In reservoir computing, info propagation is like rippling waves on the floor of a physique of water; therefore, the time period “reservoir” is used. The underwater electrode pictured is the precise multi-terminal electrode used on this examine. Credit score: Megumi Akai-Kasaya et al.
Researchers led by Osaka College reveal the wonderful info processing skills of bodily reservoirs based mostly on electrochemical reactions in Faradic present and current a easy system for computing programs utilizing electrochemical ion reactions.
After many many years of astonishing developments, advances in semiconductor-based computing are starting to gradual as transistors attain their bodily limits in dimension and velocity. Nonetheless, the necessities for computing proceed to develop, particularly in synthetic intelligence, the place neural networks typically have a number of thousands and thousands of parameters. One answer to this drawback is reservoir computing, and a workforce of researchers led by Osaka College, with colleagues from the College of Tokyo and Hokkaido College, have developed a easy system based mostly on electrochemical reactions in Faradic present that they imagine will jump-start developments on this discipline.
Reservoir computing is a comparatively latest concept in computing. As a substitute of conventional binary packages run on semiconductor chips, the reactions of a nonlinear dynamical system—the reservoir—are used to carry out a lot of the calculation. Numerous nonlinear dynamical programs from quantum processes to optical laser parts have been thought of as reservoirs. On this examine, the researchers regarded on the ionic conductance of electrochemical options.
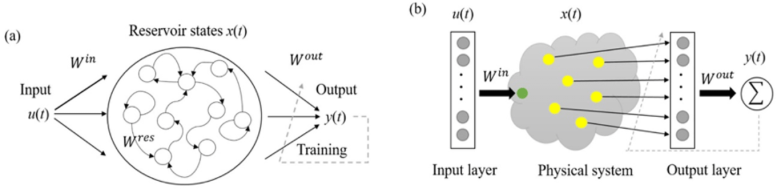
Bodily reservoir computing and the development of a molecular-based reservoir. (a) Construction of conventional reservoir computing. (b) Idea of our bodily reservoir computing system. Credit score: © 2022 Megumi Akai-Kasaya et al., Superior Science
“Our easy testing machine consists of 90 pairs of planar electrodes with an ionic answer dropped on its floor,” explains Professor Megumi Akai-Kasaya, lead writer of the examine. “The response voltage to the enter voltage is then used because the response of the reservoir.” This voltage response is because of each the ionic currents that go by way of the answer and the electrochemical present. This enter–output relationship is each nonlinear and reproducible, which makes it appropriate to be used in reservoir computing. A singular multiway information acquisition system on the machine controls the readout nodes, which allows parallel testing.
The researchers used the machine to judge two liquids: polyoxometalate molecules in answer and deionized water. The system displayed a “feedforward connection” between nodes, no matter which pattern was used. Nonetheless, there have been variations. “The polyoxometalate answer elevated the variety of the response present, which makes it good at predicting periodic indicators,” says Professor Akai-Kasaya. “But it surely seems that deionized water is greatest for fixing second-order nonlinear issues.” The nice efficiency of those options demonstrates their potential for extra sophisticated duties, comparable to handwriting font recognition, remoted phrase recognition, and different classification duties.
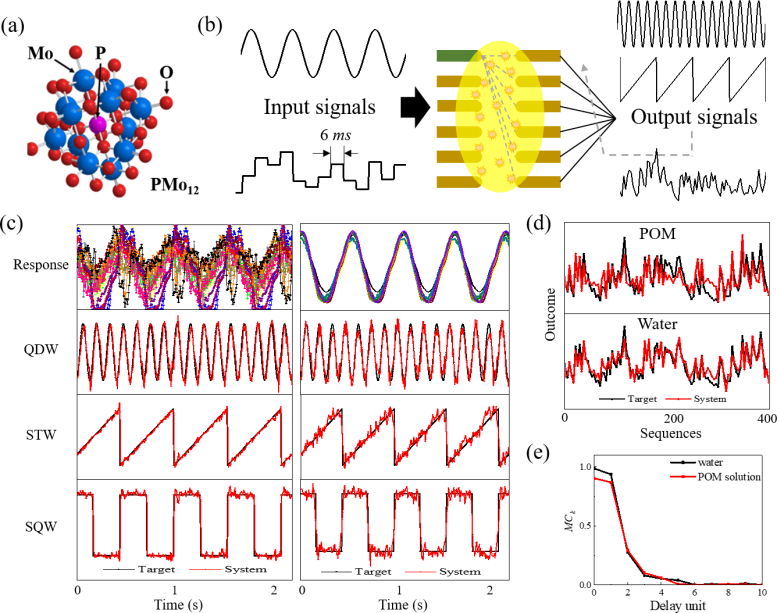
(a) Construction of the polyoxometalate (POM) molecule. (b) Schematic of the electrochemical-reaction-based reservoir. (c) Responses of the POM answer (left) and deionized water (proper) to a sinusoidal sign and their prediction performances on a quadruple sine (QDW) goal sign. (d) Prediction performances of the POM answer and water on a nonlinear goal sign. Credit score: © 2022 Megumi Akai-Kasaya et al., Superior Science
The researchers imagine that proton or ion switch with minimal electrochemical reactions over quick durations has the potential for growth as a extra computationally highly effective computing system that's low in value and energy-efficient. The simplicity of the proposed system opens up thrilling new alternatives for growing computing programs based mostly on electrochemical ion reactions.
Reference: “Bodily Implementation of Reservoir Computing by way of Electrochemical Response” by Shaohua Kan, Kohei Nakajima, Tetsuya Asai and Megumi Akai-Kasaya, 29 December 2021, Superior Science.
DOI: 10.1002/advs.202104076
Post a Comment