger than 70 components per thousand extra C12. On Earth, 98.93% of the carbon is C12 Earth, and C13 varieties the remaining 1.07%.
A brand new examine revealed within the Proceedings of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences (PNAS) offered the findings. Its title is “Depleted carbon isotope compositions noticed at Gale crater, Mars.” The lead writer is Christopher Home, a Curiosity scientist at Penn State College.
It’s an thrilling discovering, and if these outcomes have been obtained on Earth, they'd sign that a organic course of produced the abundance of C12.
On historic Earth, floor micro organism produced methane as a byproduct. They’re known as methanogens, they usually’re prokaryotes from the Archaea area. Methanogens are nonetheless current at this time on Earth, in anoxic wetlands, within the digestive tracts of ruminants, and excessive environments like sizzling springs.
These micro organism produce methane that enters the environment, interacting with ultraviolet mild. These interactions produce extra complicated molecules that rained down onto the Earth’s floor. They’re preserved in Earth rocks, together with their carbon signatures. The identical factor may need occurred on Mars, and if it did, it may account for Curiosity’s findings.
However that is Mars. If the historical past of trying to find life on Mars tells us something, it’s to not get forward of ourselves.
“We’re discovering issues on Mars which can be tantalizingly attention-grabbing, however we'd really want extra proof to say we’ve recognized life,” mentioned Paul Mahaffy, former principal investigator for Curiosity’s Pattern Evaluation at Mars lab. “So we’re what else may have brought on the carbon signature we’re seeing, if not life.”

Curiosity took this 360-degree panorama on August 9, 2018, on Vera Rubin Ridge. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS
Of their paper, the authors write, “There are a number of believable explanations for the anomalously depleted 13C noticed in advanced methane, however no single clarification may be accepted with out additional analysis.”
One of many difficulties in understanding carbon signatures like this one is our so-called Earth bias. Most of what scientists find out about atmospheric chemistry and associated issues is predicated on Earth. So on the subject of this newly-detected carbon signature on Mars, scientists can discover it difficult to maintain their minds open to new potentialities that will not exist on Mars. The historical past of the seek for life on Mars tells us this.
“The toughest factor is letting go of Earth and letting go of that bias that we've and actually attempting to get into the basics of the chemistry, physics and environmental processes on Mars,” mentioned Goddard astrobiologist Jennifer L. Eigenbrode, who participated within the carbon examine. Beforehand, Eigenbrode led a global crew of Curiosity scientists within the detection of myriad natural molecules — ones that comprise carbon — on the Martian floor.
“We have to open our minds and suppose exterior the field,” Eigenbrode mentioned, “and that’s what this paper does.”
The researchers level out two non-biological explanations for the weird carbon signature of their paper. One includes molecular clouds.
The molecular cloud speculation states that our Photo voltaic System handed via a molecular cloud tons of of tens of millions of years in the past. That could be a uncommon occasion, nevertheless it occurs about as soon as each 100 million years, so scientists can’t low cost it. Molecular clouds are primarily molecular hydrogen, however one could have been wealthy in the kind of lighter carbon detected by Curiosity in Gale Crater. The cloud would’ve brought on Mars to chill dramatically, inflicting glaciation on this situation. The cooling and glaciation would’ve prevented the lighter carbon within the molecular clouds from mixing with Mars’ different carbon, creating deposits of elevated C12. The paper states that “Glacial soften throughout the glacial interval and ice retreat after ought to go away the interstellar mud particles on the glacial geomorphological floor.”
The speculation suits since Curiosity discovered a number of the elevated C12 ranges on the tops of ridges—resembling the highest of Vera Rubin Ridge—and different excessive factors in Gale Crater. The samples have been gathered from “… a wide range of lithologies (mudstone, sand, and sandstone) and are temporally unfold all through the mission operations so far,” the paper states. Nonetheless, the molecular cloud speculation is an unlikely chain of occasions.

NASA’s Curiosity rover raised its robotic arm with the drill pointed skyward whereas exploring Vera Rubin Ridge on the base of Mount Sharp inside Gale Crater – backdropped by distant crater rim. This Navcam digital camera mosaic was stitched from uncooked photos taken on Sol 1833, October 2, 2017, and colorized. Credit score: NASA/JPL/Ken Kremer/kenkremer.com/Marco Di Lorenzo.
The opposite non-biological speculation includes ultraviolet mild. Mars’ environment is over 95% carbon dioxide, and on this situation, UV mild would’ve interacted with carbon dioxide fuel in Mars’ environment producing new carbon-containing molecules. The molecules would’ve rained down on Mars’ floor and develop into a part of the rock there. This speculation is much like how methanogens not directly produce C12 on Earth, nevertheless it’s totally abiotic.
“All three explanations match the info,” mentioned lead writer Christopher Home. “We merely want extra information to rule them in or out.”
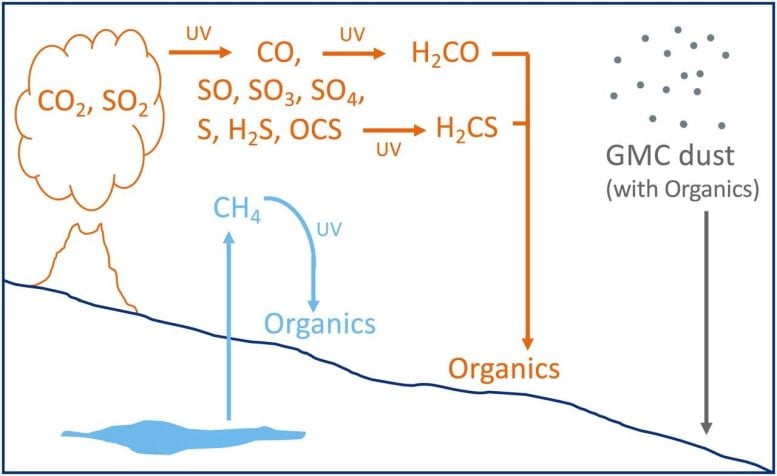
This determine from the examine exhibits the three hypotheses that might clarify the carbon signature. The blue exhibits biologically produced methane from the Martian inside, creating the deposition of 13C-depleted natural materials after photolysis. The orange exhibits photochemical reactions by way of UV mild that can lead to varied atmospheric merchandise, a few of which might be deposited as natural materials with easily-broken chemical bonds. The gray exhibits the molecular cloud speculation. Credit score: Home et al. 2022.
“On Earth, processes that may produce the carbon sign we’re detecting on Mars are organic,” Home added. “We have now to know whether or not the identical clarification works for Mars or if there are different explanations as a result of Mars could be very completely different.”
Virtually half of the Curiosity samples had unexpectedly elevated ranges of C12. They’re not solely larger than Earth’s ratio; they’re larger than scientists have present in Martian meteorites and the Martian environment. The samples got here from 5 places in Gale Crater, and all of the places had one factor in widespread: they've historic, well-preserved surfaces.
As Paul Mahaffy mentioned, the findings are “tantalizingly attention-grabbing.” However scientists are nonetheless studying about Mars’ carbon cycle, and there’s rather a lot we’re nonetheless ignorant about. It’s tempting to make assumptions about Mars’ carbon cycle primarily based on Earth’s carbon cycle. However carbon could cycle via Mars in methods we haven’t even guessed at but. Whether or not or not this carbon signature finally ends up being a sign for all times or not, it’s nonetheless beneficial information on the subject of understanding Mars’ carbon signature.
“Defining the carbon cycle on Mars is completely key to attempting to know how life may match into that cycle,” mentioned Andrew Steele, a Curiosity scientist primarily based on the Carnegie Establishment for Science in Washington, D.C. “We have now accomplished that basically efficiently on Earth, however we're simply starting to outline that cycle for Mars.”
However it isn’t straightforward to attract conclusions about Mars primarily based on Earth’s carbon cycle. Steele made that clear when he mentioned, “There’s an enormous chunk of the carbon cycle on Earth that includes life, and due to life, there's a chunk of the carbon cycle on Earth we will’t perceive as a result of in every single place we glance, there's life.”

NASA’s Perseverance rover is trying to find indicators of historic life on Mars at Jezero Crater. Outcomes from Curiosity can inform Perseverance’s sampling actions. Credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS
Curiosity continues to be engaged on Mars and can be for some time but. The which means of those samples, together with a greater understanding of Mars’ carbon cycle, lies forward. Curiosity will pattern extra rock to measure carbon isotope concentrations. It’ll pattern rock from different well-preserved historic surfaces to see if outcomes are much like these. Ideally, it could encounter one other methane plume and pattern it, however these occasions are unpredictable, and there’s no option to put together for one.
Both means, these outcomes will assist inform Perseverance’s pattern gathering at Jezero Crater. Perseverance could verify related carbon alerts and even decide in the event that they’re organic or not.
Perseverance can also be gathering samples for return to Earth. Scientists will examine these samples extra successfully than the rover’s onboard lab can, so who is aware of what we’ll be taught.
Historic life on Mars is a tantalizing prospect, however for now, at the very least, it’s unsure.
Initially revealed on Universe Right now.
For extra on this analysis, see:
- Newly Found Carbon on Mars: Origin Could Be Biologically Produced Methane
- NASA’s Curiosity Rover Measures Intriguing Carbon Signature on Mars – Doable Indication of Organic Exercise
Reference: “Depleted carbon isotope compositions noticed at Gale crater, Mars” by Christopher H. Home, Gregory M. Wong, Christopher R. Webster, Gregory J. Flesch, Heather B. Franz, Jennifer C. Stern, Alex Pavlov, Sushil Ok. Atreya, Jennifer L. Eigenbrode, Alexis Gilbert, Amy E. Hofmann, Maëva Millan, Andrew Steele, Daniel P. Glavin, Charles A. Malespin and Paul R. Mahaffy, 17 January 2022, Proceedings of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences.
DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2115651119

Post a Comment