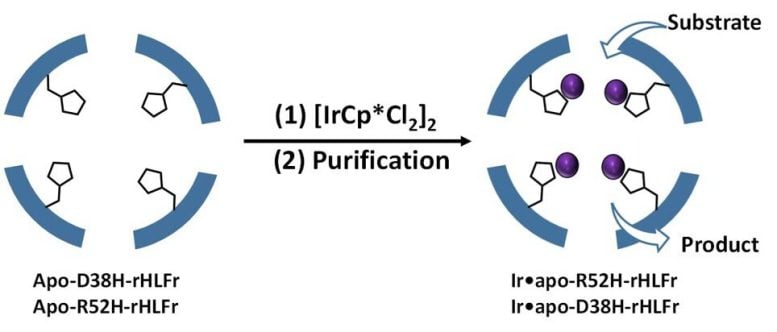
The cage was engineered with amino acid replacements by introducing site-specific mutations that allowed extra IrCp* uptake. Credit score: Takafumi Ueno from Tokyo Institute of Know-how
A novel hybrid ferritin nanocage with histidine residues reveals 1.5 instances larger steel ion uptake and improved catalytic effectivity for alcohol manufacturing, discover researchers from Tokyo Tech in a brand new research. Their findings counsel that hybrid bio-nanocages might successfully catalyze reactions to yield industrially vital merchandise.
Organic polymers can spontaneously self-assemble into advanced buildings that resemble vessels or cages, however are a lot smaller, and are known as “nano-cages.” These buildings can accommodate a variety of molecules inside them that behave as “company.” One in style instance is the “ferritin nanocage,” which is fashioned by the self-assembly of 24 subunits into the protein ferritin and may enclose steel ions which might be vital catalysts. With the assistance of those steel ions, a catalytic response converts any substrate right into a product. Though extensively recognized, the ferritin cage’s potential purposes in business have but to be absolutely explored.
To this point, most efforts to extend steel ion uptake in ferritin have resulted in cages with low stability. To make the “visitor” sit effectively throughout the cage, efficient design is the important thing. Preserving that in thoughts, a group of scientists led by Prof. Takafumi Ueno, from Tokyo Institute of Know-how, Japan (Tokyo Tech), launched site-specific mutations on the core of the ferritin nanocage and elevated its uptake of iridium advanced (IrCp*). Their findings are revealed in Angewandte Chemie. Iridium is a crucial catalyst within the alcohol manufacturing pathway and is used commercially within the pharmaceutical, meals, and chemical industries.
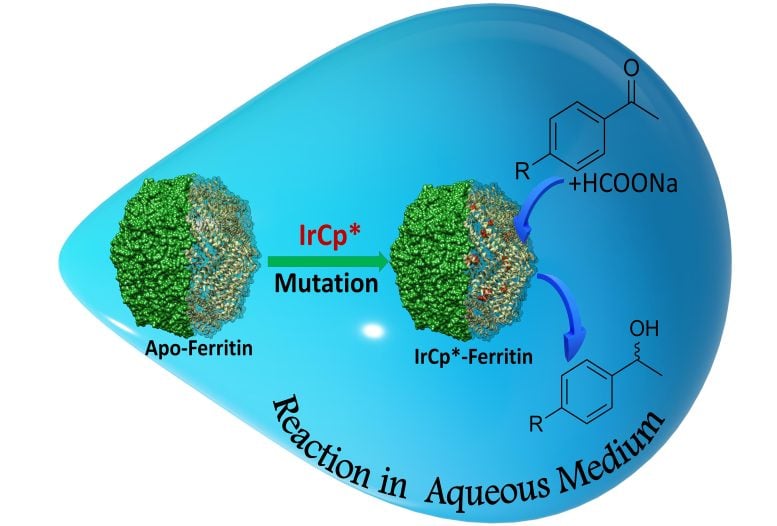
The nanocage acts as a hybrid bio-catalyst through the conversion of substrates to alcohols with excessive specificity. Credit score: Takafumi Ueno from Tokyo Institute of Know-how
Prof. Ueno explains, “Based mostly on earlier literature, we knew that the presence of coordination amino acids within the cage enhance iridium exercise, and that substituting these amino acids with acceptable residues might alleviate the issue. Since iridium advanced behaves as a catalyst, coordination residues would do the job.” The authors used the amino acid histidine to exchange two residues, arginine, and aspartic acid of the common (wild sort) ferritin cages and create the mutants R52H and D38H. Remarkably, the meeting construction or cage measurement weren't affected by these modifications.
Subsequent, they added IrCp* to the mutants and located that R52H was in a position to embed 1.5 instances extra iridium atoms than the wild sort cage (Determine 1). However, what struck them was the D38H mutant, which behaved precisely just like the wild sort! So, why didn’t each mutations have the identical impact? In keeping with Prof. Ueno, “This means that it isn't solely the presence of the histidine residue but additionally its place that's essential to find out uptake effectivity within the cage.”
Utilizing the brand new catalytic cages, the researchers had been in a position to accomplish alcohol manufacturing charges as excessive as 88%. Evidently, the mutations favored a structural re-arrangement of the response parts, which enhanced the conversion price (Determine 2).
To know how the substrate behaved contained in the cage, the researchers used simulations whereby the substrate molecules might transfer freely throughout the nanocage. They noticed some interactions between the substrate and histidine within the R52H mutant, which weren't current within the wild sort cage, i.e., the substrate confirmed preferential binding throughout the nanocage.
“These hybrid bio-nanocages had been additionally discovered to be extremely secure, suggesting that they may very well be used as viable catalysts in industrial purposes,” concludes Prof. Ueno. The present structure-based design of the steel ion binding web site analysis may very well be superior to create novel ferritin mutants with selective uptake of particular visitor molecules, for various catalytic purposes within the chemical and pharmaceutical business.
Reference: “Managed Uptake of an Iridium Advanced inside Engineered apo-Ferritin Nanocages: Research of Construction and Catalysis” by Mohd Taher, Basudev Maity, Taiki Nakane, Satoshi Abe, Takafumi Ueno and Shyamalava Mazumdar, 10 January 2022, Angewandte Chemie.
DOI: 10.1002/anie.202116623
Post a Comment