Observations of a sizzling Jupiter can also advance our understanding of planet origins and evolution.
Think about being in a spot the place the winds are so sturdy that they transfer on the velocity of sound. That’s only one facet of the environment on XO-3b, certainly one of a category of exoplanets (planets outdoors our photo voltaic system), generally known as sizzling Jupiters. The eccentric orbit of the planet additionally results in differences due to the season tons of of occasions stronger than what we expertise on Earth. In a current paper, a McGill-led analysis group, supplies new perception into what seasons seems to be like on a planet outdoors our photo voltaic system. The researchers additionally recommend that the oval orbit, extraordinarily excessive floor temperatures (2,000 levels C- sizzling sufficient to vaporize rock) and “puffiness” of XO-3b reveal traces of the planet’s historical past. The findings will probably advance each the scientific understanding of how exoplanets type and evolve and provides some context for planets in our personal photo voltaic system.
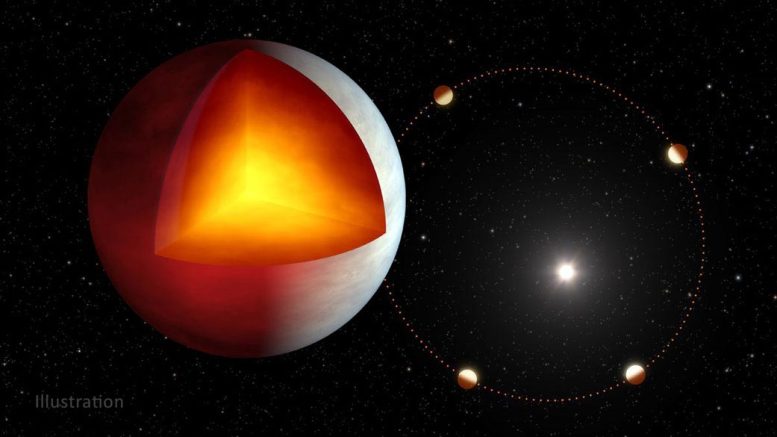
Sizzling Jupiters are large, gaseous worlds like Jupiter, that orbit nearer to their dad or mum stars than Mercury is to the Solar. Although not current in our personal photo voltaic system, they seem like widespread all through the galaxy. Regardless of being probably the most studied kind of exoplanet, main questions stay about how they type. Might there be subclasses of sizzling Jupiters with completely different formation tales? For instance, do these planets take form removed from their dad or mum stars – at a distance the place it’s chilly sufficient for molecules similar to water to turn out to be stable – or nearer. The primary situation matches higher with theories about how planets in our personal photo voltaic system are born, however what would drive a majority of these planets emigrate so near their dad or mum stars stays unclear.
To check these concepts, the authors of a current McGill-led examine used knowledge from NASA’s retired Spitzer House Telescope to take a look at the environment of exoplanet XO-3b. They noticed eccentric seasons and measured wind speeds on the planet by acquiring a section curve of the planet because it accomplished a full revolution about its host star.
Taking a look at atmospheric dynamics and inside evolution
“This planet is an especially attention-grabbing case examine for atmospheric dynamics and inside evolution, because it lies in an intermediate regime of planetary mass the place processes usually uncared for for much less large sizzling Jupiters could come into play,” says Lisa Dang, the primary writer of a paper revealed not too long ago in The Astronomical Journal, a PhD scholar at McGill College’s Division of Physics. “XO-3b has an oval orbit slightly than the round orbit of virtually all different recognized sizzling Jupiters. This means that it not too long ago migrated towards its dad or mum star; if that’s the case, it'll finally settle right into a extra round orbit.”
The eccentric orbit of the planet additionally results in differences due to the season tons of of occasions stronger than what we expertise on Earth. Nicolas Cowan, a McGill professor explains: “Your entire planet receives thrice extra power when it's near its star throughout a quick kind of summer time, than when it's removed from the star.”
The researchers additionally re-estimated the planet’s mass and radius and located that the planet was surprisingly puffier than anticipated. They recommend and that the potential supply of this heating could possibly be resulting from leftover nuclear fusion.
Extra heat and puffiness resulting from tidal heating?
Observations by Gaia, an ESA (European House Company) mission, discovered that the planet is puffier than anticipated which point out its inside could also be significantly energetic. Spitzer observations additionally hints that the planet produces a lot of its personal warmth as XO-3b’s extra thermal emission isn’t seasonal – it’s noticed all year long on XO-3b. It’s potential that the surplus heat is coming from the planet’s inside, by means of a course of referred to as tidal heating. The star’s gravitational squeeze on the planet oscillates because the rectangular orbit takes the planet farther after which nearer to the star. The ensuing modifications in inside stress produce warmth.
For Dang, this uncommon sizzling Jupiter supplies a chance to check concepts about which formation processes could producer sure traits in these exoplanets. For instance, may tidal heating in different sizzling Jupiters even be an indication of current migration? XO-3b alone gained’t unlock the thriller, however it serves as an vital take a look at for rising concepts about these scorching giants.
For extra on this analysis, see NASA’s Spitzer House Telescope Illuminates Exoplanets.
Reference: “Thermal Section Curves of XO-3b: An Eccentric Sizzling Jupiter on the Deuterium Burning Restrict” by Lisa Dang, Taylor J. Bell, Nicolas B. Cowan, Daniel Thorngren, Tiffany Kataria, Heather A. Knutson, Nikole Ok. Lewis, Keivan G. Stassun, Jonathan J. Fortney, Eric Agol, Gregory P. Laughlin, Adam Burrows, Karen A. Collins, Drake Deming, Diana Jovmir, Jonathan Langton, Sara Rastegar and Adam P. Showman, 22 December 2021, The Astronomical Journal.
DOI: 10.3847/1538-3881/ac365f
Post a Comment